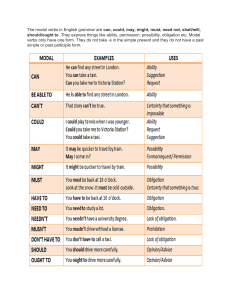
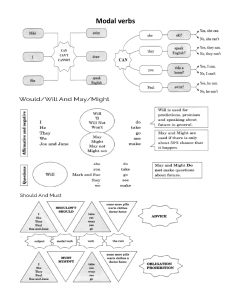
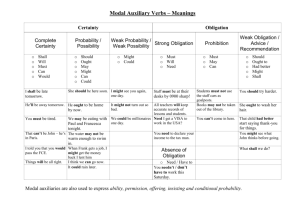
Modal Verbs Auxiliary verbs - type of verb that takes a supportive role in a sentence, second to the main verb - used mainly to create complex grammatical tenses, like the perfect and continuous tenses, which show different aspects of time, or how long an action takes place Modal verbs - a type of auxiliary verbs. - express capacity, possibility, obligation, permission, prohibition, probability, supposition, request or desire. - change the grammatical mood of a sentence. Modal verbs - list - can may will shall ought to - could might would should must can - one of the most commonly used modals in English. - used to express capacity, permission or request. - He can speak Italian. (capacity) - She can enter the room. (permission) - Can you lend me a pencil, please? (request) could - expresses possibility, past ability, suggestions and requests. - Extreme rain could cause the river to flood the city. (possibility) - He could play the guitar when he was younger. (past ability) - We could go to the cinema. (suggestion) - Could I use your laptop? (request) may - used to express possibility, as well as give / ask for permission. - He may be either at school or at home. (possibility) - You may use my computer. (give permission) - May I leave earlier today? (ask for permission) might - commonly used to indicate possibility, but could be used to make suggestions or requests. - It might rain. (possibility) - You might visit the gallery during your vacation. (suggestion) - Might I open the door? (request - British standard, formal) must - can be used to talk about probability, as well as obligation, prohibition, necessity or strong recommendation. - He must be sick, he is never late for classes. (probability) John, you must do your homework. (obligation) Students must pass an entrance exam in order to study here. (necessity) In order to stay healthy, you must drink a lot of water. (recommendation) shall - indicates a future action. - most commonly used with first person singular and plural (I and we), often found in suggestions and promises. - Shall we set the table? (suggestion) - I shall never betray you. (promise) will - most commonly used to talk about future situations. - used in the present to make a request. - used to indicate instant decisions. - I will call you later. (future action) - Will you close the window, please? (request) - I really like this shirt, I will buy it. (instant decision) would - commonly used to create conditional verb tenses. - can be used to make offers, requests and talk about past habits - Would you like some cake? (offer) - If I were you, I would work harder. (2nd conditional) - Would you turn down the volume? (request) - We would play football every day when we were kids. (past habits) should - commonly used to give recommendations or advices. - rarely used to express obligations and expectations. - When you are at school for a whole day, you should bring some snacks with you. (recommendation) - You should focus more on your studies. (advice) - I should be at school before 8 am. (obligation) - At this moment, the plane should have already landed. (expectation) ought to - used to advise or make recommendations. - can also express assumptions or exprecations. - She ought to stop eating fast food in order to lose weight. (recommendation). - John ought to get a promotion. (expectation) - The apartments ought to increase in value. (assumption) Exercises Exercises Exercises Thank you for your attention!