KINETICS & EQUILIBRIUM
advertisement

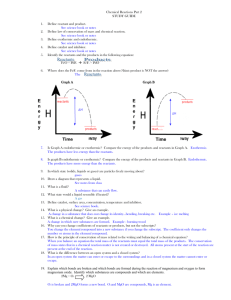
KINETICS & EQUILIBRIUM Textbook chapter 17 & 18 KINETICS = the branch of chemistry concerned with the _____________ of reactions COLLISION THEORY = in order for a reaction to occur, reactant particles must ______________. That collision must be effective with the correct ____________________ and ___________________________________ Why isn’t this a good way to chop down a tree?? It is similar to the requirements for a chemical reaction! Reactions involve the breaking of bonds and forming new bonds. SIX FACTORS THAT AFFECT REACTION RATE BY CHANGING THE MECHANISM Mechanism is the ______________ the reaction takes, or a series of steps that leads from product to reactant. The following factors change the number of effective collisions that occur between particles. 1) Nature of Reactants Depending on what the reactants are, it will take different amounts of energy to elicit an effective collision. In general, _____________ bonded substances are slower to react than _________ substances due to the greater number of bonds that must be broken for the reaction to occur. 2) Concentration Most chemical reactions will proceed at a faster rate if the concentration of one or more reactants is increased. This affects the _______________ of the colliding particles. The more particles there are in a given volume . . . the greater the chance for collision . . . the greater the chance for proper orientation . . . the greater the chance for effective collisions . . . and thus the higher the reaction rate. WHICH HAS A HIGHER RATE OF COLLISIONS? A parking lot with 100 cars or 10 cars? ____________________________ 3) Surface Area The more surface that is exposed, the more chances that the reactant particles can undergo effective collisions. Crushing a salt cube to dissolve it exposes fresh surface to react. Smaller particles of the same mass of a large cube of substance have a higher surface area. Affects only solid reactants, since liquids and gases have maximum surface area (no chunks to break up) Which would react faster, crushed garlic or a whole garlic clove? 4) Pressure An increase in pressure for gases is the same as an increase in _______________, since the gas molecules are being pushed closer together, resulting in more collisions and a faster rate. Little to no effect for liquids or solids!! Remember Boyle’s Law? 5) Catalyst Catalysts are substances that increase the rate of reaction by providing a different and easier pathway for a reaction. A catalyst takes place in the reaction, but is _________________ when the reaction is complete. 6) Temperature Increasing the temperature directly affects the ___________ of the colliding particles. The higher the temperature, the faster the particles are moving, and therefore they collide with more energy. So there will be more collisions AND the collisions will have more energy. WHICH HAS A HIGHER RATE OF COLLISIONS? Cars travelling at 30 mph or 100 mph? __________________________________ FACTOR Nature of reactants Concentration Surface Area Pressure Catalyst Temperature INCREASES RATE SAMPLE REGENTS QUESTIONS 1. Explain how a catalyst may increase the rate of a chemical reaction. 2. As the number of effective collisions between reacting particles increases, the rate of the reaction: a) increases b) decreases c) remains the same 3. Which of the following pairs of reactants will react most quickly? a) sodium chloride and silver nitrate b) water and hydrogen chloride 4. In the reaction 2Mg (s) + O2 (g) 2MgO (s), as the surface area of the Mg (s) increases, the rate of the reaction a) increases b) decreases c) remains the same 5. Which statement best explains the role of a catalyst in a chemical reaction? a) a catalyst is added as an additional reactant and is consumed but not regenerated b) a catalyst limits the amount of reactants used c) a catalyst changes the kinds of products produced d) a catalyst provides an alternate reaction pathway that requires less activation energy 6. Consider the following reaction: A (g) + B (g) C (g) As the concentration of A(g) increases, the frequency of the collisions between A(g) and B(g) a) increases b) decreases c) remains the same 7. Consider the following reaction: A (g) + B (g) C (g) The rate of the reaction can be decreased by increasing the a) pressure on the reactants b) temperature of the reactants c) concentration of A (g) d) volume in the reaction chamber POTENTIAL ENERGY DIAGRAMS = diagrams showing the changes in ____________________ contained in the chemical bonds as a reaction proceeds. X-axis = _____________________________, or progress of the reaction Y-axis = ____________________________ A potential energy diagram shows the potential energy changes that occur as reactants become products. It has five distinct regions: 1. The potential energy of the reactants 2. The potential energy gain that must take place in order for old bonds to be stretched to the breaking point This is called the ___________________________ (Ea). 