Endosymbiotic Theory Worksheet
advertisement
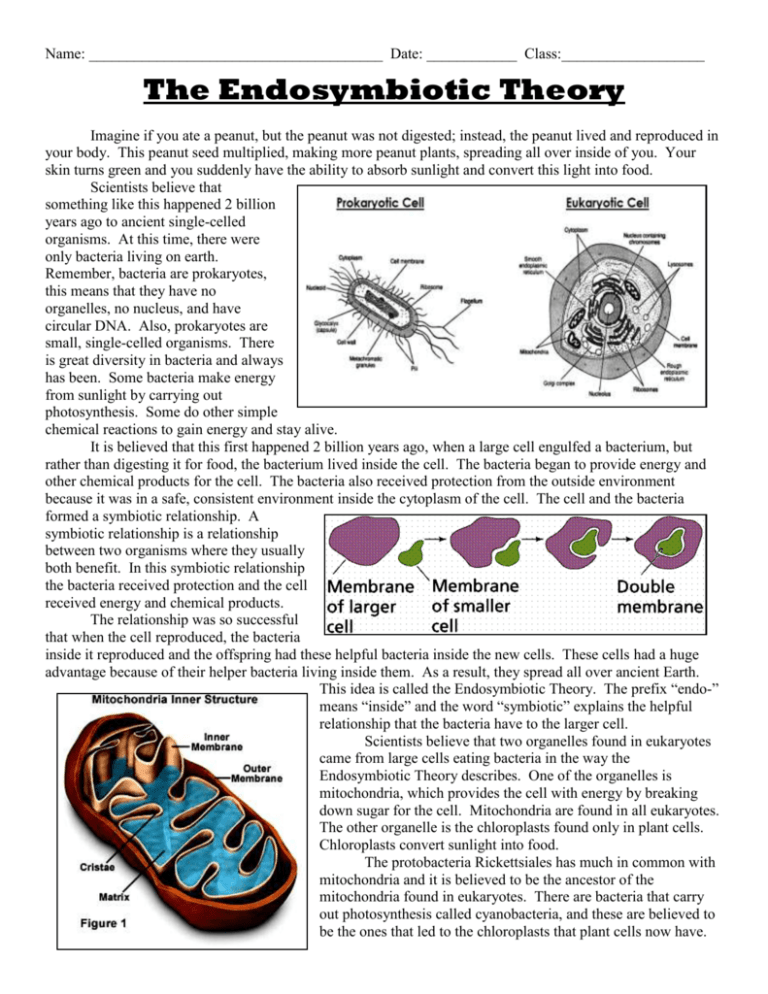
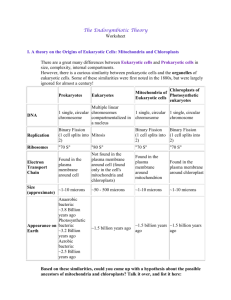
Name: _______________________________________ Date: ____________ Class:___________________ The Endosymbiotic Theory Imagine if you ate a peanut, but the peanut was not digested; instead, the peanut lived and reproduced in your body. This peanut seed multiplied, making more peanut plants, spreading all over inside of you. Your skin turns green and you suddenly have the ability to absorb sunlight and convert this light into food. Scientists believe that something like this happened 2 billion years ago to ancient single-celled organisms. At this time, there were only bacteria living on earth. Remember, bacteria are prokaryotes, this means that they have no organelles, no nucleus, and have circular DNA. Also, prokaryotes are small, single-celled organisms. There is great diversity in bacteria and always has been. Some bacteria make energy from sunlight by carrying out photosynthesis. Some do other simple chemical reactions to gain energy and stay alive. It is believed that this first happened 2 billion years ago, when a large cell engulfed a bacterium, but rather than digesting it for food, the bacterium lived inside the cell. The bacteria began to provide energy and other chemical products for the cell. The bacteria also received protection from the outside environment because it was in a safe, consistent environment inside the cytoplasm of the cell. The cell and the bacteria formed a symbiotic relationship. A symbiotic relationship is a relationship between two organisms where they usually both benefit. In this symbiotic relationship the bacteria received protection and the cell received energy and chemical products. The relationship was so successful that when the cell reproduced, the bacteria inside it reproduced and the offspring had these helpful bacteria inside the new cells. These cells had a huge advantage because of their helper bacteria living inside them. As a result, they spread all over ancient Earth. This idea is called the Endosymbiotic Theory. The prefix “endo-” means “inside” and the word “symbiotic” explains the helpful relationship that the bacteria have to the larger cell. Scientists believe that two organelles found in eukaryotes came from large cells eating bacteria in the way the Endosymbiotic Theory describes. One of the organelles is mitochondria, which provides the cell with energy by breaking down sugar for the cell. Mitochondria are found in all eukaryotes. The other organelle is the chloroplasts found only in plant cells. Chloroplasts convert sunlight into food. The protobacteria Rickettsiales has much in common with mitochondria and it is believed to be the ancestor of the mitochondria found in eukaryotes. There are bacteria that carry out photosynthesis called cyanobacteria, and these are believed to be the ones that led to the chloroplasts that plant cells now have. At first, the idea of Endosymbiotic Theory seems too mind-boggling to be true, but there is a great deal of evidence. These two organelles mitochondria and chloroplasts are unique, and have much in common with their suspected prokaryotic, bacterial ancestors. First of all, mitochondria and chloroplasts are about the same size as bacteria. Also, mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own DNA and ribosomes! The DNA of mitochondria is circular, just like it is in all prokaryotic bacteria. The DNA has the code for proteins that are very similar in structure to those of Rickettsiales and cyanobacteria and other bacterial relatives. The two organelles also reproduce when the eukaryotic cell divides. Mitochondria and chloroplasts reproduce by binary fission, the very same process that bacteria use when they reproduce. Additionally, mitochondria and chlorophyll are the only organelles with a double membrane. If the mitochondria or chloroplasts in a cell are destroyed, they cannot be remade. They are their own living cells and the eukaryotic cell can’t just re-make them from its DNA. The eukaryotic cell has a membrane surrounding the organelle, and then the organelle has its own membrane. This is called a double membrane. Mitochondria and chloroplasts live inside eukaryotic cells, but do many of the same Lynn Margulis came up with things and have similar appearance to bacteria living on their own. All the Endosymbiotic Theory. of this evidence supports the Endosymbiotic Theory