Unit 1: From Prehistory to Early Civilizations
advertisement

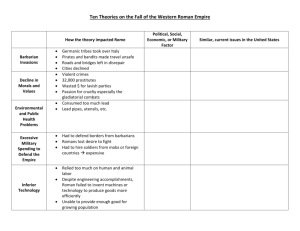
Unit 2: The Growth of Empires and Governments Chapter 6: Ancient Rome Section I: Early Rome and the Republic Pages 124-131 1. How did Rome’s location help the city to grow and prosper (trade and/or agriculture)? (Why is “where” important?) 2. Which two neighbors had an important influence on early Rome? 3. How did the Etruscans and Greeks influence the early Romans? 4. “Rome wasn’t built in a day.” Give me an example of what’s that supposed to suggest. 5. What’s an advantage in Rome having two consuls? (with each having terms of only one year) 6. How did the establishment of a republic (with elected representatives) help create stability in Rome? 7. Being an oratory (speaker) was a highly regarded position in ancient Rome. What are two qualities that would make a god orator? 8. Compare or contrast (you decide which one) Roman family life and your family life today. Read the top of page 131 (Read a Special-Purpose Map) and then answer the two questions from the map on the top of page 129 9. (Question 1) 10. (Question 2) Unit 2: The Growth of Empires and Governments Chapter 6: Ancient Rome Section II: From Republic to Empire Pages 132-137 1. This is a time of great change in the Roman Empire. How do you feel about big changes? (What is progress and is progress inevitable?) 2. Sometimes things change. What’s one positive thing that can happen with any big change? 3. What’s one negative thing that could happen with a big change? 4. What kind of a ruler did Julius Caesar appear to be? 5. Why is Julius Caesar significant in Rome’s history? 6. Why is Augustus significant in Rome’s history? 7. Why were the five “good” emperors popular with the citizens of the empire? 8. The Five “Good” Emperors are on page 135. Who was the best “Good” emperor and why? 10. There are only five good emperors – not 10 or 12… or more. Since things looked to be going well for Rome, what do you think might eventually bring about an end to the Roman Republic? There’s a much better picture of an aqueduct on the slides from class (at the end of page C) Unit 2: The Growth of Empires and Governments Chapter 6: Ancient Rome Section III: The Empire Declines Pages 138-143 1. What were 2 of the most popular forms of entertainment during Rome’s golden age? 2. What problems did the Romans face under Commodus? 3. Roman emperors declared their successors from their own family. Why would it be a good (or bad) idea if the U.S. if the President got to chose his successor? 4. What’s the most common reason for change in leadership during much of the 3rd century AD? 5. What was Diocletian’s major achievement during his reign as emperor? 6. How did Constantine try to stabilize the Roman Empire? 7. Why is the location of Constantinople so important? 8. What evidence is there that Rome was starting to fall apart? 9. What do you think was the most important cause for the decline and fall of the Roman Empire? (What forces cause change?) Put down at least 2 items for each column. This information can be found on pages 140 and 141 in your textbook. Unit 2: The Growth of Empires and Governments Chapter 6: Ancient Rome Section IV: The Development of Christianity Pages 144-147 1. Why do you think the Romans allowed people to have their own religions, even though they were part of the Roman Empire and were supposed to worship the Roman Gods? 2. What Christian belief was most difficult for Romans to accept? 3. What important role did Pontius Pilate play in the history of Christianity? 4. What were two of the beliefs and practices that all Christians shared? 5. Why do you think the Christian religion spread so quickly? 6. Why might the Romans have thought of the Christians as threatening? 7. Why do you think Christianity survived, despite persecution by the Roman authorities? 8. How was the Edict of Milan beneficial (helped to) Christians? 9. The early Christians didn’t always agree on things. What’s one way they may have come to agreements on their differences? (How do groups determine unity and separation?) If you wanted to look any of these up in your textbook, the information is on pages 126-147 Unit 2: The Growth of Empires and Governments Chapter 7: The Byzantine Empire, Russia, and Eastern Europe Section I: The Byzantine Empire Pages 150-157 1. What were 2 reasons for the founding of Constantinople? 2. What is Justinian best know for? (How is power gained, used, and justified?) 3. What is the Justinian Code? 4. Why did relations between the Byzantine Empire and western Europe worsen? 5. What happened between the Eastern Orthodox and Roman Catholic Churches in 1054? 6. What happened to Constantinople in 1453? 7. How did Byzantine art and architecture influence cultures in other parts of the world? 8. What are 2 positive elements of our culture people will be talking about in 1000 years? 9. What are 2 negative elements of our culture people will be talking about in 1000 years? Read the top of page 157 (Analyze Primary Source Documents) and then answer the four questions on the bottom of the page 11. (1). 12. (2). 13. (3). 14. (4) 1 2 3 4 Unit 2: The Growth of Empires and Governments Chapter 7: The Byzantine Empire, Russia, and Eastern Europe Section II: The Rise of Russia Pages 158-163 1. Russia is a huge place (even bigger than the U.S.). What might be one positive thing about living in such a big place? 2. What might be one negative thing about living in such a big country/territory? 3. How did Kiev become the first Russian capital? 4. How did trade affect the development of Russia? (What is the best way to make and distribute the things we need?) 5. How did Mongol rule affect Russian Merchants? 6. How did the princes of Moscow benefit from Mongol rule? 7. How did Mongol rule affect the peasants of Russia? 8. The fierce Mongol rulers were tolerant and sometimes even nice leaders. Why would they be both? (How is power gained, used, and justified?) 9. The Mongols were some of the fiercest warriors ever, Why do you think the these tough Mongols tolerated others religious difference (even in people they conquered)? 10. How did contact with the Byzantine Empire affect Russia? veto magistrate heresy Abdication Triad F T T F Pick any 2 of these to do for credit. If you want extra points, try more than 2. Making a Claim and Backing it up With Accurate Evidence Pick any of the rulers/leaders of ancient Rome by deciding which was the most important to Rome at that time. Some of your choices might be: Titus Diocletian Caesar Augustus Justinian Julius Caesar Trajan Hadrian Vespasian Marcus Aurelius Use the page with the "writing organizer" to organize your thoughts. You'll end up including: A main idea (thesis statement). An introduction this time. Three main ideas about why they were most important (Part A, Part B, and Part C). Logical (makes sense), accurate (true), and relevant (applies to the topic) evidence to support your claim (in the area for "the details"). Use any resource you want (book, technology database, our textbook, etc…). Paragraph 1 Introduction Attention Getter: Part A: Part B: Part C: Detail 1: Detail 2: Detail 3: Paragraph 3 (Part B) Main Idea: Detail 1: Detail 2: Detail 3: Paragraph 4 (Part C) Main Idea: Detail 1: Detail 2: Detail 3: Concluding Thoughts (including parts A/B/C): Paragraph 5 Conclusion Thesis Statement (Main idea) Paragraph 2 (Part A) Main Idea: “Big Finish”: