The nucleus is responsible for storing the DNA that directs
advertisement

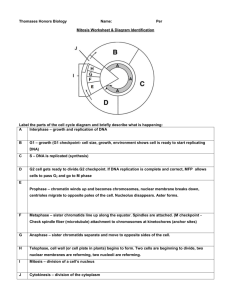
UNIT 2 EXAM – CELL REPRODUCTION MAKE NO MARKS ON THIS BOOKLET!!! PART 1 - TRUE & FALSE (A=TRUE / B=FALSE) (1 MARK EACH x 20) 1. The nucleus is responsible for storing the DNA that directs all cell activities. 2. Animal cells contain chloroplasts, an organelle that contains chlorophyll. This allows animal cells to make their own food through a process called photosynthesis. 3. Mitosis is a process in which cells divide, producing identical daughter cells. 4. Replication of the DNA ensures that each new cell contains genetically different information in its nucleus. 5. In anaphase, the centromeres split and the spindle fibers pull the sister chromatids apart to the same sides of the cell. 6. The gamete is the first body cell of a new organism. 7. Human gametes have 23 chromosomes and are called haploid. 8. The female reproductive organ in an angiosperm is called a stamen. 9. In self-pollination, two parent plants are needed to bring the gametes together. 10. Genetic variation affects the survival of a species. 11. Selective breeding involves breeding individuals with certain desirable traits to produce offspring with similar traits. 12. Reproductive technology does not require the knowledge of cell biology and DNA. 13. DNA is made of sugar, phosphate, and nitrogen bases. 14. Adenine is always combined with cytosine on the DNA molecule. 15. A codon is made of four consecutive nitrogenous bases, such as C - T - A - A. 16. Genetic engineering is a used to create transgenic organisms. 17. A karyotype is a photograph of a person's cells. 18. All human beings have 23 chromosomes in each of their body cells. 19. Biotechnology is the process that uses micro-organisms to break down the complex compounds in toxic waste. 20. Micro-organisms can be used to break down toxic waste. PART 2 – MATCHING (1 MARK EACH x 20) 21. DNA replicates. 22. Centromeres divide. 23. Spindle fibers appear. 24. Chromosomes form a line across the equator. 25. Nuclear membrane reappears. a. telophase b. anaphase c. prophase d. metaphase e. interphase 26. A small piece breaks away to form a new individual. 27. A bud forms, grows, and breaks away. 28. A reproductive cell grows through cell division. 29. An organism splits into two new organisms. 30. Injured cells are repaired or lost body parts are grown. a. binary fission b. regeneration c. spore formation d. budding e. fragmentation 31. Homologous chromosomes line up at the equator. 32. Crossing-over occurs. 33. Individual chromatids separate and move to opposite poles. 34. Individual chromosomes line up at the equator. 35. Chromosomes arrive at the poles and cell division begins. a. prophase I b. anaphase II c. metaphase I d. metaphase II e. telophase II 36. Produces seeds inside cones 37. Flowering plant 38. Seed begins to grow 39. Male and female gametes come from same plant 40. Gametes come from two different plants a. angiosperm b. germination c. self-pollination d. cross-pollination e. gymnosperm PART 3 – MULTIPLE CHOICE (1 MARK EACH x 40) 41. Which organelle is called the "powerhouse of the cell"? A) ribosome C) nucleolus B) D) endoplasmic reticulum mitochondrion 42. Where are chlorophyll molecules stored in plant cells? A) chloroplasts C) lysosomes B) D) mitochondria vacuoles 43. Which of the following is not a component of the cell theory? A) Living organisms do not depend on their individual cells for support. B) All living organisms are made of at least one cell. C) The cell is the basic functional unit of all organisms. D) All cells come from previously existing cells. 44. In which phase do spindle fibers form? A) prophase C) anaphase 45. In which phase do chromosomes line up at the equator? A) prophase C) anaphase 46. Which process produces gametes? A) mitosis C) fertilization B) D) metaphase telophase B) D) metaphase telophase B) D) meiosis variation 47. How many chromosomes are there in the nucleus of a human sperm cell? A) 3 B) 22 C) 46 D) 23 48. What do the ovaries in a flower contain? A) eggs C) pollen B) D) sperm stamens 49. What form of reproduction is best in a changing environment? A) sexual reproduction B) C) fission D) asexual reproduction all of the above 50. Where are the pollen grains during pollination? A) stigma C) pistil B) D) sepals ovary 51. Where are the seeds formed? A) stigma C) pistil B) D) pollen tube ovary 52. How do mosses reproduce? A) budding C) spores B) D) fragmentation seeds 53. What part of the moss produces spores? A) sporophyte C) seedophyte B) D) gametophyte mossophyte 54. Identify the spores that are produced by meiosis. A) diploid C) triploid B) D) haploid polyploid 55. Spores ... A) C) are light and can be carried great distances. B) can stay dormant if necessary. D) can survive harsh conditions. are all of the above. 56. Which of the following have been produced using biotechnology? A) cheese B) yogurt C) dogs D) all of the above 57. What is DNA composed of? A) phosphates C) sugars B) D) nitrogenous bases all of the above 58. What is the term for cross-pollinating two different but closely related plant species? A) inbreeding B) monoculture C) hybridization D) none of the above 59. Which of the following statements is true about the practice of monoculture? A) Monoculture increases the resistance of a crop to widespread disaster. B) Monoculture involves the production of large quantities of a single variety of a plant crop. C) There is a rich diversity of crops in monoculture. D) Crops cannot be destroyed by a single pest or disease. 