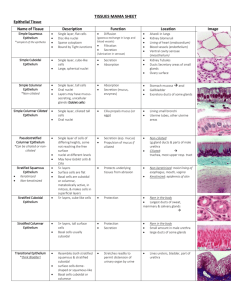
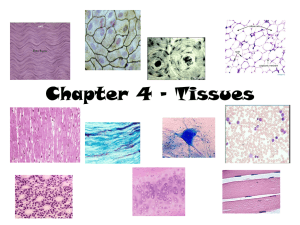
An Outline Of Histology
advertisement

An Outline of Histology Department of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology Peking Union Medical College 2009.5 Contents Epithelium .................................................................................................. 1 Connective Tissue (CT) ............................................................................. 4 Cartilage and Bone ..................................................................................... 8 Blood and Hemopoiesis ............................................................................11 Muscle Tissue ........................................................................................... 15 Nervous Tissue ......................................................................................... 18 The Circulatory System ........................................................................... 21 Immune System........................................................................................ 24 The Endocrine System ............................................................................. 28 Skin .......................................................................................................... 32 Oral Cavity and Salivary Glands ............................................................. 35 Digestive Tract ......................................................................................... 37 Digestive Glands ...................................................................................... 41 The Respiratory System ........................................................................... 45 The Urinary System ................................................................................. 48 The Male Reproductive System ............................................................... 53 The Female Reproductive System ........................................................... 57 The Eye and the Ear ................................................................................. 61 Epithelium 1. Components of epithelium 2. Characteristics of epithelium (1) Many cells with little intercellular substances (2) Shows polarity-nucleus position and shape, and special locations of organelles and inclusions (3) Rest on a basement membrane (4) Avascular 3. Classification: Covering epithelium Gland epithelium 4. Functions (1) Form a selective barrier (2) Protection (3) Absorption (4) Excretion (5) Digestion (6) Secretion (7) Sensation 5. Classification of covering epithelium A. Cell shape B. Number of layers Simple --- cells in a single layer Stratified --- cells in two or more layers (1) Simple squamous Very flattened cells presenting a minimal barrier to the passage of material, e.g. oxygen, through them. Cytoplasm is very hard to see with LM. The very similar endothelium and mesothelium, line blood and lymph vessels, and serous cavities, respectively. (2) Simple cuboidal Cell height and width are equal (3) Simple columnar Cell height exceeds width Cells have three surfaces and sealed at the top of their sides by encircling junctional complexes. Cells have three surfaces: free/luminal, lateral and basal; each may have membrane specializations, e.g. cilia at free, desmosomes at lateral, and infoldings at basal surfaces. (4) Pseudostratified columnar --- ciliated; non ciliated Nuclei lie at different levels suggesting stratified, but all cells are in contact with the basement membrane. 1 Two or more cell types are present: short basal, tall columnar (5) Stratified squamous Many cells, thick. Basal most cells are cuboidal or columnar and divide. Cells above the base become polyhedral and are held on this protective epithelium Underside of the epithelium is indented by vascular papillae of connective tissue, except in the cornea. (6) Keratinized stratified squamous Similar in its basal and middle layers to (5), but the uppermost epithelium has granular cells concerned with forming special, dead cells solidly packed together as a surface keratin layer for greater protection. (7) Stratified cuboidal (8) Stratified columnar Surface cells are cuboidal or columnar in shape, basal most cells are low columnar, and between them are polyhedral cells. (9) Transitional epithelium Several cells, thick, the surface cells vary from cuboidal in the relaxed condition to squamous in the distended condition. Basal layer are cuboidal or low columnar, intermediate layers are polyhedral. Cells of the superficial layer are often binucleate. 6. Cell adhesion in the epithelial cells’ membrane (1) Tight or occluding junction - outer parts of two cells’ membranes are fused together thereby occluding the intercellular cleft. (2) Adhering junctions - zonula adherens: macula adherens Filaments of the terminal web in each cells apical cytoplasm fasten to the complex. Desmosomes are disc-like structure scattered on cells’ surfaces; each is contributed to by membranes of two cells; cytoplasmic tonofilaments converge on and insert into thickened cell membranes. (3) Hemidesmosome - for better adhesion of the cell membrane to the basal lamina. (4) Gap junction - where two cells’ membranes come closely together with only a 2-nm gap, and the permeability to ions increases for electrical conductivity (electronic coupling). (5) Terminal bar (LM) = Junctional complex (EM). 7. Surface specialization in epithelium (1) Microvilli - on apical cell surface formed by tube-like evaginations of apical plasma membrane with a core of cytoplasm containing microfilaments of actin. (2) Stereocilia - as long slender processes of the apical surface that are nonmotile. (3) Cilia - as fine, hair-like processes of the free apical surface, which are 2 motile. 8. Basal specializations in epithelium (1) Basement membrane (2) Basal membrane infoldings --- formed by infoldings of the basal plasma membrane 9. Gland epithelium Unicellular gland --- goblet cell Multicellular gland 10. Types of glands exocrine gland endocrine gland 11. Classification of the exocrine glands (1) Shape of the secretory unit - tubular, acinar, tubuloalveolar (2) Duct system --- Simple --- nonbranching duct Compound --- duct branched (intercalated, intralobular, interlobular, and lobar duct). (3) Duct epithelium --- low cuboidal, columnar, pseudostratified columnar, and stratified. (4) Manner of secretion --- holocrine, apocrine, merocrine. 