Lesson Plan 59 - Texarkana Independent School District
advertisement

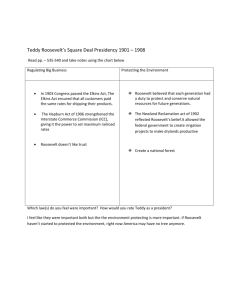
Sarah A. Huett U.S. History Lesson Plan TEKS Lesson Plan/Unit Plan Texarkana Independent School District Teacher: Sarah A. Huett Subject/Course: U.S. History Grade(s): Grade 11 Time frame: 45 minutes Lesson Plan Number: Topic/Process: T.I.S.D. 59 Roosevelt the Progressive Textbook: The Americans: Reconstruction to the Present, McDougall Littell Ch. 9, sec. 3, pgs 317-325 Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS): US1 A-B, US2 A, US3 A, US11 B, US19 A-B (1) History. The student understands traditional historical points of reference in U.S. history from 1877 to the present. The student is expected to: (A) identify the major eras in U.S. history from 1877 to the present and describe their defining characteristics; (B) apply absolute and relative chronology through the sequencing of significant individuals, events, and time periods; and (2) History. The student understands the political, economic, and social changes in the United States from 1877 to 1898. The student is expected to: (A) analyze political issues such as Indian policies, the growth of political machines, and civil service reform; (3) History. The student understands the emergence of the United States as a world power between 1898 and 1920. The student is expected to: (A) explain why significant events and individuals, including the SpanishAmerican War, U.S. expansionism, Henry Cabot Lodge, Alfred Thayer Mahan, and Theodore Roosevelt, moved the United States into the position of a world power; (11) Geography. The student understands the relationship between population growth and modernization on the physical environment. The student is expected to: (B) trace the development of the conservation of natural resources, including the establishment of the National Park System and efforts of private nonprofit organizations. (19) Citizenship. The student understands the importance of effective leadership in a democratic society. The student is expected to: (A) describe qualities of effective leadership; Sarah A. Huett U.S. History Lesson Plan T.I.S.D. (B) evaluate the contributions of significant political and social leaders in the United States such as Andrew Carnegie, Shirley Chisholm, and Franklin D. Roosevelt; and TAKS: US1 A-B, US3 A (1) History. The student understands traditional historical points of reference in U.S. history from 1877 to the present. The student is expected to: (A) identify the major eras in U.S. history from 1877 to the present and describe their defining characteristics; (B) apply absolute and relative chronology through the sequencing of significant individuals, events, and time periods; and (3) History. The student understands the emergence of the United States as a world power between 1898 and 1920. The student is expected to: (A) explain why significant events and individuals, including the SpanishAmerican War, U.S. expansionism, Henry Cabot Lodge, Alfred Thayer Mahan, and Theodore Roosevelt, moved the United States into the position of a world power; Concepts Enduring Understandings/Generalizations/Principles The student will understand that Leadership Effective leaders are often visionaries. Effective leaders motivate and inspire those they lead. Americans often look to their president to be an effective leader. Differences between people can create conflict. Social, political and economic oppression often leads to conflict. Conflict often leads to changes and reforms. Change/reform often occurs as a result of conflict. Change is inevitable. Change/reform can be positive or negative. Conflict Change/Reform Sequence of Activities (Instructional Strategies): 1. Focus: Review with students the goals of Progressivism from Lesson 57. 2. Activity: Have students work with a partner to complete a graphic organizer of the problems Teddy Roosevelt faced during his presidency. This activity should address the following: 1902 coal strike, trusts, unregulated big business, dangerous foods and medicines, shrinking wilderness and resources, and racial discrimination. Under each issue student should be able to answer the following: What steps did Roosevelt take to solve this problem? Which legislation, if any, helped to solve this problem? What goal(s) of progressivism does it address? Explain. When all students are finished, review this activity as a class. You will also want to review some of the famous political cartoons that were drawn depicting Roosevelt, including “The Lion Tamer”. Sarah A. Huett U.S. History Lesson Plan T.I.S.D. Questions to Consider in Lesson: 1) Was Roosevelt truly a “Progressive”? 2) How did Roosevelt’s way of dealing with the environmental problems impact your life today? 3) What characteristics and actions made Roosevelt the first modern president? Assessment of Activities: Classroom Observation Classroom Discussion Graphic Organizer Prerequisite Skills: 1. Construction of graphic organizers 2. Cartoon interpretation Key Vocabulary: Theodore Roosevelt, Square Deal, Meat Inspection Act, Pure Food and Drug Act, conservation, NAACP Materials/Resources Needed: Textbook, other resources, pens, paper, overheads of cartoons, projector Modifications: Allow students to have extended time to complete activities. Follow all modifications on student’s IEP. Differentiated Instruction: Have students write an original eulogy for Teddy Roosevelt. Students should include his noble characteristics, contributions and achievements in their eulogy. Students may use the internet to do additional research on Roosevelt’s life. Teacher Notes: Sarah A. Huett U.S. History Lesson Plan T.I.S.D. Sample Test Questions: 1. The______________ was founded in 1909 to promote civil rights for African Ameircans. A. B. C. D. Universal Negro Improvement Association Southern Christian Leadership Conference National Association for the Advancement of Colored People Student Nonviolent Coordination Committee 2. Muckrakers were A. politicians B. conservationists C. suffragists D. journalists Project developed and delivered through a Collaborative Research Grant between Texarkana Independent School District and TAMU-T Regents’ Initiative.