Chem Spa Gas Tests 2009 Yingxin
advertisement

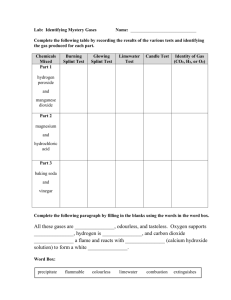
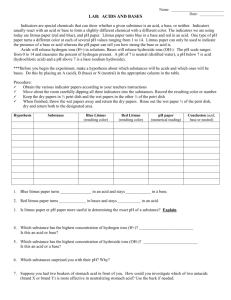
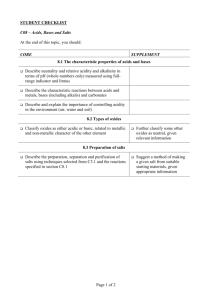
CHEM SPA! 1. Note COLOUR and ODOUR of gas. 2. Test the gas evolved with MOIST RED AND BLUE LITMUS PAPERS. 3. SPECIFIC TESTS Note COLOUR and ODOUR of gas. Colourless and odourless Colourless and pungent Greenish-yellow and pungent *colour isn’t very obvious – hold against white surface to see! H2, O2, CO2 NH3, SO2 Cl2 Test the gas evolved with MOIST RED AND BLUE LITMUS PAPERS. No colour change to the moist red and blue litmus paper is observed H2, O2 Gas evolved turns moist blue litmus paper red CO2, SO2 *CO2 cannot really be observed! Gas evolved turns moist red litmus paper blue NH3 Gas evolved turns moist blue litmus paper red and bleaches it Cl2 Gas evolved bleaches moist red litmus paper Gas is neutral Gas is acidic Gas is alkaline Gas evolved has bleaching properties, gas evolved is chlorine SPECIFIC TESTS Hold a lighted splint near the mouth of the test tube Insert a glowing splint into the test tube Bubble the gas evolved into limewater Use 2cm of limewater Hold limewater test tube on right, solution on left Heat solution – in and out of flame Limewater must be removed before solution to prevent “suck back” Hold a strip of filter paper which has been dipped in acidified potassium dichromate (VI) solution, at the mouth of the test tube Hold a strip of filter paper which has been dipped in acidified potassium manganate (VII) solution, at the mouth of the test tube Hold a piece of moist starch-potassium iodide paper near the mouth of the test tube Gas evolved extinguishes lighted splint with a “pop” sound Gas evolved relights glowing splint Gas evolved forms a white precipitate with limewater H2 Gas evolved turns acidified K2Cr2O7 solution from orange to green Gas evolved turns acidified KMnO4 solution from purple to colourless Gas evolved turns moist starchpotassium iodide paper blue-black SO2 O2 CO2 SO2 Cl2 Hydrogen 1. Colourless and odourless 2. No colour change to the moist red and blue litmus papers is observed = Gas is neutral 3. Hold a lighted splint near the mouth of the test tube = Gas evolved extinguishes the lighted splint with a “pop” sound Oxygen 1. Colourless and odourless 2. No colour change to the moist red and blue litmus papers is observed = Gas is neutral 3. Insert a glowing splint into the test tube = Gas evolved relights the glowing splint Carbon Dioxide 1. Colourless and odourless 2. Gas evolved turns moist blue litmus paper red (cannot really be observed) = Gas is acidic 3. Bubble gas evolved into limewater = Gas evolved forms a white precipitate with limewater Sulphur Dioxide 1. Colourless and pungent 2. Gas evolved turns moist blue litmus paper red = Gas is acidic 3. Hold a strip of filter paper that has been dipped in acidified potassium dichromate (VI) solution near the mouth of the test tube = Gas evolved turns acidified potassium dichromate solution from orange to green 4. Hold a strip of filter paper that has been dipped in acidified potassium manganate (VII) solution near the mouth of the test tube = Gas evolved turns acidified potassium manganate solution from purple to colourless Ammonia 1. Colourless and pungent 2. Gas evolved turns moist red litmus paper blue = Gas is alkaline Chlorine 1. Greenish-yellow and pungent 2. Gas evolved turns moist blue litmus paper red and bleaches it, gas evolved bleaches moist red litmus paper = Gas evolved has bleaching properties, gas evolved is Chlorine 3. Hold a strip of moist starch-potassium iodide paper near the mouth of the test tube = Gas evolved turns moist starch-potassium iodide paper blue-black Bunsen Burner Close air hole Adjust until non-luminous flame is obtained Adjust gas tap to obtain desired strength of flame Turn off flame when not in use (non-luminous flame is INVISIBLE) Heating Wear safety glasses When heating a solid, must use clean and dry test tube Use a test tube holder! About ¼ length from top of test tube Point mouth of test tube away from people Gently shake solution as it is being heated Move test tube in and out of flame LOOK at the test tube and the flame throughout Place all chemicals away from flame Do not touch hot test tube Cap bottles Handle apparatus properly Do not place moist litmus papers on table/wherever Amount of solutions used should be 2cm Gas Collection Depends on physical properties of gas o Solubility in water o Density compared to air Not soluble (hydrogen) or sparingly soluble (oxygen) in water – collected by downward displacement of water Soluble/react with water – air in a container is displaced by these gases. o Gas has density greater than density of air – displace air from bottom to top of upright gas jar (eg chlorine, carbon dioxide, sulphur dioxide, nitrogen dioxide) = downward delivery o Gas has density lower than density of air – displace air from top to bottom of inverted gas jar (eg ammonia) = upward delivery