Chapter 12 Poultry Production
advertisement

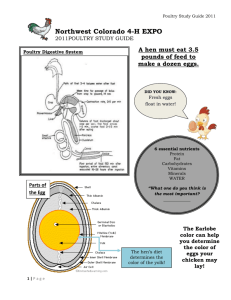
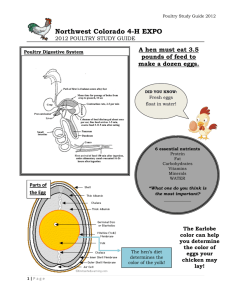
Poultry popular for holidays Chicken most popular Average American eats 75 pounds of poultry per year. Products from poultry: Meat Eggs Medicine and vaccines Feathers for clothes, pillows, fish lures Ornamental uses/hobbies Types : Chicken Turkey Ducks Geese Quail Peafowl Swans Pigeons Ratites Pheasants Common names – Fowl or Birds Most important species Raised for meat and eggs Meat of a chicken is based on age and sex Broiler – Young chicken 6-7 weeks, weighs about 4 pounds. Either sex. 7 billion are raised each year in the US. Roaster – Young chicken older and slightly larger than a broiler. Capon – Male chicken that has been neutered (castrated). 5-7 months old. Weigh 6 pounds. Spent Hen – Hen that no longer lays eggs. Used in soups, or processed foods. Layer – Mature female. Can produce around 300 eggs per year. Hen – Mature female, laying. Pullet – Young female not yet laying eggs Cock – Mature male, can be called a rooster. Cockerel – Young male that is less than one year old. White Leghorn – used in egg production. Smallest Barred Plymouth Rock – meat and eggs New Hampshire – Meat and eggs White Rock – meat and eggs. Largest. Raised primarily for meat Consumers want white meat 300 million turkeys are raised each year in the US Poult – young turkey Tom – mature male turkey or gobbler. Hen - female turkey Raised in confinement Marketed at 20 weeks Most popular is the broadbreasted white Raised for meat, eggs, down, and feathers. Down – the soft feathery covering that grows under the feathers. Duckling – young duck – still has down Drake – mature male duck Hen – mature female duck 15 million ducks are raised in the US each year. Grow faster and heavier than chickens Can swim Most raised indoors on commercial farms. Used for meat, eggs, feathers and ornamental purposes. Some used to control weeds. 1 million raised in the US each year. Resist a lot of diseases that other poultry get. Gosling – baby goose of either sex Gander – Mature Male goose Hen – Mature female goose Gaggle – flock or group of geese that are not flying. Peacock – mature male peafowl. Peahen – mature female peafowl. Train – male tail feathers. Use - for their feathers. Love water Colors range from white to black Used for ornamental purposes Flightless birds which include: Ostrich, emu, kiwi, cassowary, and rhea. Largest is the Ostrich – weighs 350 pounds – stands 10 feet tall. Life span – 70 years. Raised for – feathers, meat, skin and oil. Raised for food, as novelty bird, and to stock game preserves. Have thick shell and because of this are often used for ornamental purposes. Early Poultry Production First poultry raised was more than 5000 years ago in Asia and in Egypt about 3500 years ago. Poultry was brought to North America in 1607 Turkeys were native to North America Raised in Confinement Leading states for meat production: Georgia, Arkansas, Mississippi, Alabama, and North Carolina Leading state for egg production: California Leading states for turkey production: North Carolina, Minnesota, and California. Poultry Science – the study and use of areas of science in raising poultry. Vertical integration – more than one step in the poultry process (chick/feed/growers/broilers/buyers) Classified as Aves Vertebrates Differ in digestion and reproduction Digestion – beak and gizzard Reproduction – eggs are hatched, 21 days (chickens) 29-31 days (geese) Turkeys (27-28 days) and ducks (28-35 days). Incubation period is influenced by temperature and humidity. Appearance – yellow pigmentation – egg production. Large red comb – good health. Ragged feathers – poor health. 4 areas: Broiler Production – 6 weeks to raise Egg Production – 24 weeks to raise Egg Quality: 95% marketed are white Parts: Shell, Albumen, Yolk, Membrane Judging eggs – Candling Molting – Process of shedding and renewing feathers. Laying eggs stops during molting. Takes about 2 months to have a bird completely molt out. Pullet for egg Production Pullets begin to lay eggs at 24 weeks. Pullet and Cockerel for broiler egg production. One cockerel per 8-10 pullets Housing – Controlled environment. Litter – wood shavings Lighting – control laying cycle (14 – 16 hours) and cannibalism (red light). Temperature – 85 – 95 degrees F for babies, 70 for 6 week birds Humidity – 50 -75 % in broiler houses. Mist systems are used. Ventilation – using large fans. Helps prevent cannibalism. Automated equipment is used Use disinfectants Vaccinate Dispose of dead birds in an incinerator Diseases – mostly caused by a bacteria or virus Marek’s Disease – virus paralysis of legs and wings. Newcastle – Virus – soft eggs, affects birds gasp, twist neck around. Infectious Bronchitis – virus – nasal discharge, laying stops. Fowl Cholera – bacteria – fever, colored heads, death. Parasites – Coccidiosis – parasite – droppings get into food or water. Birds are sleepy, pale and listless. Large Roundworms – worms picked up in soil. Mites – Pest that sucks blood, use insecticides to rid. Bird is pale, droopy and listless. Tapeworm – Bird pale, looses weight. Found in soil.