Slide 1
advertisement

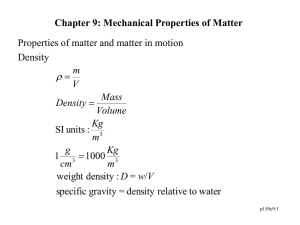
Part 2 STRESS and STRAIN ASPECTS OF ROCK • Unlike soils, pure rock (solid material between joints) is an elasto-plastic material, subject to elastic recovery AND permanent deformation, as shown in this Stress vs strain plot. • Physical phenomena associated with uniaxial compression tests of rock cylinders, under near zero confinement. • Unconfined compression tests on rock cylinders generally exhibit significant propagation of extension cracks after peak strength is exceeded, followed by friction and interlocking between cracked sections of the sample. • Example of a full-range stress-strain plot, showing how post-failure stiffness is estimated • Physical phenomena associated with gradual breakdown of rock cylinders on the post-failure side of a stress-strain plot • The stress strain behavior of a natural rock like sandstone is a combination of its mineralogical components, in this case: quartz and calcite • Most rocks exhibit increasingly plastic behavior with increasing levels of confinement, as shown in this series of jacketed triaxial tests on a marble. So, the most brittle behavior is typically exhibited under conditions of the least confinement, at the Earth’s surface. Elastic deformation Plastic deformation • Elasto-plastic behavior of Solenhofen Limestone, as seen in measured relaxation in percent axial strain after triaxial compression under significant lateral confinement • The most common physical attributes of laboratory tests on intact rock are portrayed here. The true elastic modulus can only be determined by employing load cycles. • Goodman’s concept of Modulus of Permanent Deformation, M, was introduced in 1980. It is important to appreciate in porous rocks which often exhibit “permanent set” with each loading cycle, such as sandstone. Mohr Circles are the most common technique used to describe the failure envelope and the strength parameters friction and cohesion Rock tends to exhibit a slightly curvalinear failure envelope with low tensile strength, shown at upper right • Be careful when evaluating elastic modulus values. The terms used connote different kinds of calculations, as shown here. • The elastic modulus (E) varies with the stress level and the induced strain