OVERVIEW OF RESPIRATORY DISORDERS
advertisement

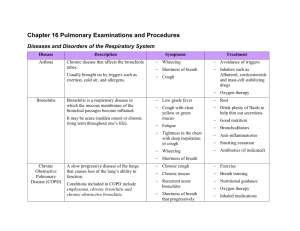
OVERVIEW OF RESPIRATORY DISORDERS Learning Objective • Classification of respiratory disorders • Define Asthma. • Define COPD. and clinical manifestation of Chronic Bronchitis and emphysema. • Pathogenesis of – Pneumonia – Lung abscess – T.B – Pulmonary embolism – Pneumoconiosis Respiratory Disorders Respiratory disorders can be classified into different groups • Respiratory tract infections Common cold, Influenza, Pneumonias, T.B • Disorders of lung inflation Pleural pain and pleural effusion • Obstructive air way disorders Bronchial asthma, COPD, Emphysema, Bronchitis • Pulmonary vascular disorder • Lung cancer Upper Respiratory Tract Nose, Paranasal sinuses, Nasopharynx and Larynx Lower respiratory Tract - Trachea and Bronchi Disease of nose and paranasal sinuses Common Cold (Acute Coryza) • Contagious, viral infectious disease of upper respiratory system • Rhinovirus • Coronavirus • Clinical features – Sore throat – Fever – watery nasal discharge eventually become thick. Influenza • • Commonly named as flu Infectious disease caused by Orthomyxoviridae family influenza virus) Clinical features • • • • • • Fever with chills Generalized aching Headache Sore throat Dry cough- can last for several week May cause prolong depression and debility known as post viral syndrome Sinusitis • Inflamation of paranasal sinus • Clinical features • • • • Frontal headache Purulent nasal discharge Facial pain Fever. Rhinitis Clinical Features: • Inflammation of nasal mucosa • Sneezing attack • Nasal discharge or blockage • Two types 1- Seasonal rhinitis (for limited time period) 2- Perennial rhinitis (occurs throughout the year) Common allergen causing rhinitis • • • • House dust mites Feces of house dust mites Pollen grains Domestic pets and moulds Epistaxis • • • Bleeding from nose Bleeding most common in the anterior septum where a confluence of veins creates a superficial venous plexus (Kiesselbach’s plexus) Predisposing factors are: Nasal trauma Rhinitis Deviated Nasal Septum Hypertension Atherosclerotic disease Drugs: Anti-platelet, anticoagulation Disease of Pharynx & Larynx Pharyngitis • Inflammation of pharynx • Viral or bacterial Clinical features • • • • Sore throat Fever Conjunctivitis Lymphadenitis of neck glands laryngitis • Inflammation of the larynx • Mostly Viral in origin • Most common cause of hoarseness Obstructive pulmonary Diseases COPD • COPD is group of disorders characterized by chronic and recurrent obstruction of air flow in the pulmonary air ways. Includes Asthma Chronic bronchitis Emphysema Clinical features • • • • Productive cough Exertional dyspnoea Wheez Chest tightness Asthma Asthma is a common chronic inflammatory disease of the airways with recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, and bronchospasm. Clinical features • • • • Wheeze Cough Chest tightness Dyspnoea Chronic bronchitis • Chronic bronchitis It is a chronic inflammation of the bronchi in the lungs. • Clinically defined as Persistent productive cough for at least three months in two consecutive years Emphysema • Emphysema is a long-term, progressive disease of the lung that causes destruction of lung tissue. • It is an abnormal permanent enlargement of air spaces with destruction of the alveolar walls and capillary beds. Difference between bronchitis and emphysema Bronchiectasis Localized, irreversible dilatation of part of the bronchial tree Clinical features: • Chronic productive cough • Worse in morning • Fever • Malaise • hemoptysis Lower Respiratory Tract Infection Pneumonia • Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung, damaging the parenchyma of lung (that is, the alveoli) and abnormal alveolar filling with fluid • Types 1.Community – acquired Caused by streptococcal pneumoniae (most common), 2. Hospital acquired Clinical features • • • Fever Cough first dry than productive Pleuritic chest pain Pulmonary Tuberculosis • Pulmonary tuberculosis is a common and often deadly infectious disease caused by various strains of mycobacteria, usually Mycobacterium tuberculosis in humans. • Types Primary Pulmonary TB Post-primary Pulmonary TB Miliary TB Clinical features • • • Chronic cough with hemoptysis Fever Weight loss Aspergillosis • Fungal infection mostly caused by Aspergillus fumigatus Clinical features • Fever • Breathlessness • Productive cough Pulmonary Vascular Disease Pulmonary hypertension is the narrowing of the pulmonary arterioles within the lung. Disease of Pleura,Chest wall Pleural Effusion • Fluid in the pleural cavity • Cause: Tuberculosis, Carcimona, Cardiac Failure, Pulmonary infarction, rheumatoid disease, SLE etc. • Clinical features: • Breathlessness • chest pain Empyema • Pus in the pleural space • Clinical features Fever Rigors Sweating Weight loss Pneumothorax • Air in the pleural space • Types 1.Spontaneous • Primary • Secondary 2. Traumatic