12. Endocrine gland (1) Cell arrangement - cords, clumps type, follicles. (2) Rich of capillaries. 3 Connective Tissue (CT) Introduction: 1. Origin: derived from mesenchyme 2. Components: cells + extracellular matrix (intercellular substances) 3. Characteristics: (1) relative few cells with more extracellular matrix (2) cells arranged loosely (3) cells without polarity (4) rich in blood vessels. 4. Classification: Loose CT Dense CT CT Proper Adipose CT Mature CT Regular Dense CT Irregular Dense CT Elastic Tissue White (Yellow) adipose CT Brown adipose CT Reticular CT Specialized CT Cartilage Bone Blood & lymph Hyaline Cartilage Elastic Cartilage Fibrocartilage mesenchyme Embryonic CT mucous CT 5. Functions: connecting, supporting, defense, nutrition, and repair. Loose Connective Tissue (areolar tissue) 1. Extracellular matrix (1) Ground substance: 1) Compositions: multiadhesive glycoproteins glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) proteoglycans a. Multiadhesive glycoproteins: fibronectin, laminin, chondronectin. b. Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) type of GAGs: hyaluronic acid, chondroitin sulfate, dermatan sulfate, keratan sulfate, heparan sulfate, etc. characteristics of GAGs: linear polymers of repeating disaccharide units composed of a hexosamine and an uronic acid, intensely hydrophilic. c. Proteoglycans: glycosaminoglycans (GAG) + core protein → proteoglycan molecular + 4 link proteins + hyaluronic acid → proteoglycan aggregates 2) Functions: Molecular sieve: a. Exchange medium b. Reservoir of hormones c. Resistance to compression d. Gel - like barrier (2) Tissue fluid: Equilibrium between formation and absorption Edema (3) Fibers: Formed by collagen or elastin 1) Types of collagen: type I、II、III、IV、V etc. 2) Formation of collagen fibril: Amino acid (e.g. glycine, proline, hydroxyproline, hydroxylysine) → a polypeptide chain × 3→ procollagen molecule → → tropocollagen molecule → fibril 64-nm periodicity transverse striation 3) Classification: a. Collagen fibers: “white” fibers Components: type I collagen collagen fibrils → collagen fibers → collagen bundles Characteristics: having great tensile strength and resistance to stretching b. Reticular fibers: argyrophilic fibers Components: type III collagen Characteristics: stained black by silver salts impregnation; PAS-positive c. Elastic fibers: “yellow fibers” Components: elastin core + microfibrils sheath Characteristics: high elasticity 2. Cells Resident cell population (permanent residents) Wandering or transient cell population (1) Fibroblasts: 1) Morphology: LM: EM: Fibroblasts ↔ Fibrocytes 2) Function: synthesis of fibers and ground substances (2) Macrophages: 1) Origin: 2) Morphology: LM: EM: 3) Functions: a. Phagocytosis: Amoeboid mobility: chemotactic factors Recognition and binding antigens 5 Ingestion: forming phagosome Digestion: proteolytic enzymes b. Secretion: c. Participating and regulating immunological reaction: Antigen-presenting cell 4) Mononuclear phagocyte system: a. Monocytes in the blood b. Macrophages in the CT c. Kupffer's cells in the liver d. Osteoclasts in the bone e. Microglia in the CNS f. Langhans cells in the skin g. Dendritic cell in the LN h. Alveolar macrophages in the lung i. Epithelioid cells & Multinuclear giant cells (3) Plasma cells: 1) Origin: 2) Morphology: LM: cartwheel or clock-face nucleus EM: 3) Function: synthesis of antibody (Ab) (4) Mast cells: 1) Morphology: LM: metachromasia granules EM: 2) Function: Storage of chemical mediators of the inflammatory response, including: heparin, histamine, eosinophil chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis (ECF-A). Leukotrienes Mediating the allergic reactions. (5) Adipose cells (adipocytes, fat cells): 1) Origin: 2) Morphology: a. Unilocular adipocytes: one large fat vacuole, “signet ring cells” b. Multilocular adipocytes: many small fat vacuoles and mitochondria 3) Function: a. Unilocular adipocytes: energy storage, insulation and cushioning of vital organs. b. Multilocular adipocytes: a source of heat. (6) Leukocytes: (7) Undifferentiated mesenchymal cells Dense Connective Tissue 1. Regular Dense CT 2. Irregular Dense CT 3. Elastic Tissue 6 Adipose Connective Tissue 1. White adipose CT 2. Brown adipose CT Reticular Tissue Reticular cells + reticular fibers + ground substance Constituting the architectural framework of the lymphatic and hemopoietic organs Embryonic Connective Tissue 1. Mesenchyme 2. Mucous Connective Tissue Umbilical cord 7 Cartilage and Bone I. Cartilage 1. Structure of cartilage 1) Perichondrium dense C.T. outer fibrous layer inner cellular layer 2) Cartilage tissue (1) Chondrocyte young ~ : elliptic, singly mature ~ : round isogenous group LM: EM: Function: lacunae cartilage capsule (2) Cartilage matrix fibers: type II collagen fibrils / elastic fibers / type I collagen fibers ground substance: (GAG rich) proteoglycans aggregates: chondroitin sulfate, keratan sulfate glycoprotein: chondronectin rich in water 3) Properties avascular, no lymphatic vessels or nerves nourished by diffusion 2. Types of Cartilage 1) Hyaline cartilage (1) Location (2) Structure perichondrium (except articular cartilage) chondrocytes cartilage matrix: type II collagen fibrils 2) Elastic cartilage (1) Location: external ear, auditory tube, epiglottis et al. (2) Structure perichondrium chondrocytes cartilage matrix : elastic fiber + type II collagen fibrils 3) Fibrocartilage transitional type (1) Location: intervertebral disks, symphysis pubis, et al. (2) Structure perichondrium: no chondrocytes: small, often arrange in long row 8 cartilage matrix: type I collagen fibers, less ground substance 3. Histogenesis and growth of cartilage 1) Histogenesis mesenchymal cells chondroblasts + perichondrium 2) Growth (1) Interstitial (endogenous) growth from inside (2) appositional (perichondrium) growth from outside II. Bone Functions: Preparations: ground bone, decalcified bone 1. Structure of bone tissue 1) Bone matrix (1) Organic matrix: (35%) fibers: type I collagen fibers proteoglycan aggregates structural glycoproteins: osteocalcin, osteonectin, et al. (2) Inorganic salts: (65%) hydroxyapatite crystals osteoid → calcified → bone matrix 2) Bone cell (1) Osteoprogenitor cell: stem cell LM: (2) Osteoblast: bone- forming cell LM: single layer, polygonal shape, basophilic cytoplasm EM: rER, Golgi complex, matrix vesicle (3) Osteocytes lacunae canaliculi LM: slender processes EM: Function: maintain the bone matrix; maintain the homeostasis of blood Ca2+ (4) Osteoclast: bone reabsorbing cell Howship’s lacunae LM: multinucleated large cell, acidophilic cytoplasm EM: ruffled border, clear zone, lysosome, mitochondria, endocytic vesicles 2. Architecture of Long Bone 1) Compact bone (1) Outer and inner circumferential lamellae (2) Haversian systems (osteon): cylindrical unit, supporting Haversian canal + concentric lamellae + osteocytes cementing substance 9 (3) Interstitial lamellae (4) Volkmann’s canal (perforating canal) 2) Spongy (cancellous) bone trabeculae: parallel lamellae + osteocytes 3) Periosteum & endosteum (1) Periosteum outer fibrous layer inner osteogenic layer Sharpey’s fibers (perforating fiber) (2) Endosteum osteogenic cells 3. Histogenesis of bone 1) Intramembranous ossification • mesenchymal cell → osteoprogenitor cell → osteoblast→ osteocyte • mesenchymal sheet → primary ossification center → primary spongy bone → primary compact bone • mesenchymal sheet → periosteum, endosteum, bone marrow 2) Endochondral ossification (1) Cartilage model formation mesenchymal cell → chondrocyte & perichondrium cartilage growth (2) Bone collar formation and Cartilage degeneration perichondrium → vascularization → periosteum osteoprogenitor cell → osteoblast → osteocyte bone collar chondrocyte hypertrophied, calcified, degenerated (3) Primary ossification center formation periosteal bud (blood vessels, osteoprogenitor cells, osteoclasts) primary ossification center marrow cavity (4) Secondary ossification center formation Epiphyseal plate zone of epiphyseal cartilage A. zone of reserve cartilage B. zone of proliferation C. zone of hypertrophy and calcification D. zone of ossification (5) Remodeling primary bone tissue (woven bone) secondary bone tissue (lamellar bone) 10 Blood and Hemopoiesis Blood male: 4.1-6 × 1012 /L Erythrocytes female: 3.9-5.5× 1012 /L Granular ~ Formed element Leukocytes ~ 45% 6-10× 109 /L Neutrophils 60-70% Eosinophils 2-4% Basophils <1% Lymphocytes 20-30% Agranular ~ Monocytes 3-8% Platelets (100-300)×109 /L Plasma ~ 55% Hematocrit: 40-50% in man & 35-45% in woman I. Plasma: yellowish & translucent 1. Compositions: Plasma proteins: albumin, ,,-globulin, clotting protein (prothrombin, fibrinogen, etc.), complement protein (C1-C9), lipoproteins (chylomicrons, VLDL, LDL, HDL). 2. Functions: transportation, regulation & defense. 3. Serum: II. Formed element: Smear and sectioned slide Wright & Giemsa stain (azures) 1. Erythrocytes (Red Blood Cell, RBC) (1) Structure: “Histologic ruler” Biconcave disc, d 7-8m, anucleate, no organelles, acidophilic, rich in hemoglobin & deformable membrane. Erythrocyte rouleaux (stacked coins) 1) Hemoglobin (Hb): globin + iron-containing heme male: 120-150g/L & female: 105-135g/L, HbA & HbF Oxyhemoglobin ↔ carbaminohemoglobin carboxyhemoglobin 11 2) Cell membrane: flexible & deformable a. Peripheral membrane proteins: spectrin, actin, and ankyrin etc. serving as a membrane skeleton. b. Integral membrane proteins: Na+-K+ pump, Ca++ pump, and glucose transport protein, band 3 protein, and glycophorins etc. Blood group, transfusion and hemolytic transfusion reaction ABO group & Rh group: (2) Function: Transporting O2 and CO2 (3) Change of RBC 1) Physical adaptation: 2) Pathological changes: d > 9m, macrocytes; d < 6m, microcytes; anisocytosis: 12 Anemia: RBC < 3 × 10 /L, Hb < 100g/L Iron-deficiency ~, Sickle cell ~, Mediterranean ~ etc (4) Osmotic equilibrium between RBC and plasma Hemolysis: blood shadow or blood ghost Isoosmotic solution: Hyperosmotic solution: Hypoosmotic solution: (5) Reticulocyte: 0.5~1.5% of RBC Anucleate, contain some organelles, e.g.: ribosomal RNA (rRNA), and demonstrated by brilliant cresyl blue methods (6) Life span: about 120days 2. Leukocytes (White Blood Cell, WBC) Inactive WBC in circulating blood → Active WBC in connective tissue diapedetis (1) Introduction: 1) Granular leukocytes a. Azurophilic granules: staining purple, lysosomes, containing acid phosphatase, myeloperoxidase, etc. b. Specific granules: c. Types: Neutrophils, Eosinophils & Basophils 2) Agranular leukocytes (mononuclear leukocytes) a. Azurophilic granules b. Types: Lymphocytes & Monocytes 3) Life span: variable (2) Classification: 1) Neutrophils: 12-15m a. Structure: Nucleus: band-form nucleus or lobulated, 2-5 lobes Sex chromosome: drumstick-like appendage of nucleus in 3% of neutrophils in female in LM Specific granules: neutrophilic granules: 12 Small, barely visible in LM, containing alkaline phosphatase, collagenase and lysozyme etc. b. Functions: Chemotaxis: Phagocytosis and destruction of microorganisms, especially bacteria. Pus & pyocyte 2) Eosinophils: 12-15m a. Structure: Nucleus: bilobed Specific granules: eosinophilic granules Large, staining orange-pink, elongated, crystalline core, refractile, and containing major basic protein, histaminase, myeloperoxidase, etc. b. Functions: Chemotaxis: Phagocytosis of Ag-Ab-complexes and destruction of parasites. 3) Basophils: 12-15m a. Structure: Nucleus: lobed, S-shaped, or irregular, often masked by the overlying specific granules Specific granules: basophilic granules: metachromasia, staining blue purple and containing heparin, histamine, and eosinophil chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis (ECF-A). leukotriene b. Functions: mediating the allergic reactions. Anaphylatic shock 4) Lymphocytes: a. Structure: Small lymphocytes: 6-8m, nucleus: cytoplasm ≈ 9:1 Deeply-stained spherical nucleus, sometimes with an indentation, located eccentrically; cytoplasm is basophilic, sky-blue, contains fine azurophilic granules. Medium-sized lymphocytes: 9-12m Large lymphocytes: 13-18m b. Classification and functions: B-Lymphocytes: 20-30%, responsible for antibody - mediated (humoral) immunity. T-Lymphocytes: 70-80%, responsible for cell - mediated immunity. Natural killer cells: 5) Monocytes: 12-20m a. Structure: oval, kidney- or horseshoe - shaped nucleus, eccentric position; cytoplasm is basophilic, bluish-gray, and contains fine azurophilic granules. b. Functions: precursor cells of the mononuclear phagocyte system 13 3. Platelets: (Thrombocytes) 2-4m (1) Structure: often in clumps 1) non-nucleate, biconvex round or ovoid discs. 