answers to review questions chapter 4
advertisement

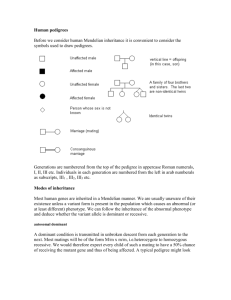
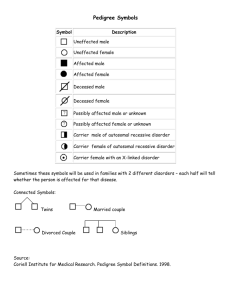
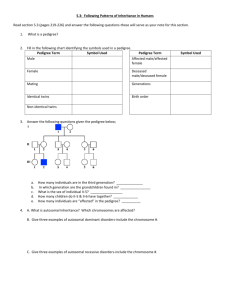
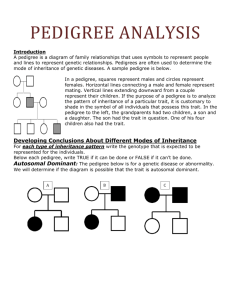
ANSWERS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS CHAPTER 4 1. HD is autosomal dominant and has a late onset. CF has an early onset and is autosomal recessive. 2. The law of segregation derives from the fact that during meiosis, alleles separate into different gametes. The law of independent assortment is based on the fact that distribution of alleles of two unlinked genes into gametes occurs at random. 3. The two laws of inheritance were derived from pea crosses. Without knowing about chromosomes, Mendel observed offspring phenotypes and predicted results of crosses. 4. a. An autosomal recessive trait is inherited from carriers and affects both sexes. An autosomal dominant trait can be inherited from one parent, who is affected. Autosomal recessive inheritance can skip generations; autosomal dominant inheritance cannot. b. Mendel's first law concerns inheritance of one trait. The second law follows inheritance of two genes on different chromosomes. c. A homozygote has identical alleles for a particular gene, and a heterozygote has different alleles (TT vs. Tt). d. The parents of a monohybrid cross are heterozygotes for a single gene. Parents of a dihybrid cross are heterozygous for a pair of genes. e. A Punnett square tracks the distribution of alleles of genes on different chromosomes from parents to offspring. A pedigree depicts family members and their inherited traits. 5. If Mendel had chosen two traits on the same chromosome, he would have observed a higher percentage of offspring inheriting two alleles together rather than independently. 6. Blood relatives share alleles inherited from common ancestors. 7. The Egyptian pedigree only traces genealogy and not inheritance of traits. The pedigree a genetic counselor would use today would trace inherited traits too. 8. The parents of a person who is homozygous dominant for HD must be heterozygotes. 9. 100% ANSWERS TO APPLIED QUESTIONS 1. a. Phenotypic ratio: 100% short. Genotypic ratio: 100% tt b. Phenotypic ratio: 100% tall. Genotypic ratio: 100% Tt c. Phenotypic ratio: 100% tall. Genotypic ratio: 100% TT 2. Vv x Vv 3. Only all white seed coats 4. Genotypic ratios: 1/16 = VVGG 2/16 = VVGg 2/16 = VvGG 4/16 = VvGg 1/16 = VVgg 2/16 = Vvgg 1/16 = vvGG 2/16 = vvGg 1/16 = vvgg Phenotypic ratios: 9 inflated green pods: 3 inflated yellow: 3 restricted green: 1 restricted yellow 5. Autosomal recessive 1 6. Autosomal recessive 7. Pedigree 8. Carriers are I3, I4, II4, III3, III4 9. 1 in 2 chance the child has double eyelashes 1 2 1 1 2 Caleb ? 1 10. Consanguinity. 11. a. Uncles and nieces having children together. b. Carriers = III-5, III-6, III-9, IV-1 and niece (V-1), IV-6, IV-11, V-4, V-5, V-6, V-9, and V-10 12. Genotypic ratios: 4/32 = BbHhEe 4/32 = bbHhEe 2/32 = BbHhEE 2/32 = BbJJEe 2/32 = BbhhEe 2/32 = BbHhee 2/32 = bbHhEE 2/32 = bbHHEe 2/32 = bbhhEe 2/32 = bbHhee 1/32 = BbHHEE 1/32 = BbhhEE 1/32 = BbHHee 1/32 = Bbhhee 1/32 = bbHHEE 1/32 = bbhhEE 1/32 = bbHHee 1/32 = bbhhee Phenotypic ratios: 9/32 = yellow urine, colored eyelids, short fingers 9/32 = red urine, colored eyelids, short fingers 3/32 = yellow urine, normal eyelids, short fingers 3/32 = red urine, normal eyelids, short fingers 3/32 = yellow urine, colored eyelids, long fingers 3/32 = red urine, colored eyelids, long fingers 1/32 = yellow urine, normal eyelids, long fingers 2 1/32 = red urine, colored eyelids, long fingers 13. a family or pet’s pedigree ANSWERS TO WEB ACTIVITIES 1. Answers vary depending on the disorder selected. Examples are 1) Glycogen storage disease type VII. This is an autosomal recessive condition that causes muscle cramps with exercise. Edna and Murray are in their 70s, and neither has experienced muscle pain with exercise although they are both sedentary, so would not know. Their son Roy is a distance runner, as is his wife, Marsha. They are surprised when their daughter Kelly wants to try out for the gymnastics team, but becomes paralyzed with cramps upon exertion. 2) Macroglossia. This is an autosomal dominant condition that causes a large tongue, feeding problems, and snoring. The McDoomis family has a long history of babies with feeding problems and loud snorers. In each generation, at least one individual has a very large tongue. 2. Answers vary depending on the disorder or trait selected. Examples are: The retinoblastoma gene on chromosome 20 and the cystic fibrosis gene on chromosome 7 independently assort. The genes for xeroderma pigmentosum and brachydactyly type B1, each on chromosome 9, do not. 3. Students create a family pedigree ANSWERS TO FORENSIC FOCUS 1. a. Not justified – she took a man’s DNA without his consent and plans to have it tested and use the information. Or, the DNA is garbage and she is justified in taking it. b. DNA reveals and confirms biological relationships, and could provide information that people do not want to know. 2. The investigators would have to genotype the OCA2 and HERC2 genes to derive the eye color of the headless corpse. ANSWERS TO CASE STUDIES AND RESEARCH RESULTS 1. a. Autosomal recessive. Both sexes are affected, and it skips generations 2. Pro tests may be a valuable guide for couples. If a couple finds they are both carriers of the same recessive trait, they may choose not to have children or even marry. Con stigmatization if an individual’s genetic tests reveal a potential disorder. Testing may be justified if the goal is to reduce suffering and it remains confidential and voluntary 3. a. Pedigree 3 b. Autosomal recessive c. Avoid further inbreeding. 4. The trait is autosomal dominant because it appears in every generation and in both sexes. 4