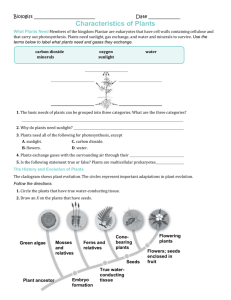
Test 2 Review
advertisement

BIO 211 Practice Exam 2 77. Land plants differ from green algae (Chlorophyta) in that plants ____. a) have cell walls containing cellulose. b) are unicellular. c) have chloroplasts. d) are heterotrophs. *e) have alternation of generations. 80. What is the closest relative to land plants? a) Rhodophyta, because both have cellulose cell walls. b) Euglenozoa, because both have green chloroplasts. *c) Charophyceans, because both have rose-shaped complexes that synthesize cellulose. d) Oomyctes, because both have cellulose cell walls. e) Archaea, because both are autotrophic. 82. Why do we think that Charophyceans are the closest relative to land plants? a) Linnaeus said so. *b) They have similar structure of flagellated sperm. c) Both have linear complexes that synthesize cellulose. d) Both A and B e) Both B and C 84. In life cycles with an alternation of generations, multicellular haploid forms alternate with ____. a) unicellular haploid forms. b) unicellular diploid forms. c) multicellular haploid forms. *d) multicellular diploid forms. e) multicellular polyploid forms. 85. Which of the following is not true about alternation of generations? *a) occurs in all sexually reproducing organisms b) is the alternation of two multicellular body forms (gametophyte, sporophyte) c) produces both zygote and spores d) includes both mitosis and meiosis e) alternates between haploid and diploid forms 86. In alternation of generations, the ______ gametophyte produces _____ by ______, which are fertilized and develop into the sporophyte of the next generation. a) diploid, spores, meiosis b) diploid, gametes, meiosis c) haploid, spores, mitosis *d) haploid, gametes, mitosis e) diploid, zygotes, fertilization 87. In alternation of generations, the _______ sporophyte produces ______ by _____ which germinate and develop into a gametophyte of the next generation. *a) diploid, spores, meiosis b) diploid, gametes, meiosis c) haploid, spores, mitosis d) haploid, gametes, meiosis e) diploid, zygotes, fertilization 89. The transition from an aquatic to terrestrial environment had a lot of challenges for the first land plants. Which of the following was not a problem for the first land plants? a) sources of water b) sperm transfer c) desiccation (drying out) *d) competition with other species 90. Bryophytes have all of the following characteristics except a) multicellularity. b) specialized cells and tissues. *c) lignified vascular tissue. d) walled spores in sporangia. e) a reduced, dependent sporophyte. 92. The following are all true about the life cycle of mosses except a) external water is required for fertilization. b) flagellated sperm are produced. c) antheridia and archegonia are produced by gametophytes. *d) gametes are directly produced by meiosis. e) gametophytes germinate from spores. 94. In Bryophytes, the _____ zygote develops into a _____ sporophyte that is _____ on the parent gametophyte. a) diploid, haploid, dependent *b) diploid, diploid, dependent c) diploid, haploid, independent d) diploid, diploid, independent e) haploid, diploid, dependent 95. In Bryophytes, the _____ spore develops into a ______ that is _____ on the parent sporophyte. a) diploid, gametophyte, dependent *b) haploid, gametophyte, independent c) haploid, gametophyte, independent d) diploid, zygote, independent e) haploid, zygote, dependent 96. In Bryophytes, ________ cells within a sporangium undergo ________ to produce ________ spores. *a) diploid; meiosis; haploid b) haploid; mitosis; haploid c) diploid; mitosis; diploid d) diploid; mitosis; haploid e) haploid; meiosis; haploid 97. The _______________ is the dominant phase in the bryophyte life cycle. *a) gametophyte b) sporophyte c) sporangium d) zygote e) archegonium 98. Which of the following is not common to all phyla of vascular plants? *a) the development of seeds b) alternation of generations c) dominance of the diploid generation d) xylem and phloem e) the addition of lignin to cell walls 100. A major change that occurred in the evolution of plants was the origin of a branched sporophyte in vascular plants. What of the following is not true about the branched sporophyte? a) A branched sporophyte could be more complex and have more unique parts. b) Branched sporophytes have an increased survival rate. c) Branched sporophytes have an increased reproductive rate. *d) Branched sporophytes can produce more sperm and eggs. e) Branched sporophytes can conduct photosynthesis. 101. Which of the following statements is not true about the sporophyte of vascular plants? a) The sporophyte stage is dominant in vascular plants. b) The sporophyte is diploid (2N) in vascular plants. *c) The sporophyte is dependent on the gametophyte. d) The sporophyte has vascular tissue. e) The sporophyte has roots and leaves. 102. Ferns and fern allies are economically important to humans because: a) They have antibacterial properties. b) They are used to make paper. *c) They are the basis to fossil fuels, like coal. d) They feed 80% of the human population. e) They are used for lumber and other wood products. 104. In ferns, sori on the underside of leaves are clusters of _____. a) female gametophytes b) male gametophytes c) vascular tissue *d) sporangia e) bisexual sporophytes 105. Why do ferns need to live in a moist environment? *a) Flagellated sperm need to swim to the archegonium. b) Ferns do not have vascular tissue. c) Ferns do not have roots. d) Spores need water to disperse. e) All statements are true. 106. Why is vascular tissue important for plant growth? a) Vascular tissue provides support to the plant so it can grow tall. b) Vascular tissue moves water through the plant. c) Vascular tissue moves sugars made during photosynthesis through the plant. d) Vascular tissue moves nutrients from the soil into the plant. *e) All statements are true. 107. Which of the following is a land plant that produces flagellated sperm and has a sporophyte-dominant life cycle? *a) fern b) moss c) liverwort d) charophycean e) hornwort 108. A heterosporous plant is one that ________. a) produces a gametophyte that bears both antheridia and archegonia. *b) produces microspores and megaspores, which give rise to male and female gametophytes. c) produces spores all year long instead of during just one season. d) produces two kinds of spores, one asexually by mitosis and the other sexually by meiosis. e) reproduces only sexually. 110. Which of the following is a difference between the fern and bryophyte life cycles? a) Only bryophytes need water to transport sperm to the egg. b) Only bryophytes have gametophyte and sporophyte phases. c) Only ferns have spores. *d) Only ferns have bisexual gametophytes. e) Only ferns use meiosis to produce haploid spores. 111. Which of the following is not true about the fern life cycle? a) Ferns need water to transport sperm to the egg. *b) Ferns have gametophytes that are dependent on the sporophyte. c) Ferns have spores. d) Ferns have bisexual gametophytes. e) Ferns use meiosis to produce haploid spores. 112. In seed-producing plants, the gametophyte is greatly reduced in size. What is the advantage of a miniaturized gametophyte? a) A small gametophyte does not need nutrients from the sporophyte. *b) The sporangium protects the gametophyte from environmental stresses. c) The gametophyte is an endosymbiont to the sporophyte; it feeds the sporophyte. d) The gametophyte can produce both sperm and eggs inside the sporophyte and does not need another individual to fertilize the egg. e) Both C and D are correct. 114. What advantages do seeds have over spores? a) Seeds are multicellular. b) Seeds carry their own food supply c) Seeds have more ways to disperse. *d) All of the above statements are true about seeds. 115. Which of the following is not part of a “seed”? a) a zygote that will grow into the a sporophyte b) a food supply for the growing zygote c) a seed coat formed by the integument tissues of the grandparent sporophyte *d) the ovule formed by the grandparent sporophyte e) Both C and D are not part of a seed 117. One trend that occurred during the history of Kingdom Plantae was: a) production of fruits and then seeds b) reduction of dependence on pollinators *c) reduction in size of the gametophyte phase d) reduction in size of the sporophyte phase e) elimination of meiosis 118. In Coniferophyta, pollen is typically dispersed by __________. a) insects *b) wind c) water d) amoeba-like movements e) bats 119. Seeds are formed from three different generations. In gymnosperms, the seed coat is formed by the _____. a) male gametophyte (N) b) female gametophyte (N) *c) adult (mature) sporophyte (2N) d) embryo (2N) e) Both A and B 121. Where would you find the male gametophyte of a pine? a) in a sporangium b) in an ovulate (seed) cone c) in an anther d) in an ovary *e) in a pollen grain 122. In gymnosperms, food for the embryo comes from the _________. *a) female gametophyte b) endosperm c) female sporophyte d) pollen tube e) sperm nucleus 123. Which of the following is true about the food that feeds a gymnosperm embryo? a) It is the result of double fertilization b) It is triploid c) It is called endosperm *d) It comes from the tissue of the female gametophyte e) Both C and D are true 124. In gymnosperms, the _____ of pollen cones produce _____ microspore mother cells, which will undergo _____ to produce haploid microspores. a) megasporangia, haploid, mitosis b) megasporangia, diploid, meiosis c) megasporangia, haploid, meiosis d) microsporangia, haploid, mitosis *e) microsporangia, diploid, meiosis 125. In gymnosperms, the _____ of ovulate cones produce _____ megaspore mother cells, which will undergo _____ to produce haploid megaspores. a) megasporangia, haploid, mitosis *b) megasporangia, diploid, meiosis c) megasporangia, haploid, meiosis d) microsporangia, haploid, mitosis e) microsporangia, diploid, meiosis 126. Pollination is when ____________. a) sperm and egg cells fuse inside the archegonium b) pollen is produced by the sporangium c) fertilization occurs *d) pollen lands on a structure that contains ovules e) the male gametophyte makes spores 127. Fertilization is when ____________. *a) sperm and egg cells fuse inside the archegonium b) pollen is produced by the sporangium c) fertilization occurs d) pollen lands on a structure that contains ovules e) the male gametophyte makes spores 131. The _____ is a group of plants with the most species. a) bryophytes b) gymnosperms c) ferns *d) angiosperms e) Chlorophyta 132. The _____ is the oldest group of plants. *a) bryophytes b) gymnosperms c) ferns d) angiosperms e) Chlorophyta 133. Angiosperms are the most successful terrestrial plants. This success is due to all of the following except ___. a) animal pollination b) reduced gametophyte size c) fruits containing seeds d) xylum with vessels *e) sperm cells with flagella 134. Which of the following is not a characteristics of angiosperms? a) coevolution with animal pollinators b) double fertilization *c) free-living gametophytes d) flowers e) fruit 135. Globally, 80% of all the calories consumed by humans come from ___ species of angiosperm crop plants. a) 3 *b) 6 c) 10 d) 20 e) humans don’t eat angiosperms 137. A seed is a mature _____; a fruit is a mature _______. a) ovary, ovule *b) ovule, ovary c) egg, zygote d) embryo; flower e) sporophyte; gametophyte 140. Only angiosperms have ____, while both angiosperms and gymnosperms have ____. *a) ovaries, ovules b) ovules, ovaries c) eggs, zygotes d) embryos; flowers e) sporophytes; gametophytes 142. In angiosperms, food for the embryo comes from the _________. a) female gametophyte *b) endosperm c) female sporophyte d) pollen tube e) sperm nucleus 144. How have fruits contributed to the success of angiosperms? a) by nourishing the plants that produce them *b) by facilitating dispersal of seeds by wind and animals c) by attracting insects to the pollen inside of the fruit d) by producing sperm and eggs inside a protective coat e) by producing triploid cells by double fertilization 146. Seed dispersal is important for the reproductive success of the plant. What structure/tissue do angiosperms use to disperse seeds? a) flowers b) endosperm c) pollen grains *d) fruit e) double fertilization 147. The term "double fertilization" means that: a) Both sperm fuse with a single egg b) Two embryos are produced by each female gametophyte c) 4N endosperm is produced *d) One sperm cell fuses with the egg; a second sperm cell fuses with two polar nuclei e) Both A and C are correct 148. In angiosperms, the pollen grain contains ___ a) One sperm cell that fertilizes the egg inside the ovule b) One sperm cell that fuses with two polar bodies c) One sperm cell that creates a pollen tube from the sticky stigma to the ovule d) Both A and C are correct *e) A, B, and C are correct 149. During the process of double fertilization, which of the following statements occur? a) One sperm cell fertilizes the egg inside the ovule b) One sperm cell fuses with two polar bodies c) One sperm cell creates a pollen tube from the sticky stigma to the ovule *d) Both A and B are correct e) A, B, and C are correct 151. Endosperm is one product of double fertilization. Why is the endosperm triploid (3N)? a) Both sperm cells fuse with a single egg b) Two embryos are produced by each female gametophyte c) One sperm cell fuses with the egg *d) One sperm cell fuses