math intro - SD43 Teacher Sites
advertisement
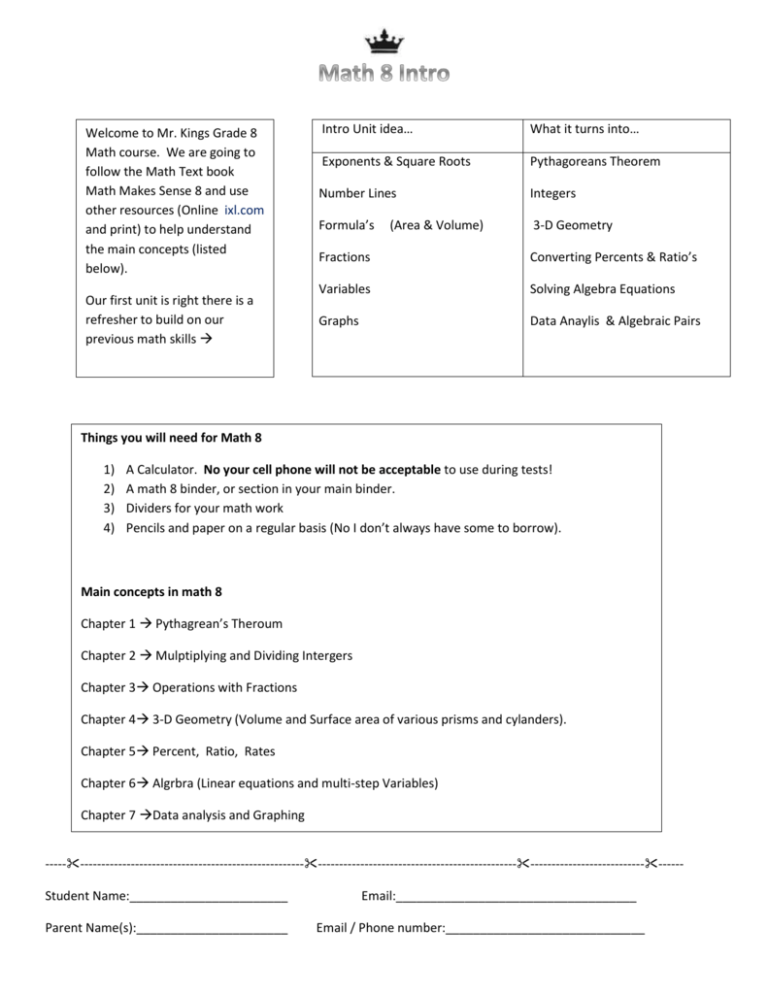
Welcome to Mr. Kings Grade 8 Math course. We are going to follow the Math Text book Math Makes Sense 8 and use other resources (Online ixl.com and print) to help understand the main concepts (listed below). Our first unit is right there is a refresher to build on our previous math skills Intro Unit idea… What it turns into… Exponents & Square Roots Pythagoreans Theorem Number Lines Integers Formula’s 3-D Geometry (Area & Volume) Fractions Converting Percents & Ratio’s Variables Solving Algebra Equations Graphs Data Anaylis & Algebraic Pairs Things you will need for Math 8 1) 2) 3) 4) A Calculator. No your cell phone will not be acceptable to use during tests! A math 8 binder, or section in your main binder. Dividers for your math work Pencils and paper on a regular basis (No I don’t always have some to borrow). Main concepts in math 8 Chapter 1 Pythagrean’s Theroum Chapter 2 Mulptiplying and Dividing Intergers Chapter 3 Operations with Fractions Chapter 4 3-D Geometry (Volume and Surface area of various prisms and cylanders). Chapter 5 Percent, Ratio, Rates Chapter 6 Algrbra (Linear equations and multi-step Variables) Chapter 7 Data analysis and Graphing -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Student Name:_______________________ Parent Name(s):______________________ Email:___________________________________ Email / Phone number:_____________________________ Solve for…. 5² Exponents Exponents are the little numbers ______________ a main number. The number Answer 9² 3 ² means 3 multiplied by _______. An Exponent to the second power) always makes the shape of a ________. A square has equal __________ & __________. 2² 8² The Square root of a number is the Answer to a squared number. 12² The Square root of 25 (√25) is 5. Its like saying WHAT times WHAT is 25. Or, if a square has the area of 25 cm² what is length of each side? Solve…. √100 = √49= √16= √36= √121= Number lines are a picture representation of positive and negative numbers. 2 + 3 means you start at 2 and jump up 3 spaces to 5, as illustrated in the below figure. As another example, 6 – 4 means start at 6 and jump down 4 spaces to 2. That is, 6 – 4 = 2, as shown in the following figure. Draw one number line example using negative number below! Formula’s Area is the amount of stuff in the middle Area of a Quadrilateral is A = Length X Width Area of a Square is A = Length ² Area of a triangle is A = Length X Width / 2 Area of a Circle is 𝐴 = 𝜋𝑟 2 Perimeter is the distance around the outside of the shape. To find the perimeter you add up all the outside edges of a shape. A square and rectangle have four edges, while a triangle has three! ASSIGNMENT Divide a piece of paper in four. (You can use the back of second page of this handout) Draw four different shapes and label them (side Length and width, name of shape) Demonstrate the four shapes AREA and Perimeter. FRACTIONS When adding fractions you need to find a common ____________ which is the number on the ___________. Then you can add the _____________, which is the number on the _________. A Percent is a fraction out of _________. Remember to always reduce your fraction to the lowest. A correct answer will always be in its “Simplest” form. Example… 4/6 is the same as 2/3 A “Greatest Common Factor” is a number that can be divided into both numbers Example… The G.C.F. of 5, and 10, is 5. 5 can be divided into 5 once, and 10 twice! Variables A Variable is an unknown. In math we are always searching for the unknown. We want to know as much as we can. But in life sometimes there are what ifs… A Variable lets us say “what if we added it by THIS or THAT”. You may have seen it written as a blank or a box… 2 + __ = 10 the answer to the blank is _____ 3+□=7 the answer to the □ is We will start using letters as the symbol(s) for variables. X is the usual one, but I avoid using X because it is confused with a multiplication symbol. Other multiplication symbols include a dot (3∙4 = 12) or even the number touching the other number [6(6)=36]. I will use y, a, and b most often… but my variables will vary! Algebra is based on finding the variable. Solve for a. 1) 3 + a = 9 A= 2) 6 – a = 2 A= 3) 3a = 15 A= 4) a + 5 – 2 = 13 A= Graphing We use our graphing skills heavily in the last two chapters. We will plot answers from algebra questions and demonstrate data that we have analyzed. Graphs have some major components we need to know… Parts of a graph include knowing which axis (line of the graph) is which. All Graphs should be titled and labeled. TITLE: The X axis is vertical and always comes first. The Y axis comes second and is horizontal . Plot these coordinates A 1, 1 B 2, -2 C -3, -3 And then connect the plotted points. D -4, 4