because it suggests that She had trouble getting her mitochondria and chloroplasts are bacteria and along time ago they did live idea accepted at first, but her on their own. perseverance paid off. Now Scientists now believe that 2 billion years ago, when a large cell ate the theory it is widely some bacteria, eukaryotes were created. The bacteria and the large cell believed by scientists. worked so well together than they spread all over the Earth. The scientist to propose this idea was met with huge disapproval and ridicule at the time. Lynn Margulis spent years doing research and wrote a book detailing the evidence for her theory. Publishers mocked her idea and refused to publish her work. So, she got in touch with other scientists and proposed her idea to them. Within a few years, a university had published her work and Endosymbiotic Theory was widely approved in the scientific community. Now eukaryotes have become very complex with many organelles, but it is believed that mitochondria and chloroplasts originated from the Endosymbiotic Theory. So, within each and every one of our cells is a huge population of bacteria, helping us to survive, and we’re helping them survive. Name: _______________________________________ Date: ____________ Class:___________________ The Endosymbiotic Theory Article Questions Answer the following questions by writing one or two complete sentences. 1. What do the parts of the phrase “Endosymbiotic Theory” mean? Why are they called that? 2. What was life like on Earth 2 billion years ago? What kinds of organisms were around? 3. Do you think that humans could survive on the Earth like it was 2 billion years ago? Why or why not? 4. If endosymbiosis had not happened, would be some organisms that wouldn’t be around today? List at least 4. Extended Answer Questions. Answer these questions by writing one short paragraph. 5. What evidence is there that supports the Endosymbiotic Theory? Provide at least 4 specific pieces of evidence. 6. Think about the kinds of organisms that were created as a result of endosymbiosis. Why do you think that they were able to evolve into more complex multi-cellular organisms, like plants, animals, and eventually into humans? Why do you think prokaryotes were not able to do this? Name: _______________________________________ Date: ____________ Class:___________________ The Endosymbiotic Theory Imagine if you ate a peanut, but the peanut was not digested; instead, the peanut lived and reproduced in your body. This peanut seed multiplied, making more peanut plants, spreading all over inside of you. Your skin turns green and you suddenly have the ability to absorb sunlight and convert this light into food. Scientists believe that something like this happened 2 billion years ago to ancient single-celled organisms. At this time, there were only bacteria living on earth. Remember, bacteria are prokaryotes, this means that they have no organelles, no nucleus, and have circular DNA. Also, prokaryotes are small, singlecelled organisms. There is great diversity in bacteria and always has been. Some bacteria make energy from sunlight by carrying out photosynthesis. Some do other simple chemical reactions to gain energy and stay alive. It is believed that this first happened 2 billion years ago, when a large cell engulfed a bacterium, but rather than digesting it for food, the bacterium lived inside the cell. The bacteria began to provide energy and other chemical products for the cell. The bacteria also received protection from the outside environment because it was in a safe, consistent environment inside the cytoplasm of the cell. The cell and the bacteria formed a symbiotic relationship. A symbiotic relationship is a relationship between two organisms where they usually both benefit. In this symbiotic relationship the bacteria received protection and the cell received energy and chemical products. The relationship was so successful that when the cell reproduced, the bacteria inside it reproduced and the offspring had these helpful bacteria inside the new cells. These cells had a huge advantage because of their helper bacteria living inside them. As a result, they spread all over ancient Earth. This idea is called the Endosymbiotic Theory. The prefix “endo-” means “inside” and the word “symbiotic” explains the helpful relationship that the bacteria have to the larger cell. Scientists believe that two organelles found in eukaryotes came from large cells