2) Hyalomere: peripheral clear zone Dense tubular system, open canalicular system & microtubules 3) Granulomere: central darker zone , , granules (2) Functions: promote blood clotting & controlling hemorrhage (3) Origin: Protoplasmic discs derived from bone marrow megakarocytes. (4) Life span: ~ 10 days. Thrombocytopenic purpura Hemopoiesis (Blood Cell Formation) I. Hemopoietic Organ: 1. Mesoblastic phase: yolk sac 3w 2. Hepatic phase: 6w - end of gestation 3. Splenic phase: 4m - end of gestation 4. Myeloid phase: bone marrow > 6m Red Bone Marrow ↔ Yellow Bone Marrow Structure of Red Bone Marrow (1) Stroma: reticular tissue (2) Hemopoietic cord: hemopoietic cells & macrophages Pluripotential hemopoietic stem cells progenitor cells (committed stem cells) [Colony-forming cells (CFC) or colony-forming units (CFU)] precursor cells (blasts) Growth Factors, colony-stimulating factors (CSF) or hematopoietins, e.g.: Erythropoietin (EPO), G-CSF, GM-CSF etc. (3) Sinusoids: Bone marrow aspiration II. Erythropoiesis ~7d Proerythroblast basophilic erythroblast polychromatophilic erythroblast orthochromatophlic erythroblast (normoblast) reticulocyte erythrocyte Major morphological changes: (1) Cell volume: (2) Cytoplasm: basophilic acidophilic (3) Nucleus: disappear; nucleoli: disappear; chromatin condensation III. Granulopoiesis ~11d Granules Myeloblast promyelocyte myelocyte metamyelocyte granulocyte IV. Thrombopoiesis Megakaryoblast promegakaryocyte megakaryocyte platelet 14 Muscle Tissue I. Introduction 1. Composition • Muscle fibers: specialized contractile cells • Extracellular matrix 2. Function Movement 3. Classification skeletal muscle voluntary striated cardiac muscle involuntary smooth smooth muscle II. Skeletal Muscle 1. Organization of skeletal muscle Epimysium Perimysium Endomysium Myotendinous junction 2. Structure of skeletal muscle fiber Terminology muscle fiber = muscle cells, sarcolemma = plasmalemma sarcoplasm = protoplasm, sarcoplasmic reticulum = sER 1) Morphology long, cylindrical, multinucleated cell with cross-striation 2) Nuclei 100-1000 nuclei per cell, located peripherally, ovoid & flattened. 3) Sarcoplasm: (1) Myofibrils: =1-2 m • long cylindrical filamentous bundles consisting of stacks of sarcomeres • A band, I band, Z line, H band, M line • sarcomere: functional unit of contraction 1/2 I band + A band + 1/2 I band • thin filament 15 actin (G-actin, F-actin), tropomyosin, troponin (TnT, TnC, TnI) thick filament: myosin: 2 heavy chains + 4 light chains rod-like portion globular head: actin binding sites, ATP binding sites, ATPase activity • cross-bridge • muscle contraction: sliding filament mechanism (2) Membrane system • transverse (T) tubule system • sarcoplasmic Reticulum • triad = T tubule + 2 terminal cisternae at A-I junction (3) Other components mitochondria, glycogen, lipid droplet, myoglobin, ribosome • 3. Types of skeletal muscle fiber red fibers (type I fibers), white fibers (type II B fibers), intermediate fibers (type II A fibers) Characteristics Red fiber White fiber Fiber diameter smaller larger Vascular supply rich poorer Myoglobin rich poor Sarcoplasmic reticulum not extensive extensive Glycogen poor rich Mitochondria numerous few Metabolism aerobic anaerobic Contraction slow, not easily fatigued, Fast, easily fatigued, weaker contraction stronger contraction 4. Innervation motor end-plate (myoneural junction) Sensitive nerves: muscle spindles 5. Development and regeneration 1) Development: myoblast myotubes myocytes 2) Regeneration: satellite cell III. Cardiac Muscle 1. Organization of cardiac muscle 2. Structure of the cardiac muscle fiber 1) Morphology: cross-striated, elongated, branched cell 2) Nuclei: 1 or 2 centrally 3) Sarcoplasm (1) Myofibrils: thinner, branched 16 (2) Membrane system • T tubule: numerous, larger • Sarcoplasmic reticulum: less developed • diads: Z disk level (3) Other components numerous mitochondria, lipid droplets, glycogen, lipofuscin, et al. 4) Intercalated disk transverse portion: zonula adherens, desmosomes lateral portion: gap junction 3. Types of cardiac muscle cell 1) Myoendocrine cells: atrial natriuretic factor (atriopeptin) 2) Impulse-generating & conducting system 4. Regeneration IV. Smooth Muscle 1. Organization 2. Structure of smooth muscle cell 1) Morphology: nonstriated, fusiform 2) Nucleus: single, centrally 3) Sarcoplasm (1) Cytoskeleton dense body and dense patch intermediate filaments: desmin, vimentin (2) Myofilament unit • thin filaments: actin, tropomyosin, calmodulin, caldesmon • thick filaments: myosin • thick filaments : thin filaments = 1:12 • contraction (3) Membrane system caveolae, rudimentary SR (4) Other components (juxtanuclear region) rER, Golgi complex, ribosome, et al. 3. Innervation • Autonomic nervous system • Hormone regulation 4. Regeneration active 17 Nervous Tissue The Neuron I. The structure of the neuron A. The Cell body 1. Cell membrane 2. Nucleus, Nucleolus 3. Cytoplasm, Perikaryon (1) Golgi Apparatus (2) Mitochondria (3) Microtubules, 20-26nm diameter (LM, neurofibril) (4) Neurofilaments, 8-10nm diameter (5) Lysosomes (6) Nissl body (rough ER and free ribosomes) B. Dendrites 1. Nissl body 2. Purkinje’s 250μm2~27,000μm2 3. Mitochondria 4. Microtubules 5. Neurofilaments 6. Dendritic spine C. Axons 1. Axon hillock 2. Collateral branch 3. Terminal arborization 4. Axolemma 5. Axoplasm (few microtubules, mitochondria, neurofilaments) 6. Axoplasmic flow II. Classification of the neuron A. Multipolar neurons: motor neurons from the spinal cord B. Bipolar neurons: olfactory cells C. Pseudounipolar neurons: central process, peripheral process, spinal ganglia III. Synapses Specialized Structures A. Types: axodendritic synapse, axosomatic synapse, axoaxonal synapse, dendrodendritic synapse B. Boutons terminaux C. Structure 1. Presynaptic element, membrane, neurotransmitters 2. Synaptic cleft, 15-30nm width 18 3. Postsynaptic element, membrane, receptor 4. Synaptic vesicle D. Chemical synapse: neurotransmitter E. Electrical synapse: gap junction Neuroglia Cell I. CNS