TN Academic Vocabulary
advertisement

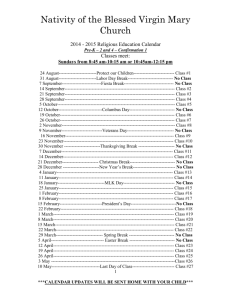
[November and December Vocabulary Calendar] Monday 7 14 6-variable 7-absolute 6-Constant value 6-coeffiecient 7-additive 8- monomial inverses 8- perfect square 21 6-Inequality and functions 7-box and whisker plot 7-coefficient 8-sequence 8- D=rt (distance=rate X time) 28 6-division, subtraction, addition properties of equality 7-cube root and functions 8- slope-intercept form 8- nonlinear equation 5 6-Relations and sequence 7-function notation 7-greatest common divisor 8- infinite 8-function 12 6-Integers 6-Negatives numbers 7-greatest common factor 7- histograms 8-quadratic equations 8 – vertical line test Tuesday 1 8 15 6- abiotic/biotic 6-atmospheric convection 7-acceleration and velocity 8-element 8-chemical equation 22 6-adaptive and assisted engineered technologies 7-acceleration and amplitude 8- acid and atom (electron, neutron, proton) 29 6-asteroid and bias 7-asexual reproduction and cell division 8- atomic mass and atomic number 6 6-biome and biosphere 7-cell organelles 8-base and biodiversity Wednesday 2 9 16 6-sidebars 6-simile 7 & 8 – allusion and antecedent Thursday 3 10 17 6-ancient and civilizations 7-Colonization 8-Philanthropy and Altruism Friday 4 11 18 Review weeks terms 2 Thanksgiving Break 24 Thanksgiving Break 25 Thanksgiving Break 30 6-metaphor 6-symbolism 7 & 8 – bias and debate 2 Review weeks terms 13 6-cause and effect and variable 7-chromosome and gene 8-chemical change 8-chemical equation 14 6-point of view 6-propaganda 7 & 8 – gerund and acronym 1 6-irrigation and Middle Ages 7-Demographics 8-Antebellum 8-Absolute 8 6- Monarchy and Feudalism 7-Urbanization 8-Exchange 8-Commerce 15 6-Nomadic and Technological 7-Impact 8-Congressional 8-Civic efficacy 7 6-text features 6-rhythm 7 & 8 – cross reference and derivation 9 Review weeks terms 16 Review weeks terms [November and December Vocabulary Calendar] Eighth Grade Science Academic Vocabulary Words Element- a pure substance that contains atoms of only 1 specified kind Chemical Equation – shorthand way of abbreviating elements that combine to form a chemical reaction Eighth Grade Language Arts Academic Vocabulary Words Allusion - a passing or casual reference; an incidental mention of something, either directly or by implication: an allusion to Shakespeare. Antecedent - a word, phrase, or clause, usually a substantive, that is replaced by a pronoun or other substitute later, or occasionally earlier, in the same or in another, usually subsequent, sentence. In Jane lost a glove and she can't find it, Jane is the antecedent of she and glove is the antecedent of it. Bias - an inclination to present or hold a partial perspective ; bias means that a person prefers an idea and possibly does not give equal chance to a different idea. Bias can be influenced by a number of factors, such as popularity (for example, a newspaper might be biased towards a particular political party due to their employees sharing the same political beliefs as that party). Clincher sentence – a concluding sentence that pulls together the preceding sentences by emphasizing the main idea. A clincher sentence is an effective way to ensure that the reader gets the overall point of the paragraph. Coherent order – all of the sentences logically fit together. Composition – a short piece of writing done as an educational exercise. Cross-reference - a reference from one part of a book, index, or the like, to related material, as a word or illustration, in another part. Debate – to engage in argument or discussion. Derivation - the source from which something is derived; origin. Dramatization - a dramatized version of a novel, historic incident, etc. Elaboration - an unconscious process of expanding and embellishing a detail, especially while recalling and describing a representation in a dream so that latent content of the dream is brought into a logical and comprehensible order. [November and December Vocabulary Calendar] Facilitator - a person responsible for leading or coordinating the work of a group, as one who leads a group discussion. Gerund – A verb form ending in –ing that is used. Inferring – reading between the lines; involves reading the text and recalling prior experiences that are similar to what you are reading. Then, you use context clues from the text to draw a logical conclusion about what might happen next. Jargon – special words and phrases used by a particular trade, profession, or other group of people Inductive reasoning – a way of thinking or explaining that begins with a series of examples and uses them to arrive at a general statement. Deductive reasoning – a way of thinking or explaining that begins with a general statement of principle and applies that principle to specific instances. Inflection – a change in pitch of a person’s voice. Enunciation – the act of speaking clearly and concisely. Rate – the number of words per minute. Pitch – modulation of the voice; change in pitch or tone of voice; highness or lowness of the voice. Participles –A verb form that can function as an adjective. Present participles end in –ing and past participles end in –ed. Persuasive writing – a type of writing that aims at convincing people to think or act in a certain way. Preface – a preliminary statement in a book by the book's author or editor, setting forth its purpose and scope, expressing acknowledgment of assistance from others, etc. Reliability – the ability to be depended on, as for accuracy, honesty, or achievement. Sensory detail – words or phrases that describe how things look, sound, smell, taste, or feel Shades of meaning – Shades of meaning is a phrase used to describe the small, subtle differences in meaning between similar words or phrases; 'kid' and 'youth' both refer to young people, but carry differing views and ideas about young people [November and December Vocabulary Calendar] Tension – a balance and interplay of opposing elements or tendencies (especially in art or literature). Thesis statement – a statement of the main idea or purpose of a piece of writing. Mood/tone - the emotion created in the reader by part or all of a literary work. Acronyms – a word formed from the initial letters or groups of letters of words in a set phrase or series of words, as Wac from Women's Army Corps, OPEC from Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries, or loran from long-range navigation. Sidebars – information which is relevant to an article, but which doesn't appear in the main text. Footnotes – Notes at the foot of the page or foot of the page. Footnotes are used instead of putting citations in parentheses within the text. A number or symbol is placed in the text where the parenthetical citation would otherwise be and a matching number or symbol at the bottom of the page identifies the citation. Endnotes - a note placed at the end of an article, chapter, or book that comments on or cites a reference for a designated part of the text. Many books use endnotes instead of footnotes. Endnotes are like footnotes in that a number or symbol is placed within the text, but the matching citations are compiled at the end of the book, chapter, or article rather than at the foot of the page. [November and December Vocabulary Calendar]