Organizational and Behavioral Interventions
advertisement

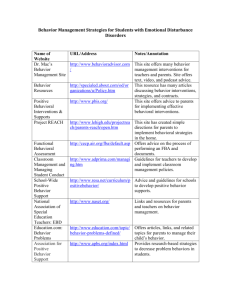
Organizational and Behavioral Interventions For Performance Improvement1 By Dr. Sohail Amjad, Pakistan Introduction: The purpose of this brief is two folds. First, it describes how suggested behavioral interventions would differ from the traditional past practices of skills training. Second, it elaborates the interaction between organizational and behavioral interventions to compliment each other. It is important that systems perspective in the developing country context is used to develop organizational and behavioral interventions. The emphasis is on improving the organizational processes which leads to performance improvement. Differences between proposed behavioral interventions and traditional past practices of skills training: The usual argument is that we have trained people in skills to implement organizational tasks (e.g. service delivery, performance data collection and reporting, data quality assurance and use etc.) but it did not work. It is the contextual or organizational factors, which leaves people demoralized. Thus, we need more emphasis on organizational support interventions. The best results are obtained by combining the individual and organizational interventions. The individual behavioral intervention should emphasize reducing negative attitudes2 towards performance 1 The interventions proposed in this manuscript specifically focus on developing countries context and for devolved/semi-autonomous local governments in public sector. Many interventions are equally applicable to other contexts. 2 ‘Attitudinal change is must for moving forward’ i.e. from “Habit to Motivation”. Habit is reflexive, without intention, without conscious deliberation and control, could be beneficial or harmful, require “external force” to acquire it. Motivation involves a voluntary, intentional, selfless devotion Dr. Sohail Amjad Organizational and Behavioral Interventions For Performance Improvement in Developing Countries. 1 improvement tasks and improving motivation3 to perform them, while organizational interventions should involve strengthening and creating mechanisms for supporting good performance and rewarding those who consistently deliver performance. Keeping this context, I will first describe how behavioral interventions are different from the past skills training and then I will illustrate organizational interventions. Differences Skills are based on the perspective of “how to do it” which leads a gap in “why to do it”. It is important that people relates to the immediate and long-term benefits to self and others to perform a certain task. Skills on performance data collection are emphasized without creating a demand for data in those who would benefit from it. Emphasis on performance improvement benefits on 1) personal; 2) management; 3) policy; 4) community; 5) advocacy, others. Emphasis on overcoming negative attitudes towards documentation, performance data collection e.g., it is wastage of time, boring, no immediate benefits to self and others, service is more important than knowing quality of service and number of people served, data quality will remain a problem in future, culture is difficult to change, etc. Shifting emphasis from performance data use for M&E to perceiving gaps as an opportunity for improvement from where we are to where we want to go Shifting emphasis from self-blame to processes which affect performance. to a cause, developing strategies for maximizing benefits to others and thus energizing oneself with creating a difference (IDEAL?). 3 Improving motivation will require, creating awareness in senior management that negative attitudes exist and affect motivation, performance and developing behavioral change communication strategy by the management that will also be part of the promotion of specific values for culture of information. Dr. Sohail Amjad Organizational and Behavioral Interventions For Performance Improvement in Developing Countries. 2 Emphasis on self-assessment as a skill and a belief for personal, organizational development and making a difference in life of people served, self-assessment as means of promoting responsibility and accountability4. Combining new skills such as data quality assessment using LQAS or others etc. Emphasis on motivation though problem solving, goal setting, role modeling, cultural practices such as work as a community service, appreciation and acknowledgement by colleagues, supervisors, community, prestige due to good work, comparison etc. Strengthening belief that service provider has a responsibility to improve life of the people served Strengthening belief that information empowers service providers to improve their own working environment through advocacy with 3 senior management and with community. Behavioral Interventions Problem solving is an important motivation technique, which help people define a problem is such a way that possibility of change is highlighted such as defining them as performance gaps and presenting gap as an opportunity for change. Second, it explores potential causes of the problem and generates appropriate strategies to address them. This is a behavioral change technique, which could be use to sort problems for carrying out organizational tasks. Goal setting is another way people use to motivate themselves for action. Accomplishing a goal or a task creates positive feeling for taking on more challenges. Thus, goal setting as a motivating People have different attitudes towards accountability and responsibility, e.g. Accountability is seen as punishment rather than a means of improving performance. Avoid responsibility by shifting blame to “system” and not acknowledging being part of the “system”. Perceiving being victim of circumstances than being empowered to bring change. 4 Dr. Sohail Amjad Organizational and Behavioral Interventions For Performance Improvement in Developing Countries. technique would be used for carrying out tasks. The staff at service delivery level should be asked to develop their service delivery goal/targets as part of their striving for making a difference in lives of people and understand it as a meaningful activity. Self-efficacy (as behavioral scientists describe) implies having confidence in one’s ability to perform a task or change things for better. This helps in creating empowerment, optimism and futuristic perspective. Thus, self-efficacy could be a major technique for motivating people for better performance. Organizational Interventions Organizational interventions involve strengthening and modifying attitudes, beliefs, practices, and management processes for effective and efficient use of resources for high motivation and better performance. Six types of interventions are suggested: A. Instituting Quality Assurance Tools for performance monitoring and evaluation B. Foster team building concepts as teams can take better decisions than individuals. C. Change in old Performance Appraisal systems and introduction of more transparent and performance-based appraisal