A. Astrocyte --- fibrous, protoplasmic types 1. Nucleus: oval, large and less dense than oligodendrocyte nucleus 2. Stellate projections 3. Perivascular feet 4. Comparison Distribution Processes Glial filament Fibrous Astrocyte white matter long, slender, abundant smooth, a few branches Protoplasmic gray matter short, thick, rough few Astrocyte many branches Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) B. Oligodendrocyte 1. Nucleus: small, dark 2. Myelin in CNS --- Each oligodendrocyte myelinates many internodes of different axons C. Microglia (gray matter) 1. Nucleus: smaller, dark, elongated shape 2. Short processes: thorny spines 3. Engulfing function: mononuclear phagocyte system in nervous tissue D. Ependymal cell 1. Line ventricular system and central canal 2. Cuboidal, columnar 3. Apical surface: microvilli, cilia II. PNS A. Schwann cells 1. Make PNS myelin 2. One Schwann cell myelinates one internode B. Satellite cells Nerve fibers I. Myelinated fibers 1. Myelin sheath Lipoprotein 19 Neurokeratin Schmidt - Lanterman’s clefts Neurolemma - plasma membrane and basement membrane of Schwann cell 2. Initial Segment 3. Node of Ranvier 4. Internode 5. Schwann cells make PNS myelin 6. Oligodendrocytes make CNS myelin II. Unmyelinated fibers 1. No myelin sheath, No node of Ranvier 2. Axons are embedded in the cytoplasm of a Schwann cell Nerve Ending I. Sensory nerve ending 1. Free nerve ending 2. Tactile corpuscle (Meissner’s corpuscle) 3. Lamellar corpuscle (Pacinian corpuscle) 4. Muscle spindle - intrafusal muscle fiber II. Motor nerve ending 1. Motor end- plate, neuro-muscular junction 2. Visceral motor nerve ending varicosity Ganglia Nerve ganglion: An aggregation of nerve cell bodies outside the central nervous system 1. Spinal ganglia Pseudounipolar neurons, satellite cell 2. Cranial ganglia 3. Autonomic ganglia multipolar neurons Peripheral Nerve 1. Endoneurium 2. Perineurium 3. Epineurium 20 The Circulatory System Blood vascular system + Lymphatic vascular system artery heart capillary ↔ tissue fluid ↔ cell lymph vein lymphatic vascular system I. Blood vascular system heart + arteries + capillaries + veins 1. General structure of blood vessels --- 3 concentric layers (1) Tunica intima 1) Endothelium + basal lamina Weibel-Palade granules (W-P bodies): especially in the endothelial cells of elastic arteries, rod-shaped, having dense matrix housing parallel tubular elements, containing Von Willebrand’s factor (factor VIII). 2) Subendothelial layer --- loose connective tissue 3) Internal elastic lamina --- a fenestrated sheet of elastin Myoendothelial junctions (2) Tunica media 1) Various numbers of smooth muscle cell layers intermingled with fibroelastic C.T. 2) External elastic lamina (3) Tunica adventitia fibroelastic C.T. Vasa vasorum: Lymphatic vessel & innervation 2. Specific structure of blood vessels (1) Capillaries 1) Composition: a. Pericytes: Morphology: having long processes, basal lamina fusing with that of endothelial cells Functions: contractility & participating in regeneration b. Endothelial cells + basal lamina Morphology: LM: EM: 2) Ultrastructure and classification of the capillaries a. Continuous Capillaries Morphology: continuous endothelium, tight junctions, continuous basal lamina, pinocytotic vesicles. Distribution: muscle, C.T., exocrine gland, lung, CNS, etc. b. Fenestrated capillaries Morphology: fenestrates (pores) with or without diaphragm, continuous basal lamina. 21 Distribution: stomach, intestine, endocrine gland, kidney, etc. c. Discontinuous sinusoidal capillaries (sinusoids) Morphology: enlarged diameter, gaps, large fenestrates without diaphragm, discontinuous or absent basal lamina. Distribution: liver, spleen, bone marrow, etc. 3) Functions: a. Permeability exchange vessels b. Metabolic functions Activation angiotensin I angiotensin II Inactivation bradykinin, serotonin, etc. Lipolysis lipoproteins Production of vasoactive factors e.g., endothelins & NO c. Antithrombogenic function 4) Microcirculation: a. Composition: precapillary sphincters Arterioles metarterioles capillaries postcapillary venules Arteriovenous anastomosis Metarterioles: with a discontinuous smooth muscle layer b. Functions: blood pressure & blood flow regulation, and thermoregulation in particular areas. (2) Arteries 1) Arterioles (Peripheral resistance vessels) Diameter < 0.5 mm (including all 3 layers) 1-2 concentric smooth muscle layers in media, thin adventitia 2) Muscular arteries a. Small arteries d < 1mm (Peripheral resistance vessels) b. Medium - sized arteries (Distributing Arteries) Prominent internal elastic lamina, 3-40 concentric smooth muscle layers in media, external elastic lamina usually visible, adventitia equal in thickness to media 3) Elastic Arteries (Conducting Arteries) yellowish color Relatively thick intima, 40-70 elastic laminae in media, thin adventitia 4) Specialized arteries and age changes in arteries: Atherosclerosis Specific receptors: a. Carotid bodies & aortic bodies: chemoreceptors, sensing O2 and CO2 tension & pH. b. Carotid sinuses: baroreceptors, sensing blood pressure. (3) Veins (Capacitance vessels) Comparing with their corresponding arteries, veins have valves and squashed, larger lumen, thinner wall, and poorly demarcated layers. 1) Venules diameter < 1mm 22 pericytes in postcapillary venules, discontinuous or no smooth muscle in media Permeability 2) Small to medium-sized veins diameter: 1-9mm 2-4 1ayers of smooth muscle cells in media, intermixed with fibroelastic C.T., thicker adventitia with or without some longitudinal arranged smooth muscle cells. One - way valves in veins > 2mm diameter Venous valves: paired, semilunar folds of the intima 3) Large veins relatively thin media, thickest adventitia with many longitudinal bundles of smooth muscles. (4) Heart 1) Tunics: a. Endocardium Endothelial cells + basal lamina Subendothelial layer Subendocardial layer Branches of Purkinje fibers in it b. Myocardium c. Epicardium (Visceral pericardium): CT + mesothelium Subepicardial layer Visceral pericardium 2) Fibrous skeleton (cardiac skeleton) Including annuli fibrosi, the trigona fibrosa & septum membranaceum. 