Modal Auxiliary Verbs – Meanings
advertisement

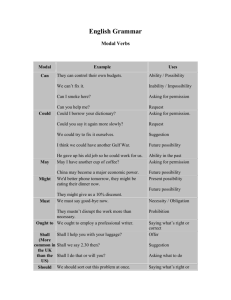
Modal Auxiliary Verbs – Meanings Certainty Complete Certainty o o o o o Shall Will Must Can Would I shall be late tomorrow. Probability / Possibility o o o o o o Should Ought May Might Can Could Weak Probability / Strong Obligation Weak Possibility o Might o Could She should be here soon. I might see you again, one day. He’ll be away tomorrow. He ought to be home by now. You must be tired. Obligation We may be eating with Paul and Francesca tonight. That can’t be John – he’s The water may not be in Paris. warm enough to swim in. I told you that you would Whan Frank gets a job, I pass the FCE. might get the money back I lent him Things will be all right. I think we can go now. It could rain later. o Must o Will o Need Staff must be at their desks by 0900 sharp! It might not turn out so bad. All teachers will keep accurate records of lessons and students. We could be millionaires Need I get a VISA to one day. work in the USA? You need to declare your income to the tax man. Absence of Obligation Prohibition Weak Obligation / Advice / Recommendation o Must o May o Can o o o o o Should Ought to Had better Might Shall Students must not use the staff cars as goalposts. Books may not be taken out of the library. You should try harder. You can’t come in here. That child had better She ought to wash her hair. start saying thank-you for things. You might see what John thinks before going. What shall we do? o Need / Have to You needn’t / don’t have to work this Saturday. Modal auxiliaries are also used to express ability, permission, offering, insisting and conditional probability. Note that intonation and stress can alter the meaning of a sentence with a modal auxiliary verb.