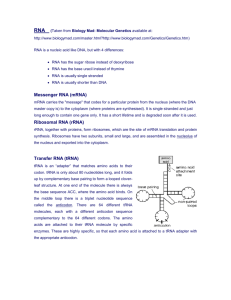
STUDY GUIDE: Transcription and Translation
advertisement

CH. 17 STUDY GUIDE: PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Transcription and Translation KEY TERMS protein synthesis termination DNA termination codon RNA nonsense codes messenger RNA (mRNA) initiation(=start) codon RNA polymerase termination(=stop) codon promoters anticodon terminators sense strand codon non-sense strand transfer RNA (tRNA) introns anticodon exons ribosomal RNA (rRNA) RNA splicing(=RNA processing) ribosome mutation subunits base-pair substitution initiation insertion initiation factors deletion reading frame frameshift elongation mutagen 1 WORD ROOTS anti - = opposite (anticodon: a specialized base triplet on one end of tRNA molecule that recognizes a particular complementary codon on an mRNA molecule) exo - = out, outside, without (exon: a coding region of a eukaryotic gene that is expressed). intro - = within (intron: a noncoding, intervening sequence within a eukaryotic gene). muta - = change; - gen = producing (mutagen: a physical or chemical agent that causes mutations). poly - = many (poly(A) tail: the modified end of the 3’ end of an mRNA molecule consisting of the addition of some 50 to 250 adenine nucleotides) trans - = across; - script = write (transcription: the synthesis of RNA on a DNA template). QUESTIONS 1. Describe Beadle and Tatum's one gene-one enzyme hypothesis. How did these guys come up with this one? How is this hypothesis stated today? 2. State three ways in which RNA differs from DNA. Name three types of RNA and give the function of each type. Describe the process of translation; describe initiation, elongation and termination and show how the sequence of bases in DNA determines the amino acid sequence in the protein. 3. Describe the process of translation; describe initiation, elongation, and termination and show how the sequence of the basis in DNA determines the amino acid sequence in the protein. 2 4. Be sure that if you are given the genetic code table, you can give the amino acid sequence for any given mRNA. 5. In a hypothetical strand of DNA the base sequence is: (3')-AAGTTTGGTTACTTC-(5') o What is the mRNA sequence transcribed from this DNA? o What is the amino acid sequence translated from this mRNA? o Does it matter in which direction the transcription occurs? Why? 6. Sketch a typical tRNA molecule, indicating the location of the anticodon and the position at which the amino acid becomes attached. 7. Describe in some detail how the genetic code is read by the ribosome. In doing so explain the terms codon, anticodon initiation(start) codon and termination(stop) codon. 8. Define mutation, give examples and indicate how mutations can be induced. 9. What agents can cause mutations? 10. What is the significance of having 64 codons in the genetic code? What is the value, if any, in the redundancy in the code? 3