3) Valves Tricuspid, mitral valves & semilunar valves A central core of dense C.T., lined on both sides by endothelial layers 4) Impulse Conducting System a. Sinoatrial (SA) node: pacemaker, in subepicardial layer b. Atrioventricular node (AV), in subendocardial layer c. AV Bundle of His, in subendocardial layer Purkinje cell: specialized cardiac muscle cells, one or two nuclei, paler cytoplasm; clear (glycogen storage) area forms “halo” around nuclei, reduced number of myofibrils. B. Lymphatic Vascular System 1. Lymphatic capillaries Blind ended vessels, endothelial cells have no fenestrate, no tight junction, and little or no basal lamina. 2. Lymphatic vessels 3. Main lymphatic trunks 23 Immune System Lymphoid Tissue Reticular cell, Reticular fiber I. Diffuse lymphoid tissue II. Lymphoid nodule (Lymphoid follicle) 1. Germinal center 2. Aggregated lymph nodule (Peyer’s Patches) Lymphoid Organ I. Central lymphoid Organ 1. Thymus (thymus dependent lymphocyte) 2. Bursa equivalent - fetal liver, bone marrow 3. Bursa of Fabricius II. Peripheral lymphoid organ 1. Lymph Nodes 2. The spleen 3. Tonsils Thymus I. The Structure of the thymus A. Capsule, interlobular septum, lobule B. Cortex 1. Thymocyte, large lymphocytes, medium - sized lymphocytes, small lymphocytes 2. Epithelial - reticular cell (1) Morphology: large nuclei, many processes, desmosome, tonofilament (2) Function a. microenvironment b. support c. secretion C. Medulla Thymus corpuscle (Hassall’s corpuscle): 30-150μm in diameter, consisting of concentric layers of epithelial reticular cells D. Blood circulation and blood - thymus barrier 1. Postcapillary venule 2. Blood - thymus barrier (1) Endothelial cell of continuous capillary 24 (2) Basement membrane of the endothelial cell (3) Pericapillary space, Macrophages (4) Basement membrane of the epithelial - reticular cell (5) Processes of the epithelial - reticular cell II. Function of the thymus 1. Cultivating T lymphocytes, P.V. 2. Secretion of hormone, thymosin Lymph Nodes I. The structure of lymph nodes A. Capsule related structures 1. Capsule 2. Trabecula 3. Afferent lymphatic vessel 4. Hilus 5. Efferent lymphatic vessel B. Cortex 1. Lymphoid nodule (1) Germinal center --- cap, light zone, dark zone (2) Dendritic cell --- Cytoplasm branches into numerous process 2. Paracortical zone (Thymus-dependent zone) (1) Location (2) Postcapillary venule a. Exhibit an unusual endothelial lining consisting of cuboidal cells. b. Lymphocytes are capable of traveling into and between the endothelial cells of this vessel C. Medulla 1. Medullary cord: mainly consisting of B lymphocytes 2. Medullary sinus D. Lymphoid sinus and lymph circulation 1. Subcapsular sinuses Cortical Sinuses 2. Peritrabecular sinuses 3. Medullary sinuses 4. Lymph circulation II. Recirculation of lymphocyte 1. Postcapillary venule 2. Lymphocyte recirculating pool B, T lymphocyte, 18-30hrs/round 25 III. Function 1. Filtering lymph 2. Immune The Spleen I. The Structure of the spleen: A. Capsule and trabecula 1. Mesothelium 2. Some smooth muscle cells B. White pulp 1. Periarterial lymphatic sheath mainly consisting of T lymphocytes, thymus - dependent zone, interdigitating cell 2. Lymphoid nodule mainly consisting of B lymphocytes, cap, light zone, dark zone C. Marginal zone 1. Many B lymphocytes and macrophages 2. The path of lymphocytes from blood flow entering lymphoid tissues 3. Playing a significant role in filtering the blood and launching an immune response D. Red pulp 1. Splenic blood sinusoid (1) They have a dilated, large, irregular lumen (2) Spaces between lining endothelial cells (3) Reticular fibers forming barrel hoop - like rings 2. Splenic cord Reticular cells and reticular fibers macrophages engulf old RBCs and platelets II. Blood circulation capillaries Splenic artery trabecular artery central artery penicillar arterioles pulp arteriole sheathed arteriole arterial capillaries sinusoid pulp vein trabecular vein splenic vein III. Function 1. Filtration of blood: marginal zone, splenic cord, macrophages 2. Production of blood 3. Blood storage. 40ml, (splenic cord, splenic blood sinusoid) 4. Immune. B lymphocyte 55% T lymphocyte 45% Macrophages 26 Tonsils Palatine Tonsils 1. Crypts 10-30 2. Lymphoid nodule 3. Infiltrated epithelium Mononuclear Phagocyte System and Reticulo-endothelial System Promonocytes monocytes macrophages (bone marrow) (blood) (tissues and organs) 27 The Endocrine System I. Introduction Terminology endocrine cells, endocrine, paracrine, autocrine, target cells / organs, hormones: steroid hormones & inclusive nitrogen hormones 1. Ultrastructure of endocrine cells 1) Peptide - secreting cell EM: rER, Golgi complex, membrane - bound vesicles 2) Steroid-secreting cell EM: lipid droplets, Mit. (tubular & vesicular cristae), sER 2. Distribution of the endocrine cells • dispersed endocrine cells • endocrine tissues • endocrine glands 3. Characteristics of endocrine gland • ductless glands • cells arrange in cords, clumps or follicles • highly vascularized by fenestrated capillaries (sinusoids) • delicate C.T. II. Pituitary gland (hypophysis) 1. Embryogenesis adenohypophysis: oral ectoderm (Rathke’s pouch) neurohypophysis: neural ectoderm (diencephalon) 2. Gross structure adenohypophysis pars distalis pars tuberalis pars intermedia anterior lobe posterior lobe pars nervosa neurohypophysis infundibular stem infundibulum median eminence 3. Adenohypophysis 1) Pars distalis arranged in cords fenestrated cap. 28 (1) Chromophils Stain affinity Acidophils 35-40% Basophils 10-15% Cell type somatotropic cells mammotropic cells thyrotropic cells corticotropic cells gonadotropic cells Hormone growth hormone prolactin (PRL) thyrotropin (TSH) corticotropin (ACTH) follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) luteinizing hormone (LH) (2) Chromophobes 50% degranulated chromophils undifferentiated cells follicular cells 2) Pars intermedia follicles & cords chromophobes & basophils 3) Pars tuberalis abundant longitudinal blood vessels cell arranged in cords basophils: may secrete gonadotropins 4. Neurohypophysis 1) Unmyelinated nerve fibers 2) Pituicytes: neuroglial cells 3) fenestrated capillaries 4) Herring bodies 5. Blood supply hypophyseal portal system superior hypophyseal A. inferior hypophyseal A. primary capillary plexus (infundibulum) capillaries (pars nervosa) portal veins (pars tuberalis) secondary capillary plexus (pars distalis) hypophyseal veins 