Math 8 Outline 2012
advertisement
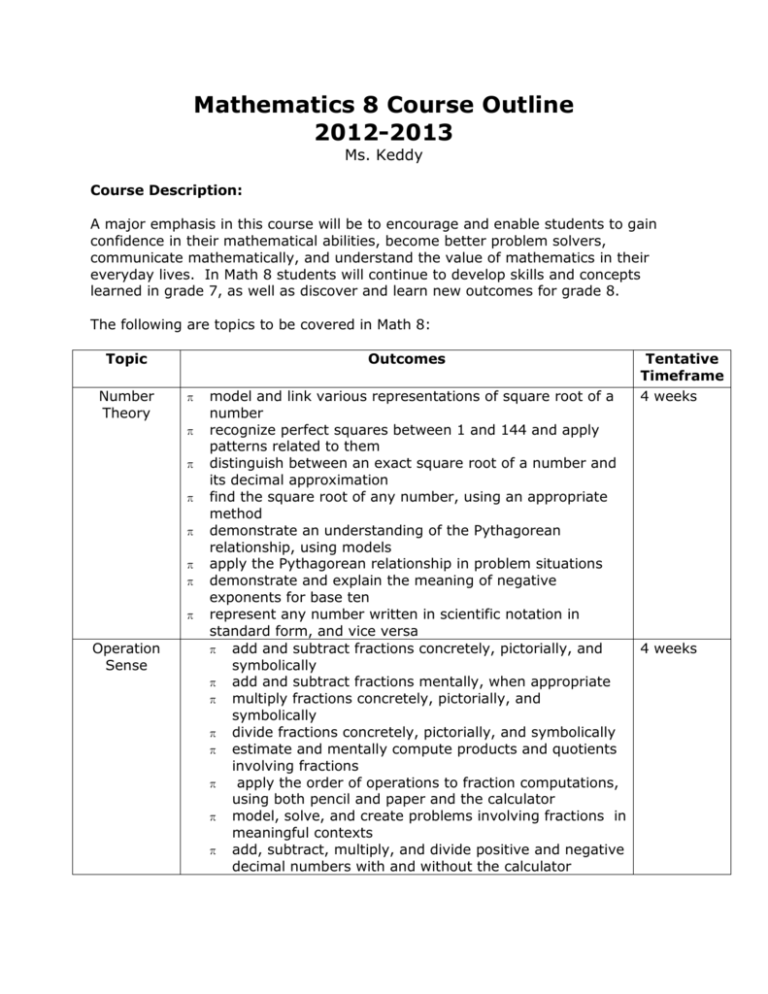
Mathematics 8 Course Outline 2012-2013 Ms. Keddy Course Description: A major emphasis in this course will be to encourage and enable students to gain confidence in their mathematical abilities, become better problem solvers, communicate mathematically, and understand the value of mathematics in their everyday lives. In Math 8 students will continue to develop skills and concepts learned in grade 7, as well as discover and learn new outcomes for grade 8. The following are topics to be covered in Math 8: Topic Number Theory Outcomes π π π π π π π π Operation Sense model and link various representations of square root of a number recognize perfect squares between 1 and 144 and apply patterns related to them distinguish between an exact square root of a number and its decimal approximation find the square root of any number, using an appropriate method demonstrate an understanding of the Pythagorean relationship, using models apply the Pythagorean relationship in problem situations demonstrate and explain the meaning of negative exponents for base ten represent any number written in scientific notation in standard form, and vice versa π add and subtract fractions concretely, pictorially, and symbolically π add and subtract fractions mentally, when appropriate π multiply fractions concretely, pictorially, and symbolically π divide fractions concretely, pictorially, and symbolically π estimate and mentally compute products and quotients involving fractions π apply the order of operations to fraction computations, using both pencil and paper and the calculator π model, solve, and create problems involving fractions in meaningful contexts π add, subtract, multiply, and divide positive and negative decimal numbers with and without the calculator Tentative Timeframe 4 weeks 4 weeks Numerical Operations π π π π π Measurement Ratios, Rates, and Proportions 2-D Geometry Data Management represent and apply fractional percents, and percents greater than 100, in fraction or decimal form, and vice versa demonstrate an understanding of the properties of operations with integers and positive and negative rational numbers (in decimal and fractional forms) create and solve problems which involve finding a, b, or c in the relationship a% of b = c, using estimation and calculation apply percentage increase and decrease in problem situations compare and order integers and positive and negative rational numbers (in decimal and fractional forms) π estimate areas of circles π develop and use the formula for the area of a circle π describe patterns and generalize the relationships between areas and perimeters of quadrilaterals, and areas and circumferences of circles π calculate the areas of composite figures π solve proportion problems that involve equivalent ratios and rates π solve problems involving proportions, using a variety of methods π construct and analyse tables and graphs to describe how change in one quantity affects a related quantity π solve problems involving the intersection of two lines on a graph π solve indirect measurement problems, using proportions π make and apply informal deductions about the minimum and sufficient conditions to guarantee the uniqueness of a triangle and the congruency of two triangles π make and apply generalizations about the properties of rotations and dilatations, and use dilatations in perspective drawings of various 2-D shapes π make and apply generalizations about the properties of similar 2-D shapes π perform various 2-D constructions and apply the properties of transformations to these constructions π make and apply generalizations about the properties of regular polygons π demonstrate an understanding of the variability of repeated samples of the same population π develop and apply the concept of randomness π construct and interpret circle graphs π construct and interpret scatter plots and determine a line of best fit by inspection π construct and interpret box-and-whisker plots π extrapolate and interpolate information from graphs 3 weeks 3 weeks 4 weeks 3 weeks 4 weeks π π π 3-D Geometry π π Measurement π π Patterns and Relations π π π π π π Probability π π π π π π determine the effect of variations in data on the mean, median, and mode develop and conduct statistics projects to solve problems evaluate data interpretations that are based on graphs and tables draw isometric and orthographic views of 3-D shapes and construct 3-D models from these views Recognize, name, describe and make and apply generalizations about the properties of prisms, pyramids, cylinders, and cones estimate and calculate volumes and surface areas of right prisms and cylinders measure and calculate volumes and surface areas