3. The potential energy of the transition state, also known as the activated complex. As particles approach each other in a collision, kinetic energy is converted to potential energy. If the particles collide in the proper orientation, and activated complex is formed. Activated complex = a temporary transitional product that may either break apart and reform ____________ or rearrange the atoms and form ___________. 4. The potential energy released as new bonds form during a chemical change 5. The potential energy of the products. When this graph is read from left to right, it is also said to be the energy of the __________________ reaction. Note that this graph can also be read for the ___________________ reaction. Potential Energy Diagram for C2H4 + HCl C2H5Cl + heat 1) PE of the Reactants The flat region labeled "Reactants" shows the potential energy of the reactants. This is the difference between the X-axis and the flat reactants line 2) Activation Energy The rising part of the graph represents the increase in potential energy that occurs when reactants collide. This is the difference between the flat reactant line and the top of the bump 3) PE of activated complex This is the difference between the X-axis and the top of the bump 4) Heat of Reaction The falling part of the curve represents the energy released when the final products are formed. The potential energy difference between the reactants and the products is called the heat of reaction (ΔH). It represents the net energy change of the reaction. TABLE I lists the Heats of Reactions for many common reactions 5) PE of the Products The second flat region represents the potential energy of the products. This is the difference between the X-axis and the flat products line Endothermic Reactions If the potential energy of the products is greater than that of the reactants, then the reaction is classified as endothermic. Energy must be ___________ into the reaction. in an ENdothermic reaction energy ENters the system ΔH is _________________ (PE products – PE reactants) Energy + A + B --> AB Exothermic Reactions If the potential energy of the products is less than that of the reactants, then the reaction is classified as exothermic. The extra energy is __________________ to the surroundings. in an EXothermic reaction energy EXits the system ΔH is _______________________ A + B --> AB + Energy CATALYSTS When a catalyst is added, the energies of the reactants and products remain the same, therefore ΔH also remains the same. The only difference is the ____________________is lowered! SAMPLE REGENTS QUESTIONS Base your answers on the information and diagram below, which represent the changes in potential energy that occur during the given reaction. Given the reaction: A + B --> C 1) Does the diagram illustrate an exothermic or an endothermic reaction? State one reason, in terms of energy, to support your answer. 2) On the diagram provided in your answer booklet, draw a dashed line to indicate a potential energy curve for the reaction if a catalyst is added. 3) Given the reaction: 2 H2(g) + O2(g) --> 2 H2O(l) + 571.6 kJ What is the approximate ΔH for the formation of 1 mole of H2O(l)? (1) -285.8 kJ (2) +285.8 kJ (3) -571.6 kJ (4) +571.6 kJ 4) According to Table I, which potential energy diagram best represents the reaction that forms H2O(l) from its elements? 5) According to Table I, which salt releases energy as it dissolves? (1) KNO3 (2) LiBr (3) NH4NO3 (4) NaCl 6) Which statement correctly describes an endothermic chemical reaction? (1) The products have higher potential energy than the reactants, and the ΔH is negative. (2) The products have higher potential energy than the reactants, and the ΔH is positive. (3) The products have lower potential energy than the reactants, and the ΔH is negative. (4) The products have lower potential energy than the reactants, and the ΔH is positive. 7) A catalyst is added to a system at equilibrium. If the temperature remains constant, the activation energy of the forward reaction (1) decreases (2) increases (3) remains the same 8) The potential energy diagram below represents a reaction. Which arrow represents the activation energy of the forward reaction? What do the other lines represent? Equilibrium We read the potential energy diagrams from left to right….reactants activated complex products. Can the reverse happen? YES! Not only can the forward and reverse reaction both occur, they both occur at the same time. When both forward and reverse reactions occur at the same rate, the condition is called __________________________. An equation representing equilibrium uses a double arrow to show that reactions are proceeding in both directions. Equilibrium is a state of balance between the rates of two opposite processes. It can only occur in a _____________ system (neither reactant nor product can leave), such as a sealed container. ** Quantities of reactants and products are not necessarily equal at equilibrium – it is the rates of the forward and reverse reaction that is equal. 