with two polar nuclei e) Both A and D are correct 152. What is a characteristic of all fungi? a) symbiotic *b) heterotrophic c) flagellated d) pathogenic e) saprobic 153. What is true of all fungi? a) They are all eukaryotic, heterotrophic plants b) They are all eukaryotic, parasitic plants c) They are all saprobic plants *d) They are all eukaryotic heterotrophs with cell walls e) They are all saprobic heterotrophs 154. Fungi are all of the following except ____. a) predators b) decomposers c) symbionts d) absorptive heterotrophs *e) autotrophs 156. In fungi, karyogamy does not immediately follow plasmogamy, which ____. a) means that sexual reproduction can occur in specialized structures. b) results in more genetic variation during sexual reproduction. c) allows fungi to reproduce asexually most of the time. *d) results in dikaryon cells. e) is strong support for the claim that fungi are not truly eukaryotic. 157. What is a fungal process involves the union of nuclei? a) mitosis b) plasmogamy c) crossing over d) binary fission *e) karyogamy 158. In sexual reproduction, fungi produce spores by a process known as ____. a) decomposition b) mitosis *c) meiosis d) hyphae e) binary fission 159. Karyogamy produces a _____. *a) diploid zygote b) haploid zygote c) spore d) mycelium e) hypha 160. Which of these contain two haploid nuclei? *a) the dikaryon stage of the fungal life cycle b) zygote c) spore-producing structures d) mycelium e) hypha 161. In most fungi, the _______ is the only 2N cell of the life cycle. *a) zygote b) plasmogamy c) asexual spore d) sexual spore e) hyphae 162. When two mycelia (positive and negative) join together to reproduce sexually, their cytoplasm mixes together, but the nuclei do not fuse. This is called _____________. a) polygamy b) karyogamy *c) plasmogamy d) oogamy e) monopoly 163. The vegetative (nutritionally active) bodies of most fungus are ___. a) composed of hyphae b) referred to as a mycelium c) usually underground d) Both A and B *e) A, B, and C 164. The primary role of the mushroom’s underground mycelium is _____. *a) absorbing nutrients b) anchoring the organism in the soil c) sexual reproduction d) asexual reproduction e) protection 165. Lichens are symbiotic associations of fungi and ______. a) mosses. b) cyanobacteria. c) green algae. d) either A or B *e) either B or C 167. Fungi have two types of spores (sexual and asexual). Why are spores useful? *a) Spores disperse offspring b) Spores disperse sperm c) Spores provide food the zygote d) Spores disperse eggs e) B and D are correct 168. Lichens are not a single organism, but a symbiotic relationship between ____ and ____. a) zygomycote fungus, angiosperm plant *b) ascomycote fungus, cyanobacteria c) angiosperm plant, unicellular algae d) ascomycote fungus, bryophyte 169. The symbiotic associations involving roots and soil fungi are considered _______. a) parasitic *b) mutualistic c) commensal d) harmful to the plant partner e) the beginning stages of the formation of lichens 171. If there were no mycorrhizae, then which of the following would be true? a) There would be fewer infectious diseases. b) We wouldn't have any antibiotics. c) There would be no mushrooms for pizza. *d) Most vascular plants would be stunted in their growth. e) Cheeses like blue cheese or Roquefort would not exist. 172. How are the vascular plants that are involved with mycorrhizae and the algae that are involved with lichens alike? *a) They provide organic nutrients to fungal partners. b) They secrete acids that keep the fungal partner from growing too quickly. c) They are in intimate associations with prokaryotic organisms. d) They are digested by fungal exoenzymes while still alive. e) They contain endosymbiotic fungi. 173. How are fungi and prokaryotes similar? *a) Both are important decomposers that recycle nutrients that are tied up in dead organic matter. b) Both have cell walls made of chitin. c) Both are important in pollination of angiosperm plants. d) Both increase the ability of most vascular plants to absorb water from the soil. e) Both A and B are correct 176. Both Oomycetes are Fungi are important decomposers, but have major differences in their structures and life cycles. Which statement is correct? a) Both have a dikaryotic stage. b) Both have a cell wall made of cellulose. *c) Only oomycetes have flagellated cells. d) Both have cell wall made of chitin. e) The dominant ploidy in oomycetes is haploid, while fungus are primarily diploid.