Activity - Taking Measurements
advertisement

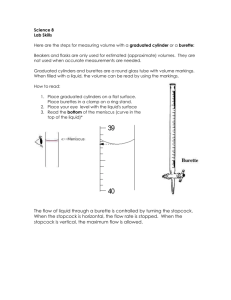
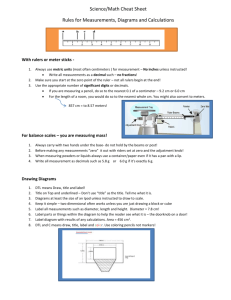
Making Measurements Name: _____________________ In Chemistry, it is important to record your data showing the correct number of significant figures and units. In this activity, you will learn how to make correct measurements and to make calculations using the measurements you collected. Each group with go to each station and make the necessary observations. Record all your observations with the correct number of significant figures and units. Do all the calculations considering the rules involving calculations of measurements. Station 1. Electronic Balance: (1 and 2 decimal point scale) Obtain two elements from your teacher, weigh one element on the 1 decimal scale and the other element on the 2 decimal scale. Balance 1 decimal point scale 2 decimal point scale Mass (g) Calculations: a. Add the mass record from the 1 decimal point scale to the mass record from the 2 decimal point scale. Station 2. Centimeter Ruler: Measure the length, width and height of the rectangular objects. Measure the mass of each object using the electronic balance. Length Width Height Mass Object Calculations: a. Calculate the volume of the object. b. Calculate the density of the object. Station 3. Odd’s and End’s Record the volumes of fluids in the following containers. Beaker (250 mL) Volume (mL) Erlenmeyer Flask (250 mL) Test Tube 25 mL Grad. Cylinder Making Measurements Name: _____________________ Station 4. Thermometer Read the temperature of ice water and boiling water (be careful!) Ice Water Boiling Water Temperature (Co) Calculations: Convert the temperature that you record into: a. Kelvin b. Fahrenheit Station 5. Burette’s: Burette #1 and #2 represent the same beaker. Burette #1 represents a burette BEFORE the stopcock has been opened. Burette #2 represents a burette AFTER the stopcock has been opened and some of the solution has been released. Measure the initial and final readings. Initial Volume (mL) Final Volume (mL) Burette #1 Burette #2 Calculations: a. Calculate the change in volume. Challenge! ~ only if time permits! Station 6. Measure Density using Archimedes Principle: Measure the mass of both masses. Fill two 25 mL graduated cylinders to about the 10 mL mark. The actual volume does not matter, but you need to record the initial volume correctly. Place the mass into the graduated cylinder, and record the final volume. Initial Volume (mL) Final Volume (mL) Mass #1 Mass #2 Calculations: a. Calculate the volume of each mass. (mL) b. Calculate the density of each mass. (in kg/m3) c. Using your phones, determine the identity of Mass #1 and Mass #2. Mass (g) Making Measurements Name: _____________________