2 types of Equilibrium PHYSICAL EQUILIBRIUM Phase equilibrium can exist between two phases of a substance. For example, melting/freezing, or evaporation/condensation. H2O (l) H2O (g) The double pointed arrow shows that both reactions are taking place at the same rate. CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM When reactants are first mixed and no products are present, only the forward reaction can occur. As time progresses the concentrations of the reactants will decrease causing the forward reaction to slow. At the same time concentrations of the products will increase, causing the reverse reaction to increase. This will continue until the rate of the forward and reverse reaction are equal and chemical equilibrium is reached. Solution equilibrium exists between the dissolving and recrystallizing of a solute NaCl (s) NaCl (aq) This equilibrium can be disturbed by temperature or pressure (for gases only!) Le Chatelier’s Principle Any change in temperature, concentration or pressure on an equilibrium system is a stress. Le Chatelier’s Principle says that a system will respond to relieve any stress on the system. Systems will shift ______________ from the stress! Concentration Changes Addition of any substance will mean the reaction that reduces the amount of that substance will occur. If reactants are added = rate of _____________ reaction will increase and more products will form If products are added = rate of _________________ reaction will increase and more reactants will form Removal of any substance will mean the reaction that produces that substance will occur. If reactants are removed = rate of __________________ reaction will decrease If products are removed = rate of _________________ reaction will decrease 4NH3 + 5O2 4NO + 6H2O + heat Stress Effect System shift Effect Effect Effect + NH3 - NH3 Temperature Changes In the following reaction, heat can be considered to be a product 3 H2 + N 2 2 NH3 + heat If the temperature is raised, the rates of both reactions will increase, but not equally. Stress + H2 - N2 Effect System shift Effect Effect Pressure Changes Pressure changes do not have an effect on the rate of reaction when only solids or liquids are involved. Pressure changes only affect _____________. An increase in pressure increases the concentration of the gas. CO2 (g) CO2 (aq) When the pressure is increased, the concentration of the gas increases shifting the reaction to the _______________. When gas is present on only one side of the equation and the pressure is increased, the reaction will shift _______________ from the gas. In the case where gas molecules are present on both sides of the equation, an increase in pressure will have a greater affect on the side with __________ gas molecules (so reactions will shift toward the side with fewer gas molecules). When there are the same number of gas molecules on either side of the reaction, pressure changes have _______________ on the system. What about a catalyst? A catalyst will affect the rate of both the forward and reverse reactions equally. A catalyst may cause equilibrium to be established more quickly but does not change any of the equilibrium concentrations. 12.6 kcal + H2(g) + I2(g) Stress Add H2 Add I2 Add HI Remove H2 Remove I2 Remove HI Increase Temperature Decrease temperature Increase pressure Decrease pressure 2HI (g) Equilibrium Shift [H2] xxxxx [I2] [HI] xxxxx xxxxx xxxxx xxxxx xxxxx Entropy & Enthalpy There are two tendencies in nature that help determine whether or not these chemical and physical changes will occur. ENTHALPY = tendency in nature to change to a state of lower ____________ (or enthalpy). ______________ reactions move toward a lower energy state because some of the energy contained in the reactants is released. The products have less Potential Energy than the reactants do. Looking at PE diagrams we can see that the activation energy of exothermic reactions is less than the activation for the reverse endothermic reactions. This means at any given temperature, the particles are more likely to collide with enough energy to react in the exothermic direction. ENTROPY = a measure of ______________________________________ There is a tendency in nature to change to a state of greater randomness or disorder. The greater the disorder the higher the entropy. _____ is used to represent entropy + S = ______________ in entropy - S = ______________ in entropy Examples of entropy change are: Physical changes from solid to liquid to gas. ___________ has the highest entropy! More ______________ than _____________. Generally the side of the equation with the greater number of molecules has a greater amount of entropy. Higher ______________________ = higher entropy