60. An advantage of genetic engineering over selective breeding is that ... A) genetic engineering is a much longer process. B) a gene that is absent in a person may be supplied through genetic engineering. C) organisms can obtain genes from other species. D) both (B) and (C) 61. The first cell produced when an egg and sperm unite is called a(n): A) Embryo B) Zygote C) Fetus D) Gamete 62. Sexual reproduction in humans includes: A) Binary fission C) Spore formation B) D) Mitosis Meiosis 63. Eggs and sperm are formed in the: A) Urinary bladder and prostate C) Testes and ovaries B) D) Vas deferens and oviduct Scrotum and uterus 64. An example of a gonad is: A) Sperm C) Vas deferens B) D) Meristem Ovary 65. An example of a gamete is: A) Sperm C) Vas deferens B) D) Meristem Ovary B) D) Prophase Anaphase 66. DNA replicates for cell division in: A) Interphase C) Metaphase E) Telophase 67. Which of the following is the first stage containing the diploid number of chromosomes? A) Sperm B) Egg C) Zygote D) Embryo 68. The structure where the female’s egg is housed until it is ready to be released from the ovary is called: A) Oviduct B) Uterus C) Follicle D) Meristem 69. Which hormone does the pituitary gland first release into the bloodstream of a woman at the start of her 28 day cycle? A) Estrogen B) FSH C) Progesterone D) LH 70. Which hormone directs the development of secondary sex characteristics in males? A) FSH B) Corpus luteum C) Progesterone D) Testosterone 71. Where are the sperm cells produced inside the testes? A) Scrotum C) Seminal Vesicles B) Vas deferens D) Seminiferous tubules 72. What is the tube-like structure that carries sperm through the penis and outside of the body? A) Urethra B) Vas deferens C) Seminiferous tubules D) Epididymis 73. Where are sperm cells stored? A) Urethra C) Seminiferous tubules B) Vas deferens D) Epididymis 74. What is the structure within an ovary that contains its egg cells? A) Ovum B) Oviduct C) Follicle D) Cervix 75. What is located at the bottom of the uterus and is connected to the vagina? A) Ovum B) Oviduct C) Follicle D) Cervix 76. Where is the location of fertilization? A) Ovum C) Follicle B) Oviduct D) Cervix 77. Which hormone causes the uterus to contract and open the birth canal? A) FSH B) Progesterone C) Estrogen D) Oxytocin 78. When new DNA arrangements are formed it is called: A) genetic engineering C) recombinant DNA B) transgenic D) gene splicing 79. Breeding individuals with certain desired traits to produce offspring with similar traits. A) biotechnology B) selective breeding C) reproductive technology D) deoxyribonucleic acid 80. A type of organism with DNA from another organism. A) genetic engineering C) recombinant DNA B) transgenic D) gene splicing PART 4 – FILL IN THE BLANKS (1 MARK EACH x 20) WORD BANK (EACH WORD WILL ONLY BE USED ONCE) Golgi Meiosis Fruit Mitosis Two Guanine Fingerprinting Biotechnology Inbreeding Mutation Angiosperms Selective Protein Fission DNA Spores Metamorphosis Wall Variations Amino 81. Unlike animal cells, plants cells have a rigid cell _______________________ that lies outside the cell membrane. 82. _______________________ bodies package useful materials and secrete them outside of the cell. 83. The four phases of _______________________ in plant and animal cells are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. 84. During interphase, a cell will grow, replicate its ______________________, and prepare for the first phase of mitosis. 85. Binary _______________________ is a form of asexual reproduction in bacteria. 86. _______________________ can develop into a new plant without being fertilized. 87. Differences in characteristics among individuals are called _______________________. 88. _______________________ produces gametes, each of which contains half the required number of chromosomes. 89. During meiosis, a cell will divide _______________________ times before the gametes are formed. 90. Complete _______________________ is a process house flies and butterflies go through before reaching the adult form. 91. The seeds of _______________________ form inside flowers. 92. In some angiosperms, the ovary becomes the _______________________ around the seed. 93. _______________________ breeding involves breeding individuals with particular desired traits. 94. Yogurt and cheese are products of _______________________. 95. The shapes of cytosine and _______________________ fit together. 96. A gene is a segment of DNA that is coded to produce a _______________________. 97. Each protein is made up of smaller units called _______________________ acids. 98. _______________________ involves mating two closely related individuals. 99. DNA _______________________can be used to identify relationships between individuals. 100. A mistake that happens during DNA replication or meiosis is called a _______________________. PART 5 - LABEL THE FOLLOWING DIAGRAMS (1 MARK EACH x 25) A – ________________________ B – ________________________ C – ________________________ D – ________________________ E – ________________________ F – ________________________ G – ________________________ H – ________________________ I – ________________________ J – ________________________ K – ________________________ L – ________________________ M – ________________________ N – ________________________ O – ________________________ P – ________________________ Q – ________________________ R – ________________________ S – ________________________ T – ________________________ U – ________________________ V – ________________________ W – ________________________ X – ________________________ Y – ________________________