eating bacteria in the way the Endosymbiotic Theory describes. One of the organelles is mitochondria, which provides the cell with energy by breaking down sugar for the cell. Mitochondria are found in all eukaryotes. The other organelle is the chloroplasts found only in plant cells. Chloroplasts convert sunlight into food. The protobacteria Rickettsiales has much in common with mitochondria and it is believed to be the ancestor of the mitochondria found in eukaryotes. There are bacteria that carry out photosynthesis called cyanobacteria, and these are believed to be the ones that led to the chloroplasts that plant cells now have. At first, the idea of Endosymbiotic Theory seems too mind-boggling to be true, but there is a great deal of evidence. These two organelles mitochondria and chloroplasts are unique, and have much in common with their suspected prokaryotic, bacterial ancestors. First of all, mitochondria and chloroplasts are about the same size as bacteria. Also, mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own DNA and ribosomes! The DNA of mitochondria is circular, just like it is in all prokaryotic bacteria. The DNA has the code for proteins that are very similar in structure to those of Rickettsiales and cyanobacteria and other bacterial relatives. The two organelles also reproduce when the eukaryotic cell divides. Mitochondria and chloroplasts reproduce by binary fission, the very same process that bacteria use when they reproduce. Additionally, mitochondria and chlorophyll are the only organelles with a double membrane. If the mitochondria or chloroplasts in a cell are destroyed, they cannot be remade. They are their own living cells and the eukaryotic cell can’t just re-make them from its DNA. The eukaryotic cell has a membrane surrounding the organelle, and then the organelle has its own membrane. This is called a double membrane. Mitochondria and chloroplasts live inside eukaryotic cells, but do many of the same things and have similar appearance to bacteria living on their own. All of this Lynn Margulis came up with the evidence supports the Endosymbiotic Theory because it suggests that mitochondria Endosymbiotic Theory. She had and chloroplasts are bacteria and along time ago they did live on their own. trouble getting her idea Scientists now believe that 2 billion years ago, when a large cell ate some accepted at first, but her bacteria, eukaryotes were created. The bacteria and the large cell worked so well perseverance paid off. Now the together than they spread all over the Earth. The scientist to propose this idea was theory it is widely believed by met with huge disapproval and ridicule at the time. Lynn Margulis spent years scientists. doing research and wrote a book detailing the evidence for her theory. Publishers mocked her idea and refused to publish her work. So, she got in touch with other scientists and proposed her idea to them. Within a few years, a university had published her work and Endosymbiotic Theory was widely approved in the scientific community. Now eukaryotes have become very complex with many organelles, but it is believed that mitochondria and chloroplasts originated from the Endosymbiotic Theory. So, within each and every one of our cells is a huge population of bacteria, helping us to survive, and we’re helping them survive. Discussion Questions 1. 2. 3. 4. Discuss the answers to the following questions with your group. What do the parts of the phrase “Endosymbiotic Theory” mean? Why are they called that? What was life like on Earth 2 billion years ago? What kinds of organisms were around? Do you think that humans could survive on the Earth like it was 2 billion years ago? Why or why not? If endosymbiosis had not happened, would be some organisms that wouldn’t be around today? List at least 4. For your Notebook Title a section of your notebook, “The Endosymbiotic Theory.” Make the below table in your notebook and complete it. In the first column, write in pieces of evidence that support the Endosymbiotic Theory. Include at least 4 separate pieces of evidence. In the second column, challenge the pieces of evidence that you wrote in the first column with an alternative hypothesis that would undermine the Endosymbiotic Theory. You creatively come up with these alternative hypotheses. Then, in the third column, explain which position you believe and why. Endosymbiotic Theory Evidence Challenges and Alternative Hypotheses Which do you believe and why?