Meteorology: the study of what goes on in the Earth`s atmosphere
advertisement

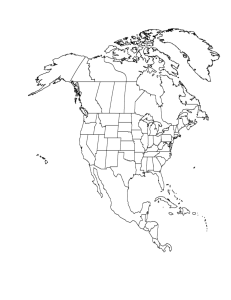
Section 12-1: The Causes of Weather Meteorology: the study of what goes on in the Earth’s atmosphere Weather vs. Climate: Weather: the current state of the atmosphere in an area, or short-term changes in the atmosphere. Climate: long-term variations in weather for a particular area. Climate is usually averaged over the course of 30 years or more. air masses: a large body of air that takes on the characteristics of the area over which it forms, such as the amount of moisture or temperature. - Air masses form over land or water - Those that form over land have less exposure to moisture, so they are drier than those that form over water. Types of air masses: Figure 12-3, page 303 Warm and dry continental tropic (cT) Warm and humid maritime tropic (mT) Cold and dry continental polar (cP) Cold and humid maritime polar (mP) Artic (A) All 5 of these air masses can be found in North America because of the closeness to the source regions associated with each air mass. (see figure 123) Examples: Maritime tropical (mT) air masses form over tropical oceans such as the Carribean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico. It brings hot, humid weather to the eastern 2/3 of the U.S. Continental polar air (cP) forms over Canada and Alaska and makes for very cold winters when the nights are long.