6. Hypothalamo - hypophyseal system 1) the hypothalamus and adenohypophysis neuroendocrine cells in tuberal nuclei, etc (releasing hormones, RH & releasing inhibiting hormones, RIH the portal system the endocrine cells in pars distalis target cells in other organs 2) the hypothalamus and neurohypophysis neuroendocrine cells in supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei secrete oxytocin & antidiuretic hormone (ADH, vasopressin) 29 III. Thyroid gland 1. Gross structure 2. Microscopic structure capsule, lobules fenestrated capillaries, C.T. 1) Thyroid follicles simple cuboidal epithelium colloid within the lumen (1) Follicle cells LM: EM: Functions: secrete the thyroid hormone (T3 & T4) (2) Mechanism of synthesis and secretion of T3 & T4 a. synthesis of thyroglobulin b. uptake of iodide & activation c. iodination of thyroglobulin d. reuptake of colloid stimulated by TSH e. digestion of iodinated thyroglobulin f. release of T3 & T4 (3) Functions of the thyroid hormone 2) Parafollicular cells Location: LM: EM: Functions: secrete calcitonin IV. Parathyroid glands 1. Gross structure 2. Microscopic structure cells arrange in cords 1) Chief cell LM: EM: Functions: secrete parathyroid hormone 2) Oxyphil cells LM: acidophilic EM: many mitochondria Function is unknown V. Adrenal (suprarenal) glands 1. Gross structure dense collagenous C.T. capsule cortex: medulla: 2. Microscopic structure of cortex 1) Cortex 30 (1) Zona glomerulosa 15% small cells arranged in rounded or arched cords secrete mineralocorticoids (aldosterone) (2) Zona fasciculate 78% arranged in straight cords cells contain many lipid droplets secrete glucocorticoids (cortisol & corticosterone) (3) Zona reticularis 7% arranged in anastomosing network cells contain lipofuscin secrete androgens, glucocorticoids 2) Medulla (1) Medullary cells (chromaffin cells): modified sympathetic postganglionic neurons LM: EM: Functions: secrete epinephrine & norepinephrine (2) Ganglion cells 3. Blood supply 31 Skin 16% body weight, total area 1.2-2.0m2 1300 nerve endings / inch2 The Structures of the skin Average thickness 1 - 4mm, the most thick 1.5mm Epidermis A. The structures Keratinocyte Nonkeratingzing cell- Melanocyte, Langerhan’s cell, Merkel cell 1. Stratum basale (Stratum germinativum) (1) Basal cell: intense mitosis basophilic cytoplasm tonofibril (2) Ultrastructure a. tonofilament: 10nm, keratin filament b. extensive desmosomes on apical and lateral surface c. hemidesmosomes basally d. numerous ribosomes 2. Stratum spinosum (1) Several layers of polygonal to slightly flattened cells Spinous cells: spiny projections, intercellular bridges (2) Mitosis observed; involucrin (3) Ultrastructure a. more tonofilaments b. desmosomes cover entire surface c. first appearance of membrane coating granules, 0.1-0.3μm in diameter, lamellar granules 3. Stratum granulosum (1) Several layers of flattened cells (2) Ultrastructure a. more membrane coating granules and they release content into intercellular space by exocytosis b. appearance of keratohyalin granules, non - membrane limited, basophilic granules 4. Stratum lucidum (1) Most pronounced in thick skin (2) Flattened, non - nucleated cells keratohyalin in cytoplasm 5. Stratum corneum (1) Terminal differentiated population 32 (2) Layers of flattened, non-nucleated cells which are totally keratinized (called horny cells) Their cytoplasm is full of keratin (3) Ultrastructure a. no organelles left b. tonofilaments c. plasma membrane: extensively thickened d. desmosomes B. Nonkeratingzing cells 1. Melanocytes (1) neural crest origin and invade epidermis at 12-14 weeks embryo (2) unicellular exocrine glands which synthesize and secrete melanin absorbs UV (3) dopa reaction (4) ultrastructure a. all organelles for synthetic function: abundant ribosomes, prominent Golgi apparatus, lots of rough ER b. no desmosomes c. no tonofilaments d. contain developmental gradient of melanosomes with ultimate maturation to melanin granules 2. Langerhans cells (1) very visible with ATPase gold chloride impregnation (2) ultrastructure a. no desmosomes b. no tonofilaments c. tennis racquet granules (Birbeck granules) Dermis average thickness 1-2mm I. Papillary layer Dermal papillae abundant capillaries Meissner’s corpuscle II. Reticular layer Contains vessels, hair follicles, sweat glands, sebaceous glands, nerves, Pacinian corpuscle Hypodermis Consisting of loose connective tissue and adipose tissue 33 Hair 1. Hair Shaft - Portion above epidermis 2. Hair Root - Portion embedded in skin 3. Hair Bulb - Basal portion of root penetrated by hair papilla rich in capillaries, hair matrix, scattered melanocytes 4. Hair Follicle - epidermal and connective tissue sheaths around root (1) Internal root sheath (2) External root sheath 5. Glassy Membrane 6. Arrector pili muscle Sebaceous Gland 1. 2. Located in dermis Acinus composed of two cell types: (1) Undifferentiated basal cells Proliferate and differentiate into acinar cells (2) Acinar cells Holocrine Sebum Sweat Glands I. Merocrine sweat glands 1. Exocytosis 2. Clear cells: large, acidophilic 3. Dark cells: small, basophilic 4. Myoepithelial cells: Long flat nuclei lying at the base of epithelial cells of the glands just inside the basement membrane 5. Ducts: Contain 2-3 layers of cuboidal or low columnar cells II. Apocrine sweat glands 1. Secretory part 2. Ducts 34 Oral Cavity and Salivary Glands Oral Cavity I. Organization II. General structure of oral mucosa Stratified squamous epithelium Lamina propria III. Tongue 1. Epithelium 2. Lamina propria 3. Skeletal muscle 4. Lingual papillae Table 1. Main Features of Lingual Papillae Papillae Shape Number Filiform ~ elongated conical Numerous Fungiform ~ mushroomlike a few Circumvallate ~ large circular 10-14 papillae, gland of von Ebner Foliate ~ leaf-like 5.Taste bud: specialized gustatory structures taste pore Type II, taste cells: taste hair, pale staining Type I, supporting cells: spindle shape, dark staining basal cells: conical shape, mitotic pool Salivary Glands I. Structure: compound tubuloalveolar glands A. General organization 1. Stroma: CT, septa, lobules 2. Parenchyma: secretory alveoli & intralobular ducts B. Alveoli Single layer of cuboidal or pyramidal cells Myoepithelial cells 1. Serous alveoli (1) basal RER, apical secretory