Name Date ______ Ecosystems STUDY GUIDE Choose the letter of
advertisement

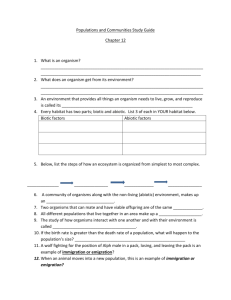
Name ______________________________________ Date _________ Ecosystems STUDY GUIDE Choose the letter of the best answer. 8.11B 1. What are some abiotic factors that organisms in an aquatic ecosystem depends on? Water, temperature, salinity, turbidity 8.11A, 8.2E 2. The graph shows changes in the populations of predator and prey over time. Explain why the population of prey increased near the end of the timeline shown on the graph? Less predators were hunting the prey, so there is more prey. Name ______________________________________ Date _________ 8.2E 3. The graph shows temperature and precipitation data for major biomes. How would the classification of a temperate rain forest change if it were an average of 10°C warmer? (Hint: Step 1. Identify the temperature range of a temperate rain forest. Step 2. Add 10°C to that range. Step 3. Interpret the graph to identify the biome with a similar temperature range.) tropical rain forest. 8.11A 5. What are pairs of producer/consumer organisms that a scientist could be investigating in a lake? Water plants Fish algae snails cattails ducks water lily pads turtles Name ______________________________________ Date _________ 8.11A, 8.2E, 8.3B 4. The diagram below shows a desert food web. Which would be the most direct cause of an increase in the cacti population? kangaroo rats and beetles will decrease 8.11D, 8.2E 7. The graph shows the global status of fish stocks. What recommendation would you make based on the graph? (Hint: Step 1. Use the graph key to analyze the data in the graph. Step 2. Decide which course of action would best suit the data on the graph.) Decrease the harvesting of fish globally because most fish stocks are fully or overexploited and need to be conserved Name ______________________________________ Date _________ 8.11A, 8.2E, 8.3B 6. The diagram below shows a mangrove swamp food web. Molds are consumed by some organisms. They are also decomposers in ecosystems. How would this food web change to show the role of mold as decomposers? (Hint: Step 1. Recall how the flow of energy is shown in a food web. Step 2. Recall how decomposers get their energy. Step 3. Use this information to determine how to illustrate the flow of energy to a decomposer.) If the small fish died, an arrow would point from the small fish to the mold. 8. The diagram below shows the carbon cycle. What is happening at Point 1, 2, 3 and 4? Point 1 involves living organisms that are letting out CO2 through respiration. Point 2 involves photosynthesis taking in CO2 and releasing O2. Point 3 involves humans burning fossil fuels. Point 4 involves dead organisms and waste products returning Carbon to the environment. Name ______________________________________ Date _________ 8.11C, 8.2E 9. The graph shows the running speed of rabbits in a population. It also shows the running speed of a new group of predators that recently moved into the area due to habitat loss. Predict how the graph might change in the long-term due to the change in the rabbits’ environment. A larger percentage of the rabbit population will be faster because the slower rabbits died and were not able to pass on their slow trait. 8.2C 10. A sea turtle traveled nearly 8,000 km across the Atlantic Ocean to its nesting grounds. The journey took the turtle 180 days. What was the average speed of the turtle in kilometers per hour? time has to be converted from days to hours 180 days X 24 hours = ? average speed distance/time 8,000 km / ? = answer for average speed 8.11A 11. Distinguish between the following feeding relationships in ecosystems: definition of predator/prey (e.g., The predator hunts and eats the prey.) definition of producer/consumer (e.g., The producer makes its own food; the consumer eats the producer and/or other consumers.) Name ______________________________________ Date _________ 8.11A 12. Choose an ecosystem and diagram a food web that might occur there. Include at least five organisms in your food web. Use arrows to indicate the flow of energy. Within your food web, identify a producer/consumer relationship. 8.11A, 8.2C, 8.3B 13. The diagram below shows a pond food web. In the space below, sketch one food chain based on this food web. Label each organism in your food chain as a producer, primary consumer, secondary consumer, or tertiary consumer. 8.11C 14. Describe two examples of changes to ocean environments caused by human activities. Give an example of a short-term effect and a long-term effect of each of the changes. description of environmental changes caused by humans (e.g., habitat loss and water pollution from an oil spill) examples of short-term effects (e.g., Habitat loss: Organisms are immediately displaced; water pollution: Organisms are immediately killed.) examples of long-term effects (e.g., Habitat loss: Displaced organisms populate surrounding habitats; water pollution: Environments are polluted and cannot support any populations of organisms.)