Vocabulary—Cell Structure and Heredity
advertisement

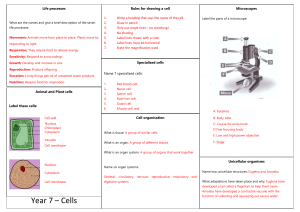
Vocabulary—Cell Structure and Heredity 1. Parts of a microscope – I am responsible for labeling the following parts of a microscope: eyepiece, tube, arm, nosepiece, low power lense, medium power lense, high power lense, stage, stage clamps, coarse adjustment knob, fine adjustment knob, diaphragm, light source, and base. 2. Microscope – an instrument that aids a scientist in studying the details of a cell 3. Progression of a living thing from least to most complex – cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism. 4. Cell – the basic unit of life. All living things are made of cells. Some may be one cell; some may be a combination of millions or more. 5. Tissue – A group of similar cells working together to perform the same function. Examples would be the muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and epithelial tissue. 6. Organ – Groups of tissues working together to carry out certain activities. Examples would be your heart, brain, and liver. 7. Organ system – Different organs working together to carry out specific functions. Examples would be the circulatory, respiratory, and digestive systems. 8. Organism – All organ systems working together. These systems create a living thing that can carry out its basic life functions on its own. Some organisms can do all this though in just one cell such as an amoeba or bacteria. 9. Basic functions of a cell – respiration, excretion, digestive/nutrition, growth, response, movement, and reproduction. 10. Respiration – a process requiring oxygen that “unlocks” the energy in sugar. The sugar molecule is broken down when the cell takes in oxygen. This occurs after the food is digested in the cell. 11. Excretion – the removal of wastes by the cell in the form of carbon dioxide and water. 12. Nutrition/digestion – the intake and use of food by the cell. 13. Growth – to either increase in size or in the amount of material contained. 14. Response – reacting to changes in your surroundings. 15. Movement – a possible response of a cell to its surroundings. 16. Parts of cells that I am responsible for: cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, organelle, cell wall, and chloroplasts. 17. Cell membrane – the outer covering of the cell through which water and gases may pass. It acts like a tollbooth allowing movement in and out of the cell. 18. Organelle – the structures located in the cytoplasm of the cell. Examples would be the nucleus and chloroplasts. 19. Cytoplasm – the gel-like substance inside the cell that contains a large amount of water. It contains the organelles.