Terms related to Meiosis … and some perspective
advertisement

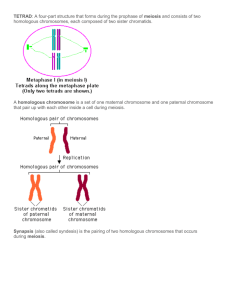
Terms related to Meiosis … and some perspective. Define the following terms: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Homolgous chromosomes (homologs) Haploid Diploid Synapsis Tetrad Crossing over Chaiasma(ta) Gamete Somatic cell In some organisms (fungi and the spore plants - mosses and ferns), meiosis does not produce egg (oogenesis) and sperm (spermatogenesis), but for the present, we will focus our attention on meiosis in the context of gametogenesis (formation of egg/sperm… the gender-neutral term). Meiosis is a two part division (Meiosis I and Meiosis II) of germ line cells…those that are destined to become egg or sperm. Meiosis begins just as mitosis does; with the replication of DNA and condensing of chromosomes. The difference is evident in PROPHASE I. Homologous chromosomes (maternally and paternally derived chromosomes carrying equivalent genetic information) somehow find each other and become intimately entwined. This is synapsis, and since there are 4 (total) sister chromatids in this formation, it is called a tetrad. It is during this time (prophase I) that portions of a maternal chromatid and a paternal chromatid break off at a very specific location - the chaiasma - and exchange these chromosome regions. It is important to note that 1. Precise chromosome packaging is critical, and 2. The chaiasma can occur at numerous locations along the chromatids. However, the chaiasma MUST be at the exact same point in both. This exchange of portions of chromatids and the genes that go with them is called crossing over. Meiosis proceeds through metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During meiosis I, sister chromatids DO NOT SEPARATE, however, homologous chromosomes go to either one or the other of the daughter cells. The parent cell was diploid (both homologous chromosomes present), but the two cells that result from meiosis I are haploid (only one or the other of each chromosome pair). During meiosis II, the sister chromatids are separated at the centromere. The result of meiosis II is 4 genetically unique haploid cells that (in animals) mature to egg or sperm (gametes).