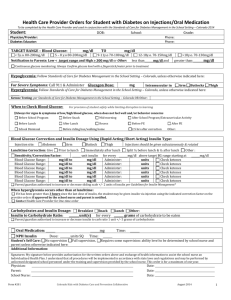
Correction Dose
advertisement

Managing Illness and Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) when taking a mixed insulin twice daily When you are ill, your body becomes more resistant to the insulin you are taking so you will always require more. In addition, you will produce stress hormones that will cause your glucose levels to rise. At these times increasing your mixed insulin to reduce your glucose levels can be problematic as the extra insulin will not necessarily work quickly enough and has a longer duration than desired. To try and overcome this you have been supplied with ……………… which is a very short acting insulin which has an immediate effect and will hopefully assist you to manage your illness more effectively. This dose will be based on a “correction dose calculation” -see below The following gives you guidelines on when the ……………insulin maybe be needed as well as your regular………… mixed insulin twice a day. Correction Dose This varies between people based on the amount of insulin they require daily, but is usually calculated using the formula below: 100 total daily dose of insulin = correction dose The correction dose tells you how many mmols your blood glucose will change for every 1 unit of rapid-acting insulin you inject. My correction dose is100 total daily dose of insulin = So 1 unit of rapid-acting insulin changes my blood glucose by ………… mmol 1 Symptoms of hyperglycaemia Symptoms of high blood glucose levels (hyperglycaemia) may include: Passing lots of urine Thirst Weakness/tired Blurred vision Abdominal pain Leg cramps Nausea and vomiting Acetone/pear drop breath Possible causes: Illness Infection Stress Hormonal Steroids Insulin degradation (inadvertent freezing, out of date etc.) Omitting insulin Implications of ketone levels In the absence of sufficient insulin, the body’s cells cannot use glucose for energy. The cells will switch to an alternative energy source and body fat will be broken down to supply the necessary energy . This rapid breakdown of fat can cause the build-up of substances known as ketones. Eventually, the blood glucose and ketones rise to levels that cause the blood to become acidic and this is known as diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). The only treatment for DKA is insulin and fluids. Ketones can be measured in urine by various brands of ketone stix or in blood by using a MediSense Optium or Glucomen LX plus meter. It is advisable to check the expiry date on urine and blood strips before use. As DKA can develop and progress quickly and makes you feel very unwell, please use the following guidelines if you are ill. 2 Managing illness if glucose levels are high It is recommended that you test your blood or urine for ketones if your blood glucose levels are over 14 mmol/l. What should I do if I have a positive ketone test? You should take ………. (rapid acting insulin) as soon as you can. Take double your correction dose My doubled correction dose is: 2 units of ………………. will lower blood glucose by ………… mmols Drink plenty of water and sugar-free fluids Test blood glucose every 2 hours and repeat the above dose until blood/urine is negative to ketones Try to identify cause of high blood glucose level and seek treatment if necessary Contact diabetes team if high glucose and ketones levels persist Diabetes Specialist nurse contact details: Office: …………………………………… Mobile……………………………………… Email…………………………………….. Contact GP/ Accident and Emergency Dept if you are vomiting as dehydration may occur Urgent hospital admission required if ketones persist with either any shortness of breath, abdominal pain or continuous vomiting Continue with usual amount of …………… mixed insulin at breakfast and evening meal 3 What should I do if I’m ill and my blood glucose levels are high but I do not have ketones? You should continue to test for ketones every 2 hours if your blood glucose levels remain above 14 mmol/l. If you have a positive ketone test, treat as above If your ketone test is negative, but your blood glucose levels remain above 14 mmol/l, take your usual correction dose and this can be repeated at each mealtime My usual correction dose is: 1 unit of ……….rapid-acting insulin will lower blood glucose by ……mmols Drink plenty of water and sugar-free fluids Try to identify cause of high blood glucose level and seek treatment if necessary Continue with usual amount of……………… mixed insulin at breakfast and evening meal Safety advice for illness Always continue taking your mixed insulin and use the rapid acting insulin to compensate for high glucose levels. Use guide for correction doses based on being no ketones or hyperglycaemia/illness with ketones Test for ketones if your blood glucose levels are above 14 mmol/l Positive ketone tests always require treatment What if I cannot eat? If you are feeling unwell and off your food then healthy eating is not a priority and so you may prefer foods with a higher sugar or fat content. Try soups, milky puddings or fruit and ice cream rather than full meals It maybe easier to have regular small snacks rather than three main meals If you are unable to eat, you can obtain carbohydrate from alternative sources such as fizzy soft drinks, milky drinks,soups, fruit juice or ice cream If you are vomiting try to sip small amounts of non diet coke or lemonade 4 The below table gives examples of foods that contain 10g carbohydrate per portion that could be taken in 2-3 servings 4-5 times per day when you are unwell and unable to manage proper meals. Type of drink Ribena original Fruit Juice Amount=10g carbohydrate per portion 2 Diluted in water tablespoons 100ml 4floz ½ glass Cola (not diet) Lemonade (not diet) Milk 100ml 4floz ½ glass 200ml 8floz 1 glass Soup 200ml 8floz 1 mug Ice cream 50g 2oz 150 – 200ml 6floz ¾ - 1 glass 1 large scoop Complan 3 level tsp Drinking Chocolate Ovaltine or Horlicks Dextrose tablets 2 level tsp 2 level tsp 3 tablets 5 A Quick Guide to Calculate Correction Doses 1 unit ………….(rapid acting insulin) will bring my blood glucose level down by ……..mmols in the absence of ketones 2 unit ………… (rapid acting insulin) will bring my glucose levels down by ……………mmols when ketones are present My blood glucose level is I need this much extra insulin to bring me down to …………mmols I need this much extra insulin when I have KETONES to bring me down to …………mmols 11 mmols 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 If regularly giving corrections doses as well as normal mixed insulin (when ketones are not present), this is likely to suggest that the mixed doses need to be increased. Please seek help from your Diabetes Specialist Nurse for advice on how to increase the doses appropriately. 6 7