Geol 101: Physical Geology
advertisement

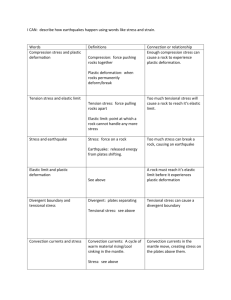
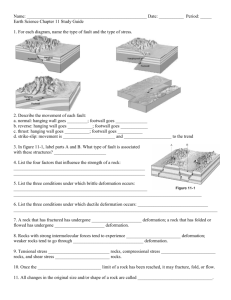
Geol 101: Physical Geology PAST EXAM QUESTIONS LECTURE 19: CRUSTAL DEFORMATION I 19. Stress is the same as: A. force B. pressure C. strain D. force divided by area E. pressure divided by volume 19. The speed that deformation occurs inside rocks is: A. without exception, extremely slow B. about 3 cm per year C. called the strain rate D. fast enough to observe on a day-to-day basis E. very rapid for the case of ductile deformation 19. An example of high strain rate deformation is: A. folding B. elastic deformation C. plastic flow D. bending E. earthquakes 19. If a rock deforms under the influence of a stress, but then returns to its original shape when the stress is removed, then the deformation behavior is described as: A. brittle B. plastic C. elastic D. ductile E. magical 19. Elastic deformation in a rock indicates that: A. the strength of the rock has been overcome B. the rock has undergone fracturing C. the rock is behaving in a plastic manner, like salt water taffy D. the rock can release stored energy and return to its original shape E. the rock will eventually cause an earthquake 19. Which part of the Earth is most prone to brittle deformation? A. crust B. mantle C. outer core D. inner core E. all of the above 19. If a rock deforms by flowing or bending, the deformation is said to be: A. elastic B. plastic C. ductile D. either A or B above E. either B or C above 19. For rocks that are being deformed inside the crust, as the temperature increases: A. the rocks get more brittle B. the rocks get less brittle C. the rocks get less ductile D. the strain rate increases E. the pressure must start to decrease 19. The tensional stress that formed a joint: A. was oriented parallel to the orientation of the joint B. was oriented perpendicular to the orientation of the joint C. was oriented obliquely to the orientation of the joint D. cannot be determined from the joint orientation E. was produced by the cooling of basalt lava