Melting Ice: Change of State Question: What happens in regards to
advertisement

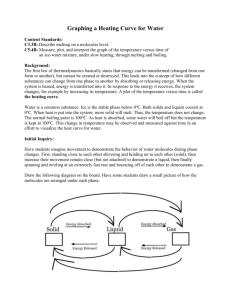
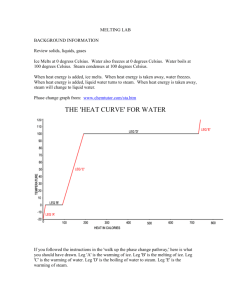
Name: Date: Block #: Ice Melt Lab Melting Ice: Change of State I. Question: What happens in regards to thermal energy and temperature when water changes state from solid to liquid to gas? II. Background Information Review solids, liquids, gases When heat energy is added, ice melts. When heat energy What is the difference in the is taken away, water freezes. When heat energy is added, particle arrangement? liquid water turns to steam. When heat energy is taken away, steam will change to liquid water. Ice Melts at 0 degrees Celsius. Water also freezes at 0 degrees Celsius. Water boils at 100 degrees Celsius. Steam condenses at 100 degrees Celsius. Kinetic Theory 1. All matter is made of atoms and molecules that act like tiny particles. 2. These tiny particles are always in motion. The higher the temp., the faster the particles move. 3. At the same temperature, more massive (heavier) particles move slower than less massive (lighter) particles. Pre-Lab: In the space provided, draw what you think the temperature vs. time graph will look like for the heating of ice. III. Hypothesis: IV. Materials (per group) 250 mL beaker ice to fill beaker thermometer hot plate Ring stand with clamp to hold thermometer Graph paper Timer V. Procedure 1. Fill the 250 mL beakers with ice. Place on the hotplate. 2. Put the thermometer in the middle of the ice in one beaker. Allow the temperature to settle for about 1-2 minutes. 3. Start the computer taking temperatures and turn on the hotplate to high. 4. For the thermometer, take reading every 30 seconds until you reach boiling. 5. Record the temperatures for the thermometer on the data table. 6. After you finish, turn off all hotplates. 7. Graph your data from the thermometer using the graph paper provided. VI. Data Create a data chart to keep track of your data. Use graph paper to graph your data when you are finished with the lab. VII. Conclusion Questions 1. Label the melting point, boiling point, and any phase changes on your graph. 2. At the boiling point, is there still heat transfer? Why or why not? 3. What happens to the temperature during a change of state? What happens to the thermal energy during a change of state? 4. Compare the graph that you drew before the lab with the graph you made from the data. Did your prediction match the data that you graphed from the lab? Explain. 5. What have you learned about thermal energy and temperature during a change of state? How does graphing your data help you understand this concept? Name: Date: Block #: Change of State Lab Worksheet Background Information: Explain the difference in particle arrangement of solids, liquids and gases? Pre Lab Hypothesis: Data Chart Time Temp Time Temp 30 6 1 6.5 1.5 7 2 7.5 2.5 8 3 8.5 3.5 9 4 9.5 4.5 10 5 10.5 5.5 11 *Indicate where boiling occurred and freezing occurred Conclusion Questions: