16.3 Winds Notes
advertisement

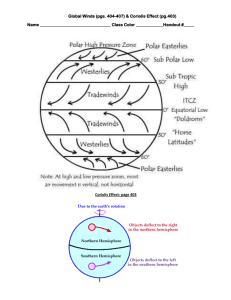
16.3 Winds Name_____________________ Objectives Explain what causes winds. Distinguish between local winds and global winds. Describe the major global wind belts and where they are located. What Causes Winds? Air is a ________ and can move easily from ______________________________. The force that makes air move is caused by a ______________________________. Fluids move from areas of __________________ (good weather) to areas of _________pressure (bad weather). Wind - _____________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________. All winds are caused by differences in _______________________. These differences in air pressure are caused by _____________ heating of the atmosphere. Measuring Wind Winds are described by their _____________ and ______________. Wind direction is determined with a wind ____________. The end that points is in the _________________ of the wind. Wind speed is measured with an _________________. An anemometer _______________________________________________________ ___________________________________. The wind turns the _________. A speedometer shows the _________________ that is attached to the axle. Wind-chill factor - __________________________________________. Local Winds Local winds - _______________________________________________________. Local winds are caused by ______________________________________________. Cool air blows inland from the _____________ and moves underneath the _______ air. During the day, cool air moves from the ________ to the land, creating a sea ________. At night, cooler air moves from the _____________ to the sea creating a _______ breeze. Monsoons Monsoons - ____________________________________________________________ ________________________. The summer monsoon in South Asia and Southeast ________is very important for the __________ grown there. The air is very _____________________. This produces heavy ____________ that supply water needed by ______________and other crops. Global Winds _________________________________________________________ are called global winds. Global winds are created by ________________________________ of earth’s surface. Near the ________________, energy from the sun strikes Earth almost ______________. Near the poles, the same amount of energy is _______________ over a larger area. Global Convection Currents Temperature difference produce giant _____________________ currents. Warm air at the equator rises and ________________ at the poles. Air pressure is ________________ at the equator and high at the _________________. At Earth’s surface, winds blow from the ___________________________. In the atmosphere, winds blow away from the ________________________________. This movement causes ________________ winds. The Coriolis Effect Coriolis effect - ____________________________________. It is named for the _________________ mathematician, Gaspard de Coriolis who studied and explained it in 1835, As Earth rotates, the Coriolis effect turns winds in the Northern Hemisphere toward the _____________. In the Southern Hemisphere, winds curve toward the ______________. Global Wind Belts The major wind belts are the doldrums, horse latitudes, _________________________ _____________________________________________________________. Doldrums Doldrums - _____________________________________________________. Very calm winds. Horse Latitudes Warm air that rises at the equator divides flow both north and south. Latitude is the ___________________________________________________. At about ______ degrees north and south latitudes, the air stops moving toward the poles and _______________. In each of these regions, another belt of calm air forms. Hundreds of years ago, sailors becalmed (To render motionless for lack of wind) in these waters ran out of food and water for their horses and had to throw the ______________ overboard. Trade Winds These steady easterly (come from the east) winds are called the ____________ _______________ at the 30 degree north and south latitudes toward the equator. Prevailing Westerlies In the mid-latitudes, winds that blow towards the poles are turned towards the east by the ___________________. Because they blow from the _______ to the east, they are called the ____________________________. Polar Easterlies Cold air near the poles sinks and lowers back toward lower latitudes. The Coriolis effect shifts these polar winds to the _____________, producing winds called the polar ________________. Jet Stream About 10 km above Earth’s surface are bands of high-speed winds called ___________ _____________________. They are hundreds of km wide but only a few km deep. They blow from east to west at speeds _______________ km per hour wandering north and ________________. Airplanes are aided by a jet stream when traveling _________________. Pilots can save ___________ and ______________ when flying east in a jet stream. However, airplanes flying at jet stream altitude are slowed down when _____________ west against the jet stream winds.