AP Chemistry Practice Midyear Exam
advertisement

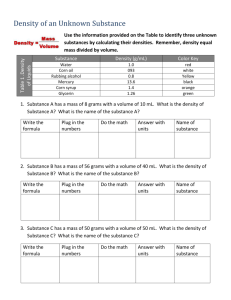
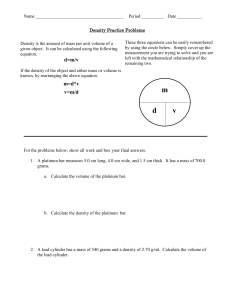
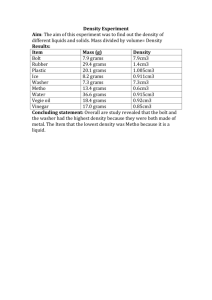
AP Chemistry Practice Midyear Exam 07-08 1. How much heat is gained when 400 g of copper is warmed from 22.6º C to 81.0 º C? The specific heat of copper is 0.385° C. a) 3000 J b) 5000 J c) 7000 J d) 9000 J e) 11, 000 J 2. Which of these types of radiation has the most energy? a) Radio waves b) Infrared c) Microwaves d) Ultraviolet e) Visible 3. The angular momentum number, l, is best associated with the a) energy of the orbit b) energy of the orbital c) number of orbitals in a sub-energy level d) orientation in space of an orbital e) shape of an orbital 4. The maximum number of electrons that can occupy the third energy level is a) two b) four c) eight d) ten e) eighteen 5. What is the electron configuration of Fe +3? a) [Ar] 4s2 3d 6 b) [Ar] 4s1 3d 7 c) [Ar] 3d 5 d) [Ar] 4s2 3d8 e) [Ar] 4s1 3d 8 6. Chemical reactions between nonmetals and nonmetals primarily involve a) interactions between protons b) interactions between protons and electrons c) interactions between protons, electrons, and neutrons d) transfer of electrons e) sharing of electrons 7. All of the following substances are isoelectronic except a) Ca+2 b) Mg+2 c) Cld) Ar e) S-2 8. Analysis of a carbohydrate showed that it contained 6.70 % hydrogen and 40.0 % carbon by mass. What is its simplest formula? a) CHO b) CH2O c) CH3O d) C2H3O e) C2H5 O 9. Which of the following substances would have an odd number of valence electrons? a) O3 b) SO2 c) NO2 d) OCNe) SO4-2 10. Choose the name-formula pair that does not match a) ammonium carbonate, (NH4)2CO3 b) sodium chlorate, NaClO4 c) calcium oxalate, CaC2O4 d) perchloric acid, HClO4 e) potassium hydroxide, KOH 11. Which statements describe the bonding in a methane molecule? 1. polar covalent 2. π bond 3. sp3 hybridization a) 1 only b) 2 only c) 3 only d) 1 and 2 only e) 1 and 3 only 12. Which of the following diatomic molecules has the greatest bond strength? a) Cl2 b) HCl c) CO d) H2 e) HF 13. Which of the following has the highest electronegativity value? a) K b) Ba c) Si d) Br e) As 14. What is the mass in grams of 0.7500 moles of glucose, C6H12O6? a) 120.0 grams b) 125.0 grams c) 130.0 grams d) 135.0 grams e) 140.0 grams 15. Which of the following statements is (are) true? 1. The reaction vessel becomes warmer when an endothermic reaction occurs. 2. An exothermic reaction has a negative value of ∆ H. 3. Heat is produced when an exothermic reaction occurs. a) 1 only b) 2 only c) 3 only d) 2 and 3 only e) 1, 2, and 3 16. The molecular shape of boron trichloride is: a) trigonal pyramidal b) octahedral c) tetrahedral d) trigonal planar e) linear 17. Which of the following compounds is expected to have the highest boiling point? a) CH3OCH3 b) CH3CH2OH c) CH3CH2CH2CH3 d) CH3CH2CH3 e) CH3Cl 18. The Lewis structure for phosphine, PH3 has a) four bonding pairs b) two bonding pairs and two lone pairs c) three bonding pairs and one lone pair d) one bonding pair and three lone pairs e) four lone pairs 19. The boiling points of the hydrogen halides are the following HF 19º C HCl - 85º C HBr - 67º C HI - 35º C Which of the following accounts for the high boiling point of HF? 1. HF has the strongest H-X bond. 2. HF molecules form hydrogen bonds. 3. HF molecules have the strongest van der Waals forces a) 1 only b) 2 only c) 3 only d) 1 and 2 only e) 2 and 3 only 20. The principle quantum number of the valence electrons in an atom of lead is a) 2 b) 3 c) 4 d) 5 e) 6 21. How many moles of gas are in a gas sample occupying 0.250 L at 0.50 atm and 300 K? a) 0.00508 b) 0.00289 c) 0.0345 d) 0.416 e) 1.27 22. Which of the following consists primarily of dipole-dipole intermolecular forces? a) asbestos b) H2S c) CH3CH3 d) NaCl e) iron 23. For which of the following equations is the enthalpy change at 25º C and 1 atm is equal to ∆ H f HCOOH (l)? a) CO2 (g) + 2 H2 (g) HCOOH (l) b) CO (g) + H2O (l) HCOOH (l) c) C (s) + 2 H (g) + 2 O (g) HCOOH (l) d) C (s) + H2 (g) + O2 (g) HCOOH (l) The following are choices for questions 24 through 27. a) Rutherford b) de Broglie c) Planck d) Einstein e) Bohr 24. Who formulated a theory that particles of matter show characteristics of waves? 25. Who discovered the nucleus of an atom? 26. Which scientist first postulated that electrons going from high energy levels to lower energy levels caused the sharp lines in the emission spectra of elements? 27. Which scientist explained the photoelectric effect by postulating that light has both wave properties and particle properties? 28. Which of the following indicates the existence of strong intermolecular forces of attraction in a liquid? a) a very low boiling point b) a very low vapor pressure c) a very low critical temperature d) a very low viscosity e) a very low heat of vaporization 29. Which of the following compounds (each as a liquid) would be the best solvent for carbon disulfide? a) CH3OH (l) b) NH3 (l) c) HOH (l) d) C8H18 (l) e) H2S (l) 30. All of the following are covalent network solids except a) quartz b) silicon carbide c) iron d) diamond e) graphite 31. Which of the following molecules primarily exhibits London intermolecular forces? a) CH4 b) CH3OH c) PH3 d) HBr e) CaH2 32. What is the change in enthalpy for the reaction of 2.00 moles of iron (II) oxide? 6 FeO (s) + O2 (g) 2 Fe3O4 (s) + 635 kJ a) - 635 kJ b) - 212 kJ c) -106 kJ d) 106 kJ e) 635 kJ 33. At standard conditions, 2.75 liters of gas weighed 5.39 grams. The gas is a) N2 b) N2O c) NO d) F2 e) NF3 34. Which of the series of elements listed below would have nearly the same atomic radius? a) Sc, Ti, V, Cr b) Na, K, Rb, Cs c) B, Si, As, Te d) F, Cl, Br, I e) Na, Mg, Al, Si The following choices are for questions 35 through 37. a) I (g) + e- I- (g) b) I2 (g) 2 I (g) c) I (g) I + (g) + e d) Na (g) + I (g) NaI (s) e) Na (s) + ½ I2 (s) NaI (s) 35. Which process represents the heat of formation? 36. Which process represents electron affinity? 37. Which process represents ionization energy? 38. All of the following compounds are soluble in water except: a) NaC2H3O2 b) ZnCl2 c) BaSO4 d) (NH4)2CO3 e) KNO3 39. The three isotopes of carbon differ with respect to the number of a) protons b) atomic number c) electron configuration d) neutrons e) nuclear charge 40. All of the following are postulates of the Kinetic Theory of an Ideal Gas except: a) The force of repulsion between gas particles is very weak or negligible. b) Most of the volume of a gas is empty space. c) When gas particles collide, they gain kinetic energy. d) The average kinetic energy of a gas is proportional to the absolute temperature. e) The gas particles move in a straight line. B) Reaction Predictions 41. For each of the following six reactions, in part (i) write a balanced equation and in part (ii) answer the question about the reaction. In part (i), coefficients should be in terms of lowest whole numbers. Assume that solutions are aqueous unless otherwise indicated. Represent substances in solutions as ions if the substances are extensively ionized. Omit formulas of any substances that remain unchanged by the reaction. (Write net ionic equations.) a) Solid glucose is heated strongly in air. (i) (ii) If one mole of solid glucose is heated strongly in air, then what is the sum of the coefficients of the products? b) A strip of aluminum is placed in a solution of copper (II) chloride. (i) (ii) As the reaction proceeds, describe the change in color of the copper (II) chloride solution. c). Solid calcium carbonate is added to a solution of hydrochloric acid. (i) (ii) Describe how ancient marble statutes have been affected by acid rain. d) Lithium metal is heated strongly in nitrogen gas. (i) (ii) Which substance is being reduced? e) Equal volumes of 0.1 M solutions of lead (II) nitrate and magnesium iodide are reacted. (i) (ii) List the names of the spectator ions. f) Solid potassium chlorate is strongly heated. (i) (ii) What is the change in oxidation number of chlorine? C) Problems 2002 42. Consider the hydrocarbon pentane, C5H12 (molar mass = 72.15 grams) a) Write the balanced equation for the combustion of pentane to yield carbon dioxide and water. b) What volume of dry carbon dioxide, measured at 25C and 785 mm Hg, will result from the completion combustion of 2.50 grams of pentane? c) The complete combustion of 5.00 grams of pentane releases 243 kJ of heat. Based on this information, calculate the value of H for the complete combustion of one mole of pentane. d) Under identical conditions, a sample of an unknown gas effuses into a vacuum at twice the rate that a sample of pentane effuses. Calculate the molar mass of the unknown gas. e) Pentane has three isomers. Draw the structural formula for two isomers of pentane. 1996 43. Five identical balloons containing CO2, O2, He, N2, and CH4 are filled to the same volume at 25C and 1.0 atmosphere pressure. a) Which balloon contains the greatest mass of gas? Explain. b) Compare the average kinetic energies of the gas molecules in the balloons. Explain. c) Which balloon contains the gas that would be expected to deviate most from the behavior of an ideal gas? Explain. d) Twelve hours after being filled, all the balloons have decreased in size. Predict which balloon would be the smallest. Explain. 2001 44. Account for each of the following observations about the pairs of substances. In your answers, use appropriate principles of chemical bonding and/or intermolecular forces. In each part, your answers must include references to both substances. a) Even though NH3 and CH4 have similar molecular masses, NH3 has a much higher normal boiling point (- 33C) than CH4 (- 164C). b) At 25 C and 1.0 atm, ethane (C2H6) is a gas and hexane (C6H14) is a liquid. c) SiO2 melts at a much higher temperature (1,410 C) than Cl2 (-101 C.) d) MgO melts at a much higher temperature (2,852 C) than NaF (993 C) 45. How much heat is produced when 34.0 grams of ammonia reacts with excess oxygen gas? The equation is 4 NH3 (g) + 5 O2 (g) 4 NO (g) + 6 HOH (g) where the heats of formation are the following: NH3 (g) = - 45.9 kJ/mole NO (g) = 90.3 kJ/mole HOH (g) = - 241.8 kJ/mole 46. Calculate the energy, wavelength, and frequency for a 63 electron drop in the hydrogen atom. 47. For each of the following below, do the following: a) Sketch the Lewis structure, including all resonance structures if applicable. b) Write the name of the molecular geometry and indicate the bond angle c) Indicate whether the molecule is polar or nonpolar. d) State the hybridization. CO3 -2 SeCl4 48. Given the Alkali family of elements: lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, and cesium. a) Rearrange these elements in order of increasing atomic radius. b) Rearrange the above elements in order of decreasing ionization energy. c) Rearrange the above elements in order of increasing chemical reactivity. 49. Write the electron configuration, orbital notation, dot symbol, and quantum numbers for the nineteenth electron and twentieth-fourth electron found in the chromium atom. 50. A sample of oxalic acid, found in many plants and vegetables, contains the elements carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. If 513.0 milligrams of oxalic acid is burned in oxygen, 510.0 milligrams of carbon dioxide gas, and 103.0 milligrams of water vapor result. Determine the following: a) the mass percent of each element b) the empirical formula c) the molecular formula if the molar mass is 90.04 grams/mole D) Laboratory Experiments 51. Write a sentence or two, explaining how chemical and physical methods could be used to differentiate between each pair of compounds/solutions: a) sodium carbonate (s) vs. lithium chloride (s) b) potassium iodide (s) vs. sodium acetate (s) c) silver nitrate (aq) vs. potassium chloride (aq) d) ammonium chloride (s) vs. calcium sulfate (s) 52. Spectroscopy Experiment a) In a sentence or two, state the Beer-Lambert Law. b) What is the mathematical relationship between absorbance and Percent Transmittance? c) Sketch a rough graph of absorbance vs. concentration. What type of relationship exists between these two quantities? d) Why can the Beer-Lambert method be used to determine the concentration of Cr(NO3)3 but is not appropriate to determine the concentration of a NaCl solution? 53. The Masses of Equal Volumes of Gases Experiment Given the following data: Gas Name Apparent Mass Actual mass Volume of gas Moles of Gas Air - 0.020 g 0.035 L CO2 0.032 g 0.035 L If the density of the air is 1.19 g/L, then fill in the table above. Please try to Remember that this a Sample Midyear Test! The real test can vary somewhat in content, but not in format: Multiple Choice, Reaction Predictions, Problems (math oriented and short-answer), and Laboratory Experiments.