Catalase Teacher`s Notes pH
advertisement

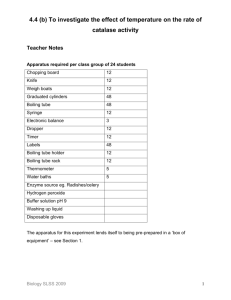
4.3 (b) To investigate the effect of pH on the rate of catalase activity Teacher Notes Apparatus required per class group of 24 students Chopping board 12 Knife 12 Weigh boats 12 100 ml Graduated cylinders 36 Boiling tube 36 Syringe 12 Electronic balance 3 Dropper 12 Timer 12 Labels 36 Thermometer 12 Water bath 3 Enzyme source eg. Radishes/celery Hydrogen peroxide Range of buffer solutions pH paper Washing up liquid Disposable gloves The apparatus for this experiment lends itself to being pre-prepared in a ‘box of equipment’ – see Section 1. Advance preparation o Prepare buffer solutions. o Obtain fresh celery. Biology SLSS 2009 1 Advance chemical preparation (a) Hydrogen peroxide (Prepares 250 ml of 1M/’12 vol’ solution) o Wearing gloves, measure out 29 ml of ‘100 vol’ hydrogen peroxide into a measuring cylinder. o Make up to 250 ml with water, add to a labelled bottle and mix well. o Alternatively, small quantities of hydrogen peroxide can be purchased in the local pharmacy. Safety precautions o Hydrogen peroxide is both oxidising and corrosive. For further information see MSDS. Expected outcome of experiment o Catalase from celery has an optimum pH of 9. This buffer solution should result in the greatest volume of foam produced. o At pHs above and below 9 the activity of catalase decreases, less foam will be produced. Disposal and post-experiment work o To dispose of hydrogen peroxide add small quantities (100 ml) in 10L of water and run to foul water drain. For the datalogging method for this experiment, please see Section 3. Biology SLSS 2009 2 4.3 (b) To investigate the effect of pH on the rate of catalase activity Student Notes Apparatus required per group o Chopping board o 3 x Labels o Knife o Thermometer o Weight boat o Trough o 3 x Graduated cylinders o Celery o 3 x Boiling tubes o Hydrogen peroxide o Syringe o Buffer solutions o Electronic balance o pH paper o Dropper o Washing-up liquid o Timer o Disposable gloves Assembled apparatus Biology SLSS 2009 3 Method 1. Add 20 ml of one of the selected buffers to a 100 ml graduated cylinder. 2. Using a dropper, add one drop of washing-up liquid to the cylinder. 3. Add 5 g of finely chopped celery to the cylinder. 4. Add 2 ml of hydrogen peroxide to a boiling tube. 5. Stand the cylinder and the boiling tube in the water bath at 25OC. 6. Pour the hydrogen peroxide into the cylinder. 7. Note the volume in the cylinder immediately and record. 8. Read the volume again after a measured amount of time, e.g. 2 minutes, and record. 9. Subtract the initial volume from the final volume to get the volume of foam and record. 10. Repeat the procedure from step 1 for each of the other buffer solutions. 11. A graph should be drawn of enzyme activity (volume of foam) against pH. Put pH on the horizontal axis. 12. At the end of the experiment, clean all of the equipment and replace it in its correct place. Results: pH of buffer Initial volume Final volume Volume of (ml) (ml) foam produced (ml) Conclusion/Comment Biology SLSS 2009 4