Scientific Tools & Measurement Worksheets KEY
advertisement
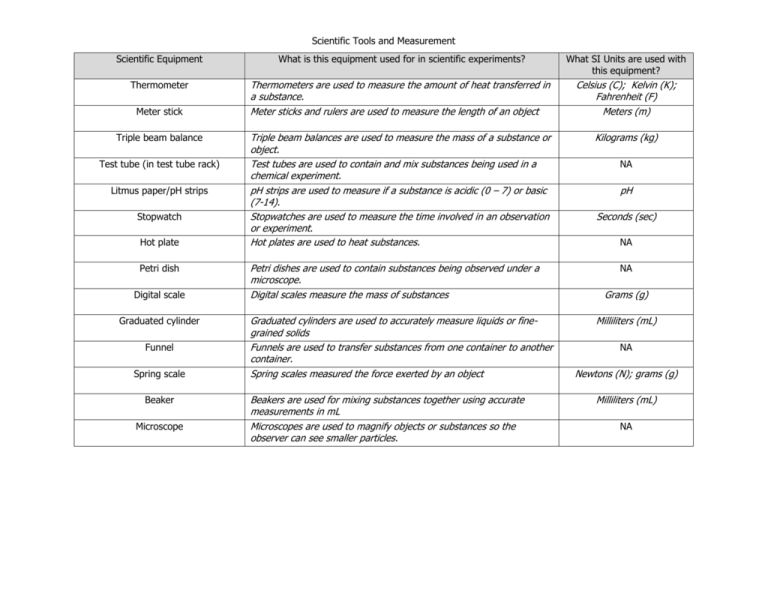
Scientific Tools and Measurement Scientific Equipment What is this equipment used for in scientific experiments? What SI Units are used with this equipment? Thermometer Thermometers are used to measure the amount of heat transferred in a substance. Meter sticks and rulers are used to measure the length of an object Celsius (C); Kelvin (K); Fahrenheit (F) Meters (m) Triple beam balances are used to measure the mass of a substance or object. Test tubes are used to contain and mix substances being used in a chemical experiment. pH strips are used to measure if a substance is acidic (0 – 7) or basic (7-14). Stopwatches are used to measure the time involved in an observation or experiment. Hot plates are used to heat substances. Kilograms (kg) Meter stick Triple beam balance Test tube (in test tube rack) Litmus paper/pH strips Stopwatch Hot plate Petri dish Digital scale Graduated cylinder Funnel Spring scale Beaker Microscope Petri dishes are used to contain substances being observed under a microscope. Digital scales measure the mass of substances Graduated cylinders are used to accurately measure liquids or finegrained solids Funnels are used to transfer substances from one container to another container. Spring scales measured the force exerted by an object Beakers are used for mixing substances together using accurate measurements in mL Microscopes are used to magnify objects or substances so the observer can see smaller particles. NA pH Seconds (sec) NA NA Grams (g) Milliliters (mL) NA Newtons (N); grams (g) Milliliters (mL) NA Scientific Tools and Measurement Scientific Measurement FORCE LENGTH MASS TEMPERATURE TIME VOLUME Which scientific equipment would be used for this measurement? Use a spring scale to measure the amount of force exerted on an object. Use a ruler or meter stick to measure how long an object is. Use a triple balance or scale to measure the amount of matter that something contains. Use a thermometer to measure how hot (or cold) something is Use a stopwatch to measure variables in minutes, seconds, or hours. Use a ruler, meter stick, or grad. cylinder to determine the amount of space that something occupies or contains. What SI Units are used with this measurement? Newtons (N) Meters (m) Kilograms (km) Kelvin (K) Celsius (C) Seconds (sec) Cubic meters (cm) Milliliters (mL) Use the table provided below to design an experiment that you could complete using at least 3 pieces of the scientific equipment shown in this activity. Start by writing a question that you want to answer using this equipment. Include the equipment you would need and the measurements you would record. You may also draw your experiment on a separate page to help you visualize your scientific plan. EXPERIMENTAL QUESTION: HYPOTHESIS: EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN Equipment Needed Other Materials Needed Procedures for the Experiment (Describe the steps you will follow to complete your experiment) Scientific Tools and Measurement SAFETY RULES FOR SCIENCE SAFETY RULE NOTES Eye Safety Ask you teacher for permission before starting an experiment and seek his/her advice about unfamiliar symbols or procedures. Remain seated during experiments to avoid spills and equipment damage. Wear safety goggles when conducting experiments involving chemicals, loose materials, or sharp-pointed objects. Safety Equipment Locate the nearest fire alarms, eyewash and shower stations, and fire extinguishers. Neatness Keep your work area neat and be sure your hair, clothing, and jewelry are contained away from your experiment. Sharp/Pointed Objects Use knives with extreme care and never use them to cut an object that is in your hand. Heat Wear safety goggles and heat resistant gloves while working with a hot plate. Never touch the hot plate surface. Start Out Right Electricity Chemicals Animal Safety Plant Safety Glassware Place electrical cords safely to avoid tripping hazards or areas where the cord could become entangled in other equipment. Water and electricity do not mix. Keep your hands dry. Wear safety goggles and protective clothing when working with chemicals. Do not mix any chemicals together unless instructed to do so by your teacher. Do not bring animals to school. Do not handle animals observed in class unless instructed to do so by your teacher. Wash your hands thoroughly before and after handling animals. Do not eat plants observed in the classroom. When in nature, do not touch plants unless instructed to do so by your teacher. Wash your hands thoroughly before and after handling plants. Examine glassware for cracking and chips before use. Tell your teacher if damaged is observed or damage occurs during class. Use your book to record the correct label beneath each of the safety symbols illustrated below: Eye Protection Clothing Protection Hand Safety Animal Safety Heating Safety Sharp Objects Plant Safety Electric Safety Chemical Safety Scientific Tools and Measurement Pre-Assessment Observe the different pieces of scientific equipment displayed in the classroom and record the correct name to the number listed below. 1. Beaker 8. pH Strips 2. Ruler/Meter Stick 9. Petri dish 3. Compass 10. Stopwatch 4. Funnel 11. Syringe 5. Graduated cylinder 12. Test tube 6. Hot plate 13. Thermometer 7. Microscope 14. Triple beam balance Match the correct equipment you would use to measure each of the following: 15. Force: Spring scale (not in display) 16. Length: Ruler/Meter Stick 17. Mass: Triple beam balance 18. Temperature: Thermometer 19. Time: Stopwatch 20. Volume: Graduated cylinder (ruler) Design an experiment using 3 of the pieces of equipment displayed in class. Start by developing a scientific question you could answer by using the 3 pieces of equipment chosen and then describe how you would complete your experiment to answer your question. 21. Write your experimental question here: 22. List the equipment you would use: 23. List other materials or supplies you would need: 24. Describe the procedures you would follow to complete your experiment: Scientific Tools and Measurement Write the correct label beneath each of the safety symbols illustrated below: Eye protection Clothing protection Hand Safety Animal Safety Heating Safety Sharp Objects Plant Safety Electric Safety Chemical Safety