Answer
advertisement

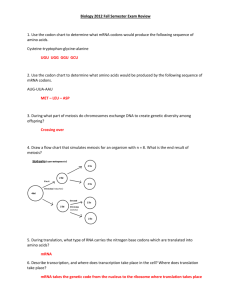
Answers to 2007 form of EOC Biology Review 3.01 1. Type of sugar Number of strands of nucleotides Location Bonding pattern Types DNA Deoxyribose 2 RNA Ribose 1 Nucleus only A to T : G to C Nucleus and cytoplasm A to U : G to C Messenger RNA, Transfer RNA, Ribosomal RNA 2. Adenine form hydrogen bonds with Thymine, Guanine forms hydrogen bonds with Cytosine 3. Protein 4. DNA replication 5. Each newly formed strand of DNA contain one of the original DNA template strands. 6. Mutations will result change in DNA code, which will in turn affect the correct formation of the proteins the code represents. 7. S (synthesis) of Interphase 8. Holds double strand of DNA together 9. RNA 10. ribosome 11. DNA 12. tRNA 13. peptide 14. polypeptide 15. protein 16. Start (Met), Ser, Ala, Stop 17. Differences occur due to differences on the expression of genes. 18. Cell respond to changes in the environment by producing different amount of proteins. 19. Cells will increase the amount of insulin produced. 20. Injury repair 21. cancer 22. diabetes(insulin) or stunted growth (growth hormone) 23. mitosis 24. meiosis 25. meiosis 26. meiosis 27. 2 28. 4 29. meiosis 30. meiosis 31. meiosis 32. genetic variation 33. homozygous dominant, heterozygous, homozygous recessive 34. Tt x Tt; (1) TT, Tall; ( 2 ) Tt, Tall; (1) tt, short 35. genotype and environment 36. Gregor Mendel 37. Dominant traits mask recessive alleles 38. gender and chromosomal abnormalities leading to disorders 39. 23rd pair 40. male 41. Down syndrome 42. Klinefelter syndrome 43. Turner Syndrome 44. incomplete dominance 45. co-dominance 46. Huntington’s disease 47. having more than two alleles for a trait 48. Both parents are IAi 49. polygenic traits 50. polygenic inheritance 51. Genes located on the sex (X ) chromosome 52. color blindness, hemophilia 53. Males only need one gene to express the trait 54. XcXc x XCY, none of the daughters, all of the sons 55. After meiosis, only one member of each homologous chromosome pair can be found in a gamete. No gamete will end up with two homologues. Alleles on different chromosomes will sort independently from one another. 56. The reassortment of chromosomes and the genetic information they carry either by crossing over or independent assortment results in genetic recombination and is a major source of variation in organisms. 57. homozygous recessive 58. pedigree chart 59. heterozygous 60. One 61. Heterozygous or homozygous dominant 62. recessive 63. homozygous dominant 64. both parents heterozygous 65. Phenotype: 3:1, Genotype: 1: 2: 1 66. homozygous recessive 67. International effort to sequence chromosomal DNA to identify the location of every gene. 68. Useful in determining if individuals carry genes for genetic conditions and in developing gene therapy. 69. technique used to separate molecules based on size. 70. DNA patterns unique to each individual that can be used to identify the person from which them came. 71. Identification of suspects in a crime in forensics. 72. medicine, pharmaceutical ( insulin ), research, 73. moral, ethical, economic, religious, cultural 74. Natural selection is the process by which favorable traits that are heritable become more common in successive generations of a population of reproducing organisms, and unfavorable traits that are heritable become less common. Natural selection acts on the phenotype, or the observable characteristics of an organism, such that individuals with favorable phenotypes are more likely to survive and reproduce than those with less favorable phenotypes. If these phenotypes have a genetic basis, then the genotype associated with the favorable phenotype will increase in frequency in the next generation. Over time, this process can result in adaptations that specialize organisms for particular ecological niches and may eventually result in the emergence of new species. 75. Biogenesis is the idea that life comes from living things and abiogenesis is the idea that living things may arise from nonliving things. 76. Fish from mud, rats from grain, maggots from meat 77. Francesco Redi and Loius Pasteur. 78. Pasteur set up an experiment in which air but no microorganisms, was allowed to contact a broth that contained nutrients. He showed that microorganisms do not arise in broth even in the presence of air. 79. He hypothesized that energy from the sun, lightening, Earth’s heat triggered chemical reactions to produce small organic molecules from the substances present in the atmosphere, then rain washed the molecules into oceans to form a primordial soup. 80. Miller and Urey’s experiment showed that under the proposed conditions in early earth, small organic molecules such as amino acids could form. 81. Since early earth lacked oxygen, the first organisms would have been anaerobic. 82. Endosymbiosis in which involved symbiotic relationships between ancient prokaryotes. 83. Eventually photosynthesizing prokaryotes capable of releasing oxygen from water evolved. As oxygen concentration increased, organisms that could respire aerobically would have increased and thrived. 84. Fossils provide evidence of organisms that lived long ago. 85. Relative dating: relies on the position of rock layers and results in relative dates. Absoulte dating (radiometric dating) relies on half-lives of radioactive elements and provides a more exact age. 86. The fossils found in the bottom rock layers are most likely the oldest, while those found in the upper rock layer are most likely the youngest. 87. Almost all organisms have shared DNA, ATP, and many enzymes among their biochemical molecules. Groups that share more similarity are thought to be more closely related and as sharing a closer ancestor. 88. Structural similarity is viewed as evidence that organisms evolved from a common ancestor. 89. Darwin proposed that organisms produce many offspring with variations, some of which enable offspring to reproduce and pass on their genes. Variations with a survival advantage are widespread among descendants. 90. A new species can evolve when a population has been physically isolated to a new geographic location. 91. Different adaptations are useful in different environments, and the gene pool will in time reflect the differences. 92. Some organisms will have a genetic resistance to antibiotics or pesticides that allow them to survive the initial exposure, and these organisms will pass the resistance on to their offspring, eventually resulting in newly evolved resistant populations. 93. Only bacteria that are totally resistant to the antibiotic survive. Goal 4. 4.01 1. Eubacteria, Archaebacteria, Protists, Fungi, Plants, Animals 2. K, P, C, O, F, G, S 3. species 4. Homo 5. 6. Analyze common ancestry; organisms with close ancestry indicate close relations. 7. Organisms with similar DNA and Biochemistry indicate close relationships. 8. Closely related organisms have similar embryological development patterns. 9. The presence of many shared structures implies that species are closely related. 10. Recent 11. Eukaryote: membrane bound organelles present, contain ribosomes, linear chromosomes, larger than prokaryote Prokaryote: no membrane bound organelles, contains ribosomes, circular chromosome, smaller than eukaryote. 12. Protists Fungi Plant Animal Cell Structure Cell Wall Cell Wall Cell wall No cell wall No. of Cells Unicellular Multicellular Multicellular multicellular Reproduction Mostly Asexual Mostly Asexual Mostly Sexual Mostly Sexual Nutrition Autotrophic Absorption Autotrophic Heterotrophic 13. See attachment A. 4.03 Assess, describe, and explain adaptation affecting survival and reproductive success. 14. Plants: cuticle, vascular system, Animals: internal fertilization, care of young, outer covering 15. Protein coat and nucleic acid core 16. HIV, influenza, smallpox 17. streptococcus (strep throat) 18. Antibiotics 19. Co-evolution: when two or more organisms evolve in response to each other. For example, hummingbirds have long narrow beaks, are attracted to the color 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. red, and a poor sense of smell. The fuchsia plant, has red flowers, little fragrance, and long, narrow leaves. The fuchsia rely on hummingbirds as its pollinator. Individuals heterozygous for sickle cell are less likely to carry malaria. Tobacco use increases the chance of lung/mouth cancer. The skin stores vitamin D. Folic acid is thought to reduce the risk of skin cancer and excess sun exposure is thought to increase the risk of skin cancer. Diabetes can be managed by one’s diet, and exercise, and though there is an underlying genetic cause. PKU can be managed by removing phenylalanine from the diet.