Syllabus
advertisement

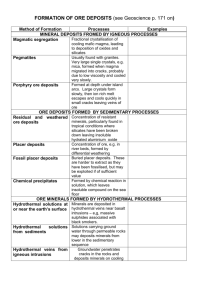
Geology of Earth Resources Course objectives: The objectives of this course in Earth Resources are: (i) acquainting students (majors and non-majors) with the basic tools necessary for studying earth resources, (ii) understanding the different types of Earth resources, (iii) understanding the processes of formation of various economic ore deposits, (iv) understanding the processes and conditions necessary for the formation of oil and gas deposits, (v) understanding the relationship between the distribution of ores, oil, gas, and coal, and Plate Tectonics, and (vi) gaining some knowledge of the environmental problems associated with the extraction and utilization of earth resources. Textbooks: Most reading assignments will be from: "Ore Geology and Industrial Minerals: An introduction" by Anthony Evans. Additional readings will be assigned from a number of other textbooks, which are either available in the library, or will be placed in 228. Some lecture notes will be handed out throughout the semester. The students are advised not to rely entirely on the lecture notes which will only contain a brief outline of the subject matter, and are thus encouraged to take notes during lectures and do all the assigned reading. Field trips: This class has one field trip to a nearby area of some economic significance/ potential. Labs: Possible, depending on the emphasis/ curriculum/ departmental policy/ sample availability. Lab exercises would focus on textures of ore deposits, identifying ores, assessing reserves, identification of ore minerals using reflected light microscopy. Other Useful Textbooks Evans, A. M., 1997: An introduction to Economic Geology and its environmental impact. Blackwell Scietific publications, 364 pp. Beydoun, Z. R., 1991. Arabian Plate Hydrocarbon Geology and Potential. AAPG, 77 pp. Guilbert, J. M. and Park, C. F., 1986. The Geology of Ore Deposits. W. H. Freeman & Co, 984 pp. Hunt, J. M., 1996. Petroleum Geochemistry and Geology. W. H. Freeman & Co, 743 pp. Levorsen, A.I., 1967. Geology of Petroleum. W. H. Freeman & Co. 724 pp. Selley, Richard C., 1998. Elements of Petroleum Geology. Academic Press. 470 pp. Earth Resources Syllabus & Tentative Schedule lecture 1-3 Topic Reading Introduction and basic principles Definitions: Resources, Ore, Protore, Gangue, Grade, Cutoff grade, Reserves, Industrial rocks and minerals. Overall market trends and relative importance of Ore and industrial rocks & minerals Mechanisms of concentration 1-25 4, 5 Classification of Ore deposits Descriptive classifications, Genetic classifications A modified form of Lindgren's Classification. Chapter 6 6 Morphology of ore deposits Syngenetic and epigenetic ores, Structures of ore bodies 7 8, 9 MT exam 1 Textures of Ore Deposits Textures of magmatic ore deposits Textures of hydrothermal ore deposits: Replacement textures, Open space filling textures Textures characteristic of surface or near surface deposits 10 - 13 Mineralogical, Geochemical and geochronological techniques used 42 – 51; 84 for studying ore deposits 95 Mineral Parageneses, paragenetic sequences and zoning Wall rock alteration Geochemical characterization of wall rock alteration and ore body zoning Fluid inclusions and their applications to the study of mineral deposits. Geothermometry and geobarometry Stable isotopes Geochronological techniques 14 15 16 17 18 19 Magmatic Ores A- Deposits associated with ultrabasic and basic rocks Chromite deposits, PGM’s. Cu-Fe-Ni sulfides Diamonds in Kimberlites Carbonatites B- Deposits associated with acid and intermediate rocks Pegmatites Greisens Hydrothermal ore deposits Origin, Properties, Migration, Metal transport capability, Deposition and ground preparation. Types of Hydrothermal deposits. Types of hydrothermal veins 20 Volcanogenic Massive Sulfides 21 MT exam 2 22, 23 Porphyry Cu deposits Definition, Classification, Characteristics, Origin. 24 Base Metal Lode Deposits General characteristics of Mesothermal deposits Characteristics of Base Metal Lode Deposits Origin Chapter 2 40 - 42 Chapter 10 Chapter 11 Chapter 7 Chapter 8 Chapter 9 Chapter 12 55 - 69 202 - 210 p. 171 - 186 213 – 215; 217 - 221 25 Epithermal Deposits General characteristics Types: epithermal Au veins, disseminated Au deposits, Ag deposits (Creede - type), U vein deposits, Unconformity associated U deposits (Athabasca type), Sn and W vein deposits. 221 – 231 Chapters 17 & 18 27, 28 29 30 Sediment hosted and Sedimentary Ore Deposits (stratiform, stratabound & placer) Types; Processes of Ore formation Stratiform Cu deposits Mississippi Valley Type Deposits Mn ores & BIF’s Placer deposits 31 Residual Deposits and Supergene enrichment Chapter 19 32 - 33 Industrial Minerals Chapters 20 & 21 34 - 36 Oil & Gas (UTM International Week: Oil in the Middle East). notes 37, 38 Coal notes 39, 40 Geothermal & nuclear energy notes 41, 42 Ore Deposits in Space and time Chapters 23 & 24 26 190 - 202 233 - 239 253 - 261 244 - 253 Metallogenic Epochs Plate Tectonic Setting of Ore Deposits 43, 44 Environmental impact of mineral exploitation notes