of composite 3-D shapes represent patterns and relationships in a variety of formats and use these representations to predict unknown values Analyse polygons to determine their properties and interrelationships interpret graphs that represent linear and non-linear data construct and analyse tables and graphs to describe how change in one quantity affects a related quantity link visual characteristics of slope with its numerical value by comparing vertical change with horizontal change solve problems involving the intersection of two lines on a graph solve and verify simple linear equations algebraically create and solve problems, using linear equations conduct experiments and simulations to find probabilities of single and complementary events determine theoretical probabilities of single and complementary events compare experimental and theoretical probabilities demonstrate an understanding of how data is used to establish broad probability patterns 2 weeks 3 weeks 3 weeks 2 weeks Required Materials: Students are expected to come to each class prepared with: π π π π π π binder looseleaf pencils and erasers math set scientific calculator graph paper Assessment: All of the work completed will be to demonstrate student understanding and achievement of the Grade 8 math outcomes. Assessment of learning is ongoing and could take a variety of forms, some of which include tests, quizzes, mental math, exit cards, portfolio, assignments, projects, observation, discussion, math dictionary, etc. Letter grades will be used to describe the level of achievement students have demonstrated during each school term: A—the student demonstrates achievement of the expected learning outcomes B—the student demonstrates achievement of most of the expected learning outcomes C—the student demonstrates achievement of some of the expected learning outcomes D—the student demonstrates achievement of few of the expected learning outcomes General Information An organized binder is one of the keys to success in this course. Your math binder should only have one subject – MATHEMATICS. It should be divided into the following sections: 1. Math Starters: solving activity. Each class will start with a mental math and/or problem 2. Math Dictionary: New vocabulary introduced in each unit should be kept here. 3. Notes and Sample Problems: Important notes and examples of key questions should be written in this section. 4. Class Work: This contains completed questions and homework exercises. All work should have the date and page numbers from the textbook listed. 5. Assignments/Projects: All marked assignments and projects go in this section. 6. Tests and Quizzes: Tests and quizzes will be reviewed in class. Students are required to make corrections to their work using a different coloured pen or pencil. Tests and quizzes must be signed by a parent/guardian. General Information: π All math work must be completed in PENCIL. Work done in pen will NOT be accepted. π Practice questions will be assigned on a regular basis. While these questions will not always be collected and marked, the completion of these questions is essential to the development of concepts taught in this course and must be completed. Additional questions will often be provided for students who need/wish to have more practice to solidify concepts and ensure understanding. π If you miss a class it is very important that you find out what was covered that day. Please see me beforehand if you know you will be absent the day of a quiz or test. Assignments are due on the assigned day at the beginning of class. π Homework, announcements, a class calendar, and course documents can all be accessed via a classroom website. This will be updated on a daily basis. Please feel free to access this site to remain up-to-date with class activities. To get to the site, go to the ICS website http://sharepoint.tcrsb.ca/ics/default.aspx and click on Classroom Links. Nova Scotia Grade 8 Mathematics Assessment π In 2011-2012 the Nova Scotia Department of Education implemented a Grade 8 Mathematics Assessment. This assessment covers math outcomes from elementary through to grade 8. The assessment consists of both multiple choice and constructed response questions and will be written in early June of 2013. Further information will be sent home later in the school year. Extra Help! π Extra help sessions are available at the following times: Morning: 8:15 – 8:45 on Day 1 and Day 2 in the MPR Afternoon: 3:15 – 3:45 on Day 1 in the MPR Lunch: 12:15 – 12:40 on Day 2 in the classroom Please feel free to contact me with questions or concerns at any time. School: 839-6300 Email: juliekeddy@staff.ednet.ns.ca Student Signature: ___________________________ Parent/Guardian Signature: ____________________________