Day 005- Titration Lab HCl NaOH revised Jan 2013
advertisement

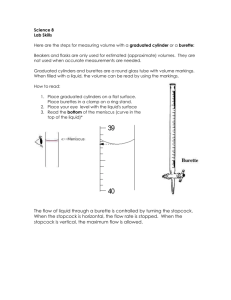
Chemistry 11 Lab: Titration Introduction: Acids and bases are part of many industrial processes as well as part of our daily lives. As such, the determination of the concentrations of solutions of acids and bases is essential for both these processes and for safety. The determination of the concentration of solution of an acid or base is made possible by the fact that these solutions neutralize each other. An indicator, which changes colour based on pH changes, can be used to identify when this neutralization has occurred. This technique of determining the concentration of a solution of an acid or base is called a titration. In this lab you will be given a solution of hydrochloric acid of unknown concentration as well as a base (NaOH) of known concentration. Using the technique of titration, the concentration of the acid will be determined. Lab Report Details: Begin a new page in your notebook and complete your title block at the top of the page. Record the purpose of the lab in complete sentences. Draw a proper data table for your quantitative ovservations (include initial burette reading, final burette reading and volume of base added for at least 4 trials) and a data table for your qualitative observations (include the colour of the final solution for each trial). Answer the analysis questions. Include the marking scheme with your lab report. Materials Apron and goggles Burette Burette clamp Retort stand 10 mL pipette and pump (at station) Bottle of distilled water Erlenmeyer flask Large waste beaker 50 mL beaker Small funnel White paper Phenolphthalein 0.20 mol/L NaOH Unknown HCl solution Procedure 1. Collect your materials as directed by your teacher. You do not need a pipette and pump- they will be ready for you at the acid station. 2. Clamp the burette clamp onto the retort stand and attach the burette. 3. Obtain about 50 mLof 0.20 mol/L NaOH in a DRY 50 mL beaker. 4. To rinse the burette with NaOH, place the funnel on top of the burette (stopcock closed) and carefully add about 5 mL of the NaOH solution to the burette. 5. Remove the burette from the clamp, tilt it horizontally and rotate to rinse the walls with the NaOH. 6. Return the burette to the clamp, open the stopcock and dispense the NaOH into a waste beaker. 7. Close the stopcock and now fill the burette with the NaOH solution. 8. Read the initial burette reading for trial 1. Your eye must be at the same level of the meniscus to make a proper reading. Place a white strip of paper behind the line to make the line easier to see and record all significant digits (ie. 2 decimal places for our burettes). 9. Using the pipette to obtain exactly 10.0 mL of the HCl solution from the acid station and transfer it into a clean Erlenmeyer flask. Use the same flask for all trials, rinsing with water in between. Add two drops of phenolphthalein indicator to the flask before you leave the station. Revised Jan 2013 10. Place the flask below the burette with a white piece of paper under it. 11. While continuously swirling the flask, open the stopcock on the burette and begin slowly adding the base to the solution. 12. Close the stopcock when the colour of the solution has changed to pink. Ideally you want your solution to be a very pale pink. Dark pink means you have gone past the endpoint. 13. The first titration is to determine the approximate volume of base required for the indicator to turn a pink. Keep this range finding volume in mind but do not include it in your table. 14. Dispose of the titrated solution in your waste beaker and rinse the flask clean with water. 15. Refill the burette with the NaOH if needed. 16. Obtain another 10.0 mL of the HCl into the flask and repeat the titration. Be sure to reduce the flow near the end point (when the colour is about to change). Add the base drop by drop. 17. When you think the colour is about to change, record the volume and then use a squirt bottle of distilled water to rinse down the sides of the flask and the tip of the burette. If the colour changes then use that volume. If not, add one drop at a time until the colour stays pale pink for about 15 seconds while swirling. 18. Record the volume of base added to reach the end point in your data table. 19. Dispose of the solution. 20. Repeat this process until you obtain at least two very pale pink solutions. 21. Drain the base out of your buret into a waste beaker then rinse your burette with dilute acid to clean it out. Drain the dilute acid into the waste beaker and leave your burette on the burette stand upside down with the stopcock open so it will dry out over night. Put everything else away and wipe down your lab bench. Analysis 1. a) Write the balanced equation for the neutralization reaction. b) Using the average volume of the base, calculate the concentration of the HCl solution. 2. Using the same NaOH standard solution, a) Design a method to determine the concentration of vinegar found at the grocery store. b) Write the balanced equation for the neutralization reaction. c) Include a sample calculation. (use variables instead of lab data) Revised Jan 2013 SCH-3U Sections Titration Lab Marking Scheme Level 1 Minimal requirements are met Level 2 Some of the requirements are met Level 3 Most of the requirements are met Level 4 All of the requirements are met Weight Communication Title Block - is clear, neat, and well organized - contains an appropriate title, partner’s name & date Appropriate general purpose is given in one or two sentences 1x Results - Data Table - appropriate title at the top - well organized and neat (numbers are aligned) - units are in the headings - contains all relevant data Overall clarity, neatness, spelling and grammar 2x 1x 1x /20 Overall Communication Inquiry Experimental technique as reflected by the accuracy of the results. Analysis Questions Balanced equations is complete (balanced, states) and correct Analysis Question 1 concentration of the HCl solution is calculated correctly, s.d., units Analysis Question 2 Appropriate method designed, sample calculations shown Overall Inquiry 1x 1x 2x 2x /24 Revised Jan 2013