Ch 12 Notes as_ch_12_poultry_production_
advertisement

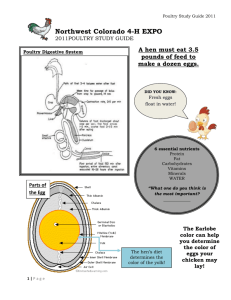
Chapter 12 Poultry Production General Information: Poultry popular for holidays Chicken most popular Average American eats 75 pounds of poultry per year. Products from poultry: o Meat o Eggs o Medicine and vaccines o Feathers for clothes, pillows, fish lures o Ornamental uses/hobbies Kinds of Poultry: Poultry – domesticated birds Use – for consumption/Pet food/Vaccines Types – Chicken, Turkey, Ducks, Geese, Quail, Peafowl, Swans, Pigeons, Ratites, and Pheasants. Common names – Fowl or Birds Chickens: Most important species Raised for meat and eggs Meat of a chicken is based on age and sex 1 Names of chickens: o Broiler – young chicken 6-7 weeks, weighs about 4 pounds. Either sex. 7 billion are raised each year in the US. o Roaster – young chicken older and slightly larger than a broiler. o Capon – male chicken that has been neutered (castrated). 5-7 months old. Weigh 6 pounds. o Spent Hen – hen that no longer lays eggs. Used in soups, or processed foods. o Layer – mature female. Can produce around 300 eggs per year. o Hen – Mature female, laying. o Pullet – young female not yet laying eggs o Cock – Mature male, can be called a rooster. o Cockerel – male that is less than one year old. Common breeds: White Leghorn – used in egg production. Smallest Barred Plymouth Rock – meat and eggs New Hampshire – Meat and eggs White Rock – meat and eggs. Largest. Turkey: Raised primarily for meat Consumers want white meat 300 million turkeys are raised each year in the US 2 Turkey Names: Poult – young turkey Tom – mature male turkey or gobbler. Hen - female turkey Facts: Raised in confinement Marketed at 20 weeks Most popular is the broad-breasted white Ducks: Raised for meat, eggs, down, and feathers. Down – the soft feathery covering that grows under the feathers. Duck Names: Duckling – young duck – still has down Drake – mature male duck Hen – mature female duck Facts: 15 million ducks are raised in the US each year. Grow faster and heavier than chickens Can swim Most raised indoors on commercial farms. Geese: Used for meat, eggs, feathers and ornamental purposes. Some used to control weeds. 1 million raised in the US each year. 3 Resist a lot of diseases that other poultry get. Geese Names: Gosling – baby goose of either sex Gander – Mature Male goose Hen – Mature female goose Gaggle – flock or group of geese that are not flying. Peafowl: Used for their feathers. Peafowl names: Peacock – mature male peafowl. Peahen – mature female peafowl. Train – male tail feathers Swans: Love water Colors range from white to black Used for ornamental purposes Ratites: Flightless birds which include: Ostrich, emu, kiwi, cassowary, and rhea. Largest is the Ostrich – weighs 350 pounds – stands 10 feet tall. Life span – 70 years. Raised for – feathers, meat, skin and oil. Guinea Fowl: Raised for food, as novelty bird, and to stock game preserves. 4 Have thick shell and because of this are often used for ornamental purposes. The Poultry Industry: Early Poultry Production o First poultry raised was more than 5000 years ago in Asia and in Egypt about 3500 years ago. o Poultry was brought to North America in 1607 o Turkeys were native to North America Modern Poultry Industry: Confinement Leading states for meat production: Georgia, Arkansas, Mississippi, Alabama, and North Carolina Leading state for egg production: California Leading states for turkey production: North Carolina, Minnesota, and California. Poultry Science – the study and use of areas of science in raising poultry. Vertical integration – more than one step in the poultry process ( chick and feed/growers/broilers/buyers) Poultry as Organisms: Classified as Aves Vertebrates Differ in digestion and reproduction Digestion – beak and gizzard 5 Reproduction – eggs are hatched, 21 days (chickens) 29-31 days (geese) Turkeys (27-28 days) and ducks (28-35 days). Incubation period is influenced by temperature and humidity. Appearance – yellow pigmentation – egg production. Large red comb – good health. Ragged feathers – poor health. Poultry Production Systems: 4 areas: Broiler Production – 6 weeks to raise Egg Production – 24 weeks to raise Egg Quality: 95% marketed are white Parts: Shell, Albumen, Yolk, Membrane Judging eggs – Candling Molting – Process of shedding and renewing feathers. Laying eggs stops during molting. Takes about 2 months to have a bird completely molt out. Pullet for egg Production Pullets begin to lay eggs at 24 weeks. Pullet and Cockerel for broiler egg production. One cockerel per 8-10 pullets Housing and Equipment: Housing – Controlled environment. o Litter – wood shavings 6 o Lighting – control laying cycle (14 – 16 hours) and cannibalism (red light). o Temperature – 85 – 95 degrees F for babies, 70 for 6 week birds o Humidity – 50 -75 % in broiler houses. Mist systems are used. o Ventilation – using large fans. Helps prevent cannibalism. Feeding and Watering Equipment: Automated equipment is used Sanitation: Use disinfectants Vaccinate Dispose of dead birds in an incinerator Diseases – mostly caused by a bacteria or virus o Marek’s Disease – virus - paralysis of legs and wings. o Newcastle – Virus – soft eggs, affects birds gasp, twist neck around. o Infectious Bronchitis – virus – nasal discharge, laying stops. o Fowl Cholera – bacteria – fever, colored heads, death. Parasites – o Coccidiosis – parasite – droppings get into food or water. Birds are sleepy, pale and listless. 7 o Large Roundworms – worm – 3 inch worms, picked up in soil. Deworm. o Mites – mite – use insecticides. Bird is pale, droopy and listless. o Tapeworm – Worm – Bird pale, looses weight. Found in soil. Deworm 8