granules (2) basal junctional complexes 2. Mucous alveoli 35 Taste buds no scattered many many (1) flattened basal nuclei, mucigen granules, cytoplasm looks foamy or empty, HE. pale staining (2) Basal junctional complexes 3. Mixed alveoli: Mixed seromucous alveoli, serous demilune C. Duct System 1. Intercalated duct: Squamous or low cuboidal epithelium myoepithelial cells 2. Striated (secretory) duct Intralobular simple columnar cells the basal cytoplasm membrane infoldings with longitudinally arranged mitochondria 3. Interlobular duct Pseudostratified columnar epithelium 4. Main duct Scattered goblet cells, stratified squamous epithelial II. Differentiation of the three major salivary glands Table 2. Main Features and Functions of Major Salivary Glands Gland alveoli intercalated striated secretions ducts ducts parotid pure serous long present amylase, a ~ little mucus Submandibular mixed, short long mucus, a ~ mostly little amylase serous Sublingual mixed, none a few short mainly ~ mostly mucus mucous with some serous demilune III. Function 1. Moistening, lubricating 2. Digestions 3. Immunoglobulins - sIgA 36 Digestive Tract I. General structure 1. Mucosa (1) Epithelium stratified squamous ~ / simple columnar ~ (2) Lamina propria loose C.T. glands gut - associated lymphatic tissue (GALT) (3) Muscularis mucosae smooth muscle inner circular layer, outer longitudinal layer 2. Submucosa dense C.T. submucosal (Meissner’s) nerve plexus lymphoid tissue submucosal glands 3. Muscularis skeletal muscle / smooth muscle inner circular layer, outer longitudinal layer myenteric (Auerbach’s) nerve plexus Enteric Nervous System 4. Adventitia serosa:mesothelium + C.T. fibrosa (adventitia): C.T. II. Esophagus 1. Mucosa 1) Nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium 2) Lamina propria esophageal cardiac glands 3) Muscularis mucosae: single longitudinal layer 2. Submucosa esophageal glands: mucus-secreting glands 3. Muscularis skeletal muscle / smooth muscle 4. Fibrosa / serosa III. Stomach Rugae, Gastric pits 1. Mucosa 1) Simple columnar epithelium surface mucous cells: 37 LM: EM: tight junction Function: secrete insoluble mucus 2) Lamina propria Gastric glands (1) Fundic glands isthmus, neck, base region a. Mucous neck cells Location: LM: EM: Function: b. Parietal (oxyntic) cells Location: LM: EM: resting phase, active phase intracellular canaliculus, tubulovesicular system, mitochondria Function: secret HCl, intrinsic factor c. Chief (zymogenic) cells Location: LM: EM: Functions: secrete pepsinogen d. Enteroendocrine cells e. Stem cells Protective mechanism: • mucous-HCO3- barrier • tight junction • rapid renewal (2) Cardiac glands shallow pits, coiled terminal portions, wide lumens secrete mucus (3) Pyloric glands: deep pits, shorter coiled secretory portions secrete mucus 3) Muscularis mucosae 2. Submucosa 3. Muscularis inner oblique layer, middle circular layer, outer longitudinal layer pyloric sphincter 4. Serosa IV. Small Intestine 1. Special structures 1) Plicae circulares (Kerckring’s valves) mucosa + submucosa 2) Intestinal villi and intestinal gland (crypts, glands of Lieberkühn) epithelium + lamina propria 3) Microvilli cell membrane + microfilaments 38 2. Mucosa 1) Simple columnar epithelium (1) Absorptive cells (enterocytes) Location: LM: striated border EM: junctional complex, glycocalyx coat Functions: digestion, absorption, secretion (2) Goblet cells (3) Enteroendocrine cells (basal granular cell) Location: LM: open type, closed type EM: Function: secrete gut hormone (4) Paneth’s cells Location: LM: acidophilic granules EM: lysozyme, defensin Functions: regulate intestinal flora (5) Undifferentiated cells stem cell 2) Lamina propria (1) Central lacteals (lymphatic capillary) (2) Lymphoid tissue • solitary nodules: duodenum, jejunum • aggregated nodules (Peyer’s patches ): ileum • microfold (M) cells Location: LM: EM: Functions: (3) Muscularis mucosae 3. Submucosa duodenal (Brunner’s) glands secrete alkaline mucus, EGF 4. Muscularis 5. Fibrosa / Serosa V. Large Intestine 1. Cecum and colon taeniae coli, haustra coli, appendices epiploicae no villi, crypts packed closely 1) Mucosa (1) Simple columnar epithelium absorptive cells, numerous goblet cells, no Paneth’s cell (2) Lamina propria rich in lymphoid tissue (3) Muscularis mucosae 2) Submucosa 3) Muscularis taeniae coli 4) Fibrosa / Serosa 39 2. Appendix small, narrow, and irregular lumen 1) Mucosa simple columnar epithelium fewer & shorter intestinal gland numerous lymphoid nodules muscularis mucosae incomplete 2) Submucosa 3) Muscularis 4) Serosa 3. Rectum and anal canal 1) Mucosa simple columnar epithelium / stratified squamous epithelium muscularis mucosae terminate at anal valves 2) Submucosa vein plexus 3) Muscularis internal anal sphincter: inner circular layer, smooth muscle external anal sphincter: skeletal muscle 4) Fibrosa 40 Digestive Glands Liver I. General Structure 1. Stroma (1) fibroconnective tissue capsule (of Glisson) collagen fibers, elastic fibers, serosa (2) lobules (3) reticular fibers 2. Parenchyma II. The liver lobule Essential structural units Prismatic polygonal units, 2×1mm Hepatic plate Central vein Sinusoid Hepatic cord Bile Canaliculus A. Hepatocyte 1. General considerations 80%, 20μm in diameter, round central nuclei, eosinophilic cytoplasm, hepatic plate (single layer), 6-8 surfaces 2. Organelles (1) Mitochondria 1,000-2,000 / cell, 20% (2) Lysosomes many, store iron (3) Peroxisomes 1,000 / cell Peroxidase catalase Peroxides free radicals (4) Golgi complexes 50 / cell (5) Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum RER Synthesizes blood albumin, fibrinogen Prothrombin (6) Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Bile Synthesis Lipids metabolism Biological transformation Detoxification (glucuronyl transferase) (7) Inclusion Lipid droplets, Glycogen, Pigment 3. Three plasma membrane regions Blood-sinusoid 41 Bile Canaliculi Cell junction surface: *gap junction B. Hepatic Sinusoid 1. Structure (1) discontinuous endothelial cells (2) 9-12 μm (3) micropinocytotic vesicles, a few organelles (4) Gaps, no diaphragm, no BM, reticular fibers (5) Macromolecules - chylomicron, VLDL 2. Kupffer cells They phagocytize blood cells, iron & debris C. Space of Disse Perisinusoidal space microvilli Reticular fibers Fