year-8-cells-task-2
advertisement

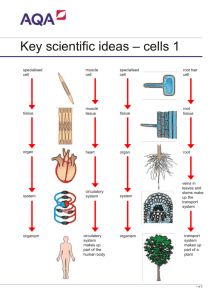
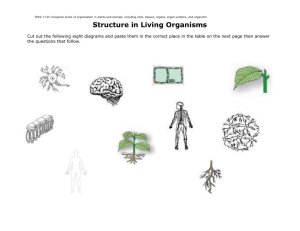
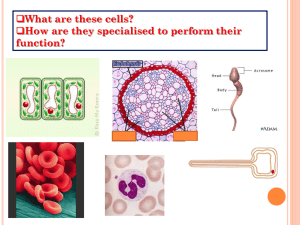
Year 8 Cells Assignment – Task 2 1) What type of specialised cell have you researched? 2) What does it look like? Describe its appearance (you can include a picture) 3) Does it contain any special organelles? (E.g. cells of a plant’s leaf contain chloroplasts for photosynthesis.) 4) What tissue and organ (if any) is formed by your chosen cell? (E.g. muscle cells form muscle tissue and certain muscle tissue forms the heart.) 5) What is the function of the tissue and organ that your cell is part of? How does it help the organism survive? 6) How does the structure of the cell help the tissue and organ achieve its role in the organism? (E.g. epithelial cells are large and flat to provide maximum coverage.) 7) Name one disease that affects your chosen tissue or organs, and hence the cells that make it up? 8) How does this disease affect the cells/tissues/organs? That is, does it kill the cells; does it damage part of the cell, etc.? 9) What treatments are available to help treat this disease? How do they work? 10) Are there any treatments that are undergoing trials or being researched? Year 8 Cells Assignment – Task 2 1) What type of specialised cell have you researched? 2) What does it look like? Describe its appearance (you can include a picture) 3) Does it contain any special organelles? (E.g. cells of a plant’s leaf contain chloroplasts for photosynthesis.) 4) What tissue and organ (if any) is formed by your chosen cell? (E.g. muscle cells form muscle tissue and certain muscle tissue forms the heart.) 5) What is the function of the tissue and organ that your cell is part of? How does it help the organism survive? 6) How does the structure of the cell help the tissue and organ achieve its role in the organism? (E.g. epithelial cells are large and flat to provide maximum coverage.) 7) Name one disease that affects your chosen tissue or organs, and hence the cells that make it up? 8) How does this disease affect the cells/tissues/organs? That is, does it kill the cells; does it damage part of the cell, etc.? 9) What treatments are available to help treat this disease? How do they work? 10) Are there any treatments that are undergoing trials or being researched?