techniques and systems. D. Change in traditional Supervisory System and making supervisors as part of performance appraisal of staff. E. Establish Reward/incentive System F. Introduction of performance feedback mechanism from topdown to bottom up on regular basis. A. Instituting Quality Assurance Performance including Data Quality Dr. Sohail Amjad Organizational and Behavioral Interventions For Performance Improvement in Developing Countries. Tools for Monitoring 4 Performance and data quality is the result of various processes. Thus, modifying those processes has the potential for improving performance. These gaps in processes could be identified through use of quality assurance tools. Some of these are: LQAS, cause and effect analysis, control chart and story board. B Establish Management Teams from bottom-up at all levels. The management teams are visualized as an effective way of performance management through participatory decision-making and support for each other for performance improvement. The appropriate levels for teams should be identified with designated team leaders responsible for team performance based on organizational structure in the country context. Thus, to improve performance and create accountability, team leader should be given more management control over team members and staff for performance management. These changes would help to create a better teamwork, planning and implementation of action plan for improving performance as evidenced by improving service coverage. C Change in Performance Appraisal system Proposed criteria are: Evaluated based on the planned targets for service coverage and deliverables at the end of each year and should achieve + 10% of the set targets. Displayed monthly monitoring information in the facility as well as in higher managerial units as confirmed by supervisory visit of the district/provincial teams and peer reviews. Conducted two performance assessments maintaining performance by end of year. Dr. Sohail Amjad Organizational and Behavioral Interventions For Performance Improvement in Developing Countries. for improving and 5 Received a certificate from Community-based Organization (CBO) for involving communities for setting coverage target, monitoring and evaluating it. Generating funds from community to rewards good outreach workers. Received a certificate after peer review of meeting district data quality standard and service coverage. Coordinated with other vertical program managers/sectors. D. Change in Supervisory System It is difficult to conduct a supervisory visit due to transport, cost and other reasons. Second, a close supervision tends to give the impression that there is no trust on reported performance. Thus, it is better to empower service providers to set their own target and meet them by providing them tools to facilitate their performance. They should feel confident about their performance to invite peers and management to confirm it. Peer review should become part of the annual performance appraisal. Two six monthly peer reviews are proposed. Proposed processes could be: Six-monthly review – service delivery outlets Sub-district has the supervisory function for service delivery outlets Some rotating mechanism between higher and lower tiers for review of performance, thus district reviewing performance of sub-districts, provinces reviewing performance of districts and national level should review provincial performance achievement of targets. E Establishing Reward/Incentives System in Public Sector Dr. Sohail Amjad Organizational and Behavioral Interventions For Performance Improvement in Developing Countries. on 6 This is the most difficult area to intervene but at the same time need attention, if organization performance improvement has resources limited is and to be thus achieved. could not Every provide financial/tangible benefits all the time. Furthermore, salary is contingent upon a certain level of performance, so why that level of performance need further incentive. And we know that, given all constraints, some staff still meet or exceed performance expectations, thus, motivation to perform is more complex than provision of tangible/ financial incentives. Therefore some trade-off need to be strike off for sustainable performance improvement practices in the organization. Here, a few interventions and processes are described, which can possibly be introduced in public sector without much resource implications. These are as follow; Institute a yearly recognition certificate (explicit criteria communicated to all) Acknowledgement in newsletter at district/provincial and national level Rotating trophy among high performers Rural to urban transfer/posting opportunity Special salary increment for those who receive recognition certificate for two years 3-6 months salary advance facility (interest free) for high performers In-service short training opportunities based on performance criteria. Priority on in-service higher studies in public sector institutions—sponsorship Introduce loan schemes based on performance (low interest rate) One salary as bonus to performance trophy winner Develop mechanisms performance Dr. Sohail Amjad Organizational and Behavioral Interventions For Performance Improvement in Developing Countries. for community rewarding good 7 Other Options: Performance Related Pay (PRP) Performance Linked Contracts (PLC) Sliding Scale Performance Appraisal (SSPA) Management by Objectives (MBO) or Management by Targets (MBT) Contracts Develop standards, criteria and mechanisms for performancebased contracts F Changes in Feedback Report on performance at all levels A regular feedback mechanism on performance should be institutionalized and these feedback reports should: Describe district/provincial and national targets for selected indicators. Describe the district/provincial/regional average on selected indicators and make comparison with assigned targets Compare outreach facilities with district average and set targets. Compare outreach facilities across time and appreciate outreach facilities which are above district average and meeting set targets. Provide reasons why some facilities are above and below average. Provide guidelines for actions to facilities Therefore, performance feedback system should describe: Progress towards district/provincial and national targets Comparison of performance on set targets Comparison of performance over time Dr. Sohail Amjad Organizational and Behavioral Interventions For Performance Improvement in Developing Countries. 8 Provide reasons for below and above average performance Formulate supportive action guidelines Conclusions Senior Management acknowledgment is needed that behavioral and organizational factors are crucial for performance improvement, leading to improved services and progress towards development outcomes. Senior Management support is essential for implementing behavioral and organizational interventions for improvements in performance. 9 Dr. Sohail Amjad Organizational and Behavioral Interventions For Performance Improvement in Developing Countries.