(eqstb) project - European Association of Tissue Banks
advertisement

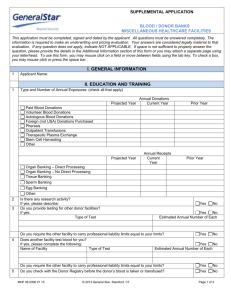
EQSTB European Quality System for Tissue Banking Agreement No 2003209 European Quality System for Tissue Banking Participants Martí Manyalich, Blanca Miranda, Esteve Trias, Clara Fernández, Aurora Navarro. Theo de By, Olivier Cornu, Alessandro Nanni Costa, Norbert Franz, Pier Maria Fornasari, Arnaud de Guerra, Martti Hirn, Artur Kaminski, Jan Koller, Bernard Loty, Stefan Poniatowski, Ioana Siska, Izabella Uhrynowska, Grigory Vabels, Jeroen Van Baare. OBJECTIVES The European Quality System for Tissue Banking is a project which has been cofunded by the European Commission; it is a DG Sanco Project (Directorate General for Health and Consumer Affairs) promoted by Hospital Clinic de Barcelona, Spain. The duration of this project has been of 3 years, from May 2004 until May 2007. 15 different national organisations and tissue establishments from 12 European countries have taken part in it: The project’s main objective was to analyse throughout four different working areas the factors that may influence the final tissue quality and safety for its transplantation providing finally a greater benefit to recipients. The project has aimed to develop the method to ensure standards of quality and safety in relation to tissue banking activities demanded by the future implementation of the European Directives on Tissue practices approved in March 2004. In order to achieve the project objectives, the tasks were divided in 4 working groups. The objectives of each one were focused in a specific area: 1. Standards Working Group: Perform a comparative analysis of the different standards followed in the participating countries to detect the tissue banking quality and safety key points. Define the number of standards or guides followed and quantify the differences and similarities among them. Study the rate of implementation of the European Directives on Tissues and Cells. Develop the Guide of Recommendations defining the quality and safety key points on tissue banking. 2. Registry Working Group: Define the common terminology and variables of tissue banking in order to create a common Registry to analyse the possibility of exchanging tissues between tissue establishments among different European countries. Define and create a prototype of a Registry Network Database for the entire tissue banking process: donation, processing, preservation, traceability, clinical application and adverse reactions after transplantation. Place the database on the Internet with a Search Function and validate the Registry prototype through a pilot data charge. European Quality System for Tissue Banking 3. Education Working Group: Design and validate a specialised training model for tissue bank personnel that could afterwards become a method of qualifying personnel and the approved training model recommended by the European Union members. This model will be based on the TE personnel’s profile and the knowledge and training needs detected. 4. Auditing Working Group: Design a European Auditing Model of tissue establishments based on the EU Directives on tissues and cells, and on the tissue banking quality and safety key points, as well as the remaining results from the other working groups. Perform 4 pilot audits using the audit model to improve and validate it. Develop a transferability report describing the applicability of the model at European level. RESULTS 1. WG1 – Standards: The Guide of Recommendations for Tissue Banking has been elaborated, and it includes the following: A description of the different quality systems that apply to tissue banking and a provision of the general quality system requirements. The legal and regulatory framework that envelops tissue banking activities in Europe, stating their requirements and deadlines (European Directives on Tissues and Cells). A description of the different standards on tissue banking activities that are available in Europe. A description of the quality and safety key points that are considered fundamental in tissue banking, divided into 4 groups: 1. General Concepts - Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) - Good Tissue Practices (GTPs) - Data protection - Coding - Environmental Conditions - Validation of processes - Organisation of Personnel Training - Audits and Inspections - Third Party Agreements 2. Donation and Procurement - Common definitions of donors - Donor Selection and Evaluation - Donor Testing - Donor Form - Tissue Procurement - Donor Registers 3. Tissues and Cells - Transport of procured tissue to TE - Reception of tissues at TEs - Processing, preservation, packaging and storage in TEs 4. Release and Allocation - Release procedures - Waiting list - Register of recipients / end user institutions - Export / Import policies - SAE/R reporting policy and Corrective Actions A study and analysis of the rate of implementation of the European Directives in the participating countries was performed and provided to the EC. European Quality System for Tissue Banking 2. WG2 – Registry: A prototype of a Tissue Registry through a multinational European network database was elaborated. The tissue which was chosen for the database was musculoskeletal tissue (due to its product variability). The variables of the database were harmonised through 4 data sets and the musculoskeletal product list. The data sets were structured into the Donor, Tissue, Allocation and Transplantation data sets. Figure 1: Registry Network Database main page 3. WG3 – Education: A specialized training model was designed and validated. It was structured into 2 complementary courses: an online program and a face-to-face course. 28 participants were trained in all the tissue banking areas and improvement of their knowledge was observed after receiving the training. The training model was afterwards improved with the suggestions of the students. A 100% certification was obtained. Figure 2: Contents of the Training Model (orange: online; blue: faceto-face) Figure 3: Virtual Platform of the online course European Quality System for Tissue Banking 4. WG4 – Audit: A model on European Tissue Banking Auditing was designed in order to comply with the European Directives’ requirements. During the first stage of the project, preliminary audit methodology and auditor profiles were defined. In order to assess the effectiveness of the model, 4 pilot audits were performed in 4 different tissue establishments from the partner countries. For each one, an audit report was made and improvements were made on the model as each audit went by. At the final phase of the project, the final audit methodology was agreed. It was decided to structure the audit as follows: a) outset, b) submission of documents, c) audit, d) post audit and e) audit result. Likewise, the final auditor profile was agreed. The audit team should be composed of 3 experts, each one specialised in the following areas: 1) quality, ISO, GMP, 2) health-organisational background, donation and transplant coordination, and 3) tissue establishment technical processes. As a result of the model design, pilot audits and diverse suggestions from partners, EC members and external project auditors, the final Guide for Auditing Tissue Establishments was elaborated. This guide provides a description of all the tissue banking key point standards, guidance for auditors on how to perform an audit and what issues to search for and a self-assessment questionnaire for TEs (for each standard). In addition, an audit report form is available. The guide also includes a ‘Site Master File’, a document to be completed by the TEs that will be audited (describing all the data needed from those TEs prior to the audit). The Audit Manual of this guide is structured into 6 main parts, which are: A) General Policies B) Tissue Donation C) Tissue Procurement D) Tissue Processing E) Tissue Storage F) Tissue Distribution Each one of these parts is itself subdivided into subparts, such as the one shown in the image (subpart C.4: Transportation to TEs). This Guide has been elaborated in order to provide tissue banking experts with the necessary tool to audit tissue establishments against the quality and safety key points and the EU Directives. It has been elaborated in a way which allows the TE to be audited by external auditors as well as by the own TE staff. The guide will be very helpful for auditors to guide them through an audit, but also, it will be quite useful for TEs to give them an idea of what is expected of them and what auditors will be searching for. The checklist with the sets of questions can be used as a self-assessment tool so that the TE can audit itself. The next page shows the table of contents of the Guide for Auditing TEs: European Quality System for Tissue Banking TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Introduction 1.1. Background 1.2. Purpose and Application 1.3. Structure, Contents and Approach 2. Regulatory Framework 3. Definitions and abbreviations 3.1. Definitions 3.2. Abbreviations 4. Audit Procedure 4.1. Outset 4.2. Document Submission 4.3. Audit 4.4. Post-audit 4.5. Audit decision 5. Audit Manual Part A: General Policies A.0 General Considerations for auditors A.1 Legal and Regulatory Framework A.2 Standard Operating Procedures A.3 Specific Aspects of the Quality System A.4 Data Protection and Anonymity A.5 Traceability A.6 Personnel Training and Qualification A.7 Health and Safety of Staff; Compliance with legal requirements A.8 Packaging and Labelling A.9 Records and Registers Part B: Tissue Donation B.1 Donor Selection and Evaluation B.2 Donor Coding B.3 Donor Testing B.4 Donor Documentation Part C: Tissue Procurement C.1 General Principles C.2 Retrieval Conditions C.3 Retrieval Documentation C.4 Transportation to TE Part D: Tissue Processing D.1 General Principles D.2 Equipment Suitability, Sterility and Traceability D.3 Environmental Controls D.4 Traceability of tissue through processing D.5 Microbiological testing of final tissue D.6 Adverse Event Management Part E: Tissue Storage E.1 General Principles E.2 Storage conditions E.3 Tissue release Part F: Tissue Distribution F.1 General Principles F.2 Transportation F.3 Reception policies at the End User F.4 Adverse Event Monitoring and Recall F.5 Waiting lists and Import/Export Policies 6. Shortcut to audit guidance parts A to F 7. Audit Report 8. Annexes Annex 1: 2006/86/EC Annex VI, Article 9 Annex 2: Site Master File European Quality System for Tissue Banking CONCLUSIONS The effectiveness, sustainability and impact of the outputs of the project were analysed and it is considered that the 2 guides that have been published are not only be very useful for experienced TE and auditors to have, but also for professionals that are starting in the tissue banking field and beginning to set up new tissue establishments. The prototype of the registry proves that it would be possible to exchange tissues between establishments across Europe with such a database. It has been challenging to harmonise the tissue product list, and for this reason, it would be interesting to have in the future a common coding system for all TE in Europe. As regards the training model, it was been assessed that such a model is effective in educating personnel on the tissue banking field so as to have professionals with excellent knowledge and expertise in this field. The Member States could adopt and/or adapt this model to training personnel from their TEs. It is recommended that the outputs of the project, including the Guide of Recommendations, the Guide for Auditing TE and the Training Model, are continuously updated so that they do not become obsolete, since new requirements will very likely come up in the future. For this reason we recommend that an organisation such as the EATB takes on this task and perhaps even a body of TE auditors is created. For more information on the EQSTB project, please visit the project website at: http://sanco-eqstb.hospitalclinic.org/sanco/index.html The guides are available for download at this site. EQSTB Final Report (EC site): http://ec.europa.eu/health/ph_projects/2003/action2/docs/2003_2_06_frep.pdf PARTNER ORGANISATIONS Hospital Clinic i Provincial de Barcelona Belgian University Tissue Bank Tampere University Tissue Bank Agence De La Biomédecine Deutsches Herzzentrum Berlin Istituti Ortopedici Rizzoli Centro Nazionale Trapianti State Forensic Medicine Centre, Latvian Tissue Bank Netherlands Bone Bank Foundation Bio Implant Services Foundation National Centre for Tissue And Cell Banking University Of Medicine and Pharmacy "Victor Babes" Ruzinov General Hospital Bratislava Organización Nacional De Trasplantes Transplant Services Foundation North London Tissue Bank Spain Belgium Finland France Germany Italy Italy Latvia Netherlands Netherlands Poland Romania Slovakia Spain Spain UK