Section 3: Volcanic Landforms
advertisement

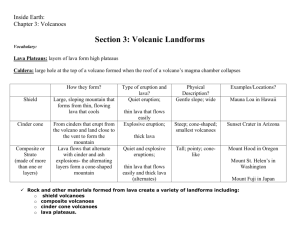
Inside Earth: Chapter 3: Volcanoes Section 3: Volcanic Landforms Vocabulary: Lava Plateaus: layers of lava form high plateaus Caldera: large hole at the top of a volcano formed when the roof of a volcano’s magma chamber collapses Volcanic neck: a deposit of hardened magma in a volcano’s pipe dike: slab of volcanic rock formed when magma forces itself across rock layers batholiths: a mass of rock formed when a large body of magma cooled inside the crust How they form? Sheild Cindercone Composite or Strato (made of more than one or layers) Large, sloping mountain that forms from thin, flowing lava that cools From cinders that erupt from the volcano and land close to the vent to form the mountain Lava flows that alternate with cinder and ash explosions- the alternating layers form a cone-shaped mountain Type of eruption and lava? Quiet eruption; thin lava that flows easily Explosive eruption; Physical Description? Gentle slope; wide Steep; cone-shaped; smallest volcanoes thick lava Quiet and explosive eruptions; thin lava that flows easily and thick lava (alternates) Tall; pointy; conelike S Rock and other materials formed from lava create a variety of landforms including: o shield volcanoes o composite volcanoes o cinder cone volcanoes o lava plateaus. Features formed by magma include: o Volcanic necks o Dikes o Sills o Batholiths o Dome mountains