Biology 2012 Fall Semester Exam Review 1. Use the codon chart to
advertisement
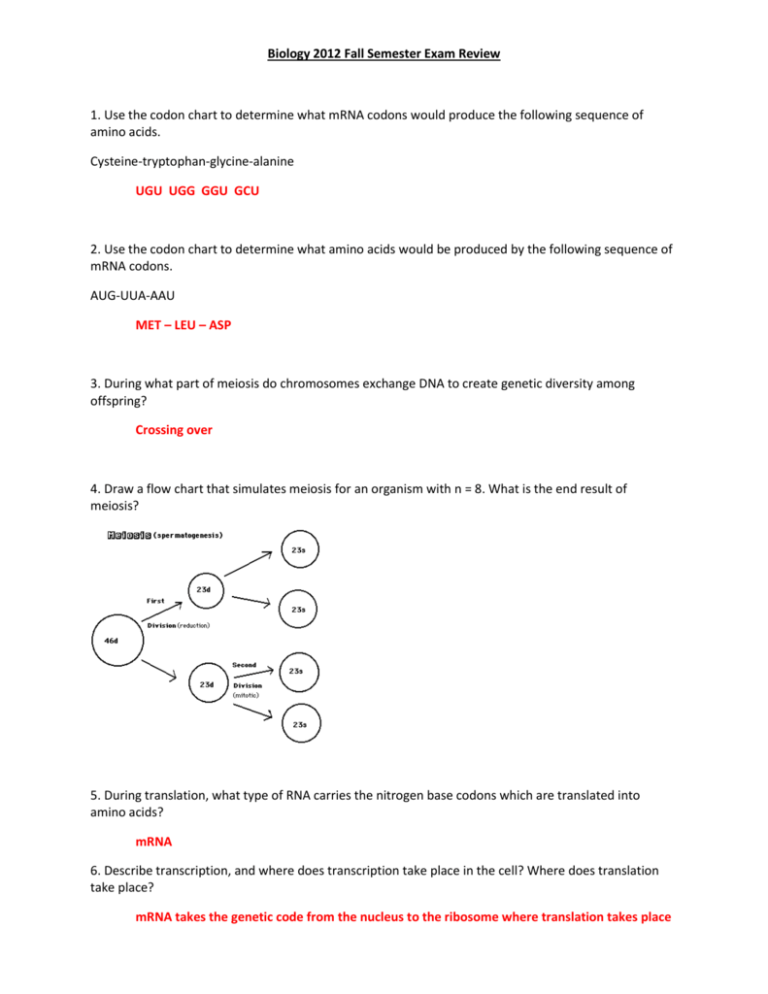
Biology 2012 Fall Semester Exam Review 1. Use the codon chart to determine what mRNA codons would produce the following sequence of amino acids. Cysteine-tryptophan-glycine-alanine UGU UGG GGU GCU 2. Use the codon chart to determine what amino acids would be produced by the following sequence of mRNA codons. AUG-UUA-AAU MET – LEU – ASP 3. During what part of meiosis do chromosomes exchange DNA to create genetic diversity among offspring? Crossing over 4. Draw a flow chart that simulates meiosis for an organism with n = 8. What is the end result of meiosis? 5. During translation, what type of RNA carries the nitrogen base codons which are translated into amino acids? mRNA 6. Describe transcription, and where does transcription take place in the cell? Where does translation take place? mRNA takes the genetic code from the nucleus to the ribosome where translation takes place 7. The variety of finch species on the Galapagos Islands in relation to their beak sizes helps to prove what aspect of the theory of evolution? Why is the development of different beaks for the various finches an example of an advantageous adaptation? 8. What chemical equation describes photosynthesis? 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 9. At what site or location does translation (protein synthesis) take place in the cell? ribosome 10. What is the probability that two people, one heterozygous for a trait, and one homozygous dominant for a trait, could produce offspring that are homozygous recessive for a trait? 0% 11. How can mutations, which are generally bad for organisms, be sometimes beneficial? When it allows the organism to adapt which increases their survival 12. What nitrogen base is found during the process of transcription that is NOT found during the process of replication? Uracil 13. What kinds of cells are produced during meiosis? gametes 14. What molecule is broken down to produce ATP during cellular respiration? glucose 15. What are the genotype and phenotype ratios that would be produced from a cross between parents that are homozygous recessive and heterozygous for a trait? 50% heterozygous 50% homozygous recessive 16. What are the four main principles of Darwin’s theory of natural selection? 17. Give an example of disruptive selection in nature and explain how it happened. 18. What are two things that can affect an enzyme’s ability to break down substances? pH and temperature 19. What occurs in the cell during replication? DNA doubles 20. How do the processes of both replication and transcription produce exact copies of the original DNA? Each base pairs with its complimentary RNA base 21. A woman that is color blind, a recessive sex-linked trait, has children with a man that is not color blind. What is the percentage of their female offspring that would be color blind? O% 22. What are the products of the light dependent reactions? ATP, NADPH, H+ and O2 23. How is RNA different from DNA? RNA is single stranded and used for protein synthesis 24. A mRNA strand has a codon that reads 5’-AUC-3’. What would the anticodon on a tRNA molecule be that matches that codon? 3’ – UAG – 5’ 25. Give an example in nature that supports Darwin’s theory of natural selection. 26. What are mutations caused by? Any change in the DNA sequence 27. What are the monomers, or subunits, of proteins? Amino acids 28. Diseases that affect cellular reproduction (asexual reproduction) affect what part of the cell cycle from occurring correctly? Mitosis (cell division) 29. What is the difference between normal body cells and gametes? Gametes have ½ the number of chromosomes = ½ the amount of DNA 30. How many chromosomes will a daughter cell produced during mitosis have in comparison to the cell it originated from? Same number of chromosomes (my “twin” sis) 31. What do organisms with homologous characteristics have in common with one another? 32. What is the difference between offspring produced sexually and asexually in terms of their genetic material? Parents & offspring have the same genetic material but DIFFERENT acquired traits 33. What are the expected genotype and phenotype ratios for a cross between 2 parents that are both heterozygous for a trait? 75% will have the dominant trait 25% will have the recessive trait 34. What are the expected genotype and phenotype ratios for a cross between a homozygous dominant parent and a homozygous recessive parent? 100% heterozygous 35. What explains how there can be many different species of a similar bird type in different environments across the United States? 36. Which part of the DNA molecule causes the expression of different traits among organisms of the same species? Nitrogen bases (rungs of the ladder) 37. In a population of Arctic Wolves thick fur (T) is dominant to thin fur (t). Black fur (B) is dominant to white fur (b). What genotypes would best survive during the winter months? TTbb or Ttbb 38. Explain why a man who is recessive for a sex-linked trait affects only his daughters, but not his sons. Sex-linked traits are on the X chromosome and the males only have one X chromosome 39. Explain how cell differentiation produces complex multicellular organisms from zygotes. Cells differentiate as they divide becoming specific tissues and organs 40. Where does transcription occur in the cell? Nucleus 41. Explain how inbreeding allows rare recessive conditions to remain in a population that would normally be bred out of larger populations that are not inbred. 42. Why is the fossil record more diverse in variety in younger rock strata than in older rock strata? 43. What occurs during anaphase of both mitosis and meiosis? Chromosomes are pulled apart 44. What is the purpose of photosynthesis for autotrophs? Allows plants to store energy in carbohydrate molecules 45. How many copies of chromosome pairs should gametes have from the original body cells they were formed from? ½ the number 46. What does DNA provide for organisms? The genetic material or code 47. What are the main differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus 48. What are people missing that causes them to be lactose intolerant? The enzyme to digest lactose 49. What are the reactants used to make glucose during the light dependent reactions? CO2 50. How many alleles can a parent contribute for a trait? One 51. What would explain a decrease in fossil species from older rock strata to younger rock strata? 52. What kind of organisms undergoes meiosis, and where in the organisms are the gametes formed? Reproductive organs in a multi-cellular organism 53. What are the only forms of life on earth that have prokaryotic cells? Bacteria 54. Explain how genetic drift can cause different species to arise in isolated locations from their ancestral homelands. 55. What is the expected phenotype ratio for a heterozygous dihybrid cross? 9:3:3:1











