Comprehensive Assessment of Spoken Language
advertisement

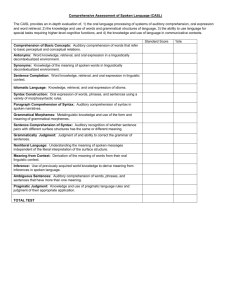
COMPREHENSIVE ASSESSMENT OF SPOKEN LANGUAGE This test measures oral language knowledge and the language skills needed for academic success. The following subtests were administered: antonyms, synonyms, sentence completion, syntax construction, paragraph comprehension, grammatical morphemes, grammatical judgment, non-literal language, inference and pragmatic judgment. Abcd achieved a Total Test standard score of 100 and a percentile rank of 50. This is in the average range of ability. Composite standard scores and percentile ranks are listed below. Composite Scores Lexical/Semantic Syntactic Supra-linguistic Receptive Expressive Total Test Standard Score Percentile Rank The standard scores and percentiles for the individual subtest are listed below. Scoring Summary Standard Score Percentile Rank Antonyms Synonyms Sentence Completion Syntax Construction Paragraph Comprehension Grammatical Morphemes Grammatical Judgment Non-literal Language Inference Pragmatic Judgment A description of each subtest follows: Antonyms: This subtest measures the ability to identify words that have opposite meanings and the ability to retrieve, generate, and produce a single word when its opposite is given as a stimulus. Synonyms: This area measures the ability to identify words that have similar meanings when given four single word response options. Sentence Completion: This measures the ability to retrieve and express appropriate words that fit the meaning of a spoken sentence. To be successful at this task the student must comprehend the vocabulary and sentence structure of the stimulus sentence and have adequate real world experiences/knowledge to generate an acceptable completion of the sentence using a single word. Syntax Construction: This area measures the ability to use sentence formulation rules in order to generate sentences that are consistent with Standard English language. Paragraph Comprehension: This measures the comprehension of syntax (sentence structure) through a series of spoken narratives. Each narrative begins with a sentence that has a designated level of syntactic difficulty. Each subsequent sentence in the narrative adds to the syntactic complexity of the previous sentence. For example the beginning sentence in the first narrative is a simple declarative sentence and the last paragraph has complex clauses, passive voice, etc. Grammatical Morphemes: This measures the ability to… Grammatical Judgment: This measures the ability to… Non-literal language: The ability to understand the intended meaning of a spoken phrase/sentence as apposed to the literal meaning. An example of a test item includes, “At 8:00 p.m. Dad said to his young daughter, ‘I think your doll is yawning.’ What did Dad really mean?” A correct response would refer to the Dad wanting his daughter to go to bed. Success on this sub-test indicates that Abcd has the ability to jump from the here and now events and concrete interpretations to a more inferential level, as well as the ability to suspend (remember) meaning until a relationship is found between the events and what the speaker is attempting to communicate. Inference: : This measures the ability to… Pragmatic Judgment: This measures the ability to judge the appropriateness of language used in specific life/social situations and use the appropriate language in those situations. For example, introducing friends to one another, answering the telephone, consoling a friend.