Lupus - Job Accommodation Network

Effective Accommodation Practices
(EAP) Series
Job Accommodations for
People with Lupus
JAN’S EAP SERIES
J OB A CCOMMODATIONS FOR P EOPLE
WITH L UPUS
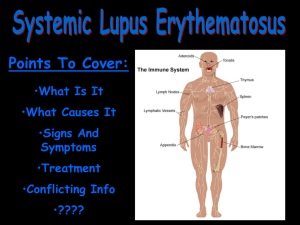
Lupus is a chronic, autoimmune disease that causes inflammation of various parts of the body. The body's immune system normally makes proteins called antibodies to protect the body against viruses, bacteria, and other foreign materials called antigens.
In an autoimmune disorder such as lupus, the immune system loses its ability to tell the difference between antigens and its own cells and tissues. The immune system then makes antibodies directed against "self." These antibodies, called "auto-antibodies," react with the "self" antigens to form immune complexes; individuals with lupus produce too many antibodies. The immune complexes build up in the tissues and cause inflammation, injury to tissues, and pain by attacking functioning organs, especially the skin, joints, blood, and kidneys. Although lupus can affect any part of the body, the most common symptoms are butterfly-shaped skin rashes; arthritis; nephritis (kidney problems); inflammation of the lungs, heart, or abdominal cavity; and gastrointestinal disorders. Other symptoms include fatigue, fever, impaired vision, weight fluctuation, headaches, frequent infections, anemia, alopecia (hair loss), seizures, and photosensitivity.
The following is a quick overview of some of the job accommodations that might be useful for people with lupus. For a more in depth discussion, access JAN's publications at http://AskJAN.org/media/atoz.htm. To discuss an accommodation situation with a consultant, contact JAN directly.
Photosensitivity:
Minimize outdoor activities between the peak hours of 10:00 am and 4:00 pm
Avoid reflective surfaces such as sand, snow, and concrete
Provide clothing to block UV rays
Provide “waterproof” sun-protective agents such as sun blocks or sunscreens
Install low wattage overhead lights
Provide task lighting
Replace fluorescent lighting with full spectrum or natural lighting
Eliminate blinking and flickering lights
Install adjustable window blinds and light filters
Fatigue/Weakness:
Reduce or eliminate physical exertion and workplace stress
Schedule periodic rest breaks away from the workstation
Allow a flexible work schedule, flexible use of leave time, and/or work from home
Implement ergonomic workstation design
Provide a scooter or other mobility aid if walking cannot be reduced
2
Fine Motor Impairment:
Implement ergonomic workstation design
Provide alternative computer access
Provide alternative telephone access
Provide arm supports
Provide writing and grip aids
Provide a page turner and a book holder
Provide a note taker
Migraine Headaches:
Provide task lighting
Eliminate fluorescent lighting
Use computer monitor glare guards
Reduce noise
Provide alternate work space to reduce visual and auditory distractions
Implement a "fragrance-free" workplace policy
Provide air purification devices
Allow flexible work hours
Allow periodic rest breaks
Allow work from home
Respiratory Difficulties:
Provide adjustable ventilation
Keep work environment free from dust, smoke, odor, and fumes
Implement a "fragrancefree" workplace policy and a “smoke-free” building policy
Avoid temperature extremes
Use fan/air-conditioner or heater at the workstation
Redirect air-conditioning and heating vents
Provide adequate exhaust systems to remove fumes from office machines
Allow individual to wear a respirator mask
Allow work from home
Cognitive Impairment:
Provide written job instructions when possible
Prioritize job assignments
Allow flexible work hours
Allow periodic rest periods to reorient
Provide memory aids, such as schedulers or organizers
Minimize distractions
Allow a self-paced workload
Reduce job stress
Provide more structure
3
Seizure Activity:
Eliminate the need to use sharp objects
Eliminate blinking and flickering lights
Replace fluorescent lighting with full spectrum or natural lighting
Use computer monitor glare guards, adjust monitor intensity and color, and decrease the cursor speed of the mouse
Provide protective clothing/equipment
Modify job tasks requiring fine finger dexterity
Allow flexible work hours
Allow periodic rest breaks
Allow work from home
Stress:
Develop strategies to deal with work problems before they arise
Provide sensitivity training to coworkers
Allow telephone calls during work hours to doctors and others for support
Provide information on counseling and employee assistance programs
Vision Impairment:
Magnify written material using hand/stand optical magnifiers
Provide large print material, screen reading software, and large-size high resolution monitor
Control glare by adding a glare screen to the computer
Install proper office lighting
Allow frequent rest breaks
Resources Specifically for People with Lupus
Lupus Foundation of America
2000 L Street, N.W., Suite 4 10
Washington, DC 20036
Toll Free: (800)558-0121
Direct: (202)349-1155
Fax: (202)349-1156 http://www.lupus.org
Updated 06/04/13.
4
This document was developed by the Job Accommodation Network (JAN). Preparation of this item was funded by the Office of Disability Employment Policy, U.S. Department of Labor, Grant Number OD-23442-12-75-4-54. This document does not necessarily reflect the views or policies of the Office of Disability Employment Policy, U.S.
Department of Labor, nor does the mention of trade names, commercial products, or organizations imply endorsement by the U.S. Government.
5