The Challenge of Antibiotic Resistance
advertisement

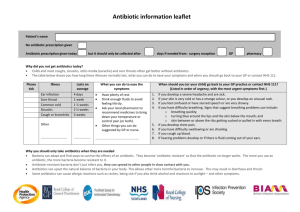
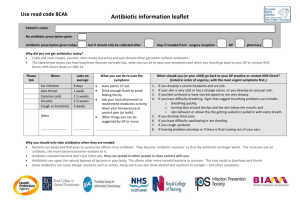
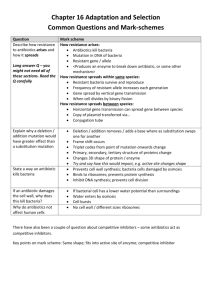
The Challenge of Antibiotic Resistance Answer the following questions. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. What is the “public health nightmare” concerning antibiotic use? Why have death rates for diseases such as tuberculosis started to rise again? Give 2 examples of how bacteria are actually a natural and needed part of life. How exactly does an antibiotic “heal” a bacterial infection? (How does it kill the microbe?) Give 2 ways in which bacteria can acquire resistance to an antibiotic. Give 2 ways that bacteria “share” their resistance traits with one another. Antibiotics often become “self defeating” by actually encouraging resistant bacteria. Give one example of how antibiotics promote resistance. 8. If you were taking an antibiotic to treat acne, explain how this could cause antibiotic resistant bacteria on the skin of another family member to rise. 9. Why is it always important to completely finish a prescription of antibiotics whether you begin feeling better or not? 10. How can the antibiotics agriculturalists use to keep livestock and crops healthy, end up in our body system? 11. Give 3 ways the public can help decrease the prevalence of antibiotic resistant bacteria. 12. Penicillin is probably the most well known antibiotic ever used. Some bacteria, though, have now become resistant to its effectiveness. Explain how a bacterium can evade the effects of this antibiotic. The Challenge of Antibiotic Resistance Answer the following questions. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. What is the “public health nightmare” concerning antibiotic use? Why have death rates for diseases such as tuberculosis started to rise again? Give 2 examples of how bacteria are actually a natural and needed part of life. How exactly does an antibiotic “heal” a bacterial infection? (How does it kill the microbe?) Give 2 ways in which bacteria can acquire resistance to an antibiotic. Give 2 ways that bacteria “share” their resistance traits with one another. Antibiotics often become “self defeating” by actually encouraging resistant bacteria. Give one example of how antibiotics promote resistance. 8. If you were taking an antibiotic to treat acne, explain how this could cause antibiotic resistant bacteria on the skin of another family member to rise. 9. Why is it always important to completely finish a prescription of antibiotics whether you begin feeling better or not? 10. How can the antibiotics agriculturalists use to keep livestock and crops healthy, end up in our body system? 11. Give 3 ways the public can help decrease the prevalence of antibiotic resistant bacteria. 12. Penicillin is probably the most well known antibiotic ever used. Some bacteria, though, have now become resistant to its effectiveness. Explain how a bacterium can evade the effects of this antibiotic. The Challenge of Antibiotic Resistance Answer the following questions. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. What is the “public health nightmare” concerning antibiotic use? Why have death rates for diseases such as tuberculosis started to rise again? Give 2 examples of how bacteria are actually a natural and needed part of life. How exactly does an antibiotic “heal” a bacterial infection? (How does it kill the microbe?) Give 2 ways in which bacteria can acquire resistance to an antibiotic. Give 2 ways that bacteria “share” their resistance traits with one another. Antibiotics often become “self defeating” by actually encouraging resistant bacteria. Give one example of how antibiotics promote resistance. 8. If you were taking an antibiotic to treat acne, explain how this could cause antibiotic resistant bacteria on the skin of another family member to rise. 9. Why is it always important to completely finish a prescription of antibiotics whether you begin feeling better or not? 10. How can the antibiotics agriculturalists use to keep livestock and crops healthy, end up in our body system? 11. Give 3 ways the public can help decrease the prevalence of antibiotic resistant bacteria. 12. Penicillin is probably the most well known antibiotic ever used. Some bacteria, though, have now become resistant to its effectiveness. Explain how a bacterium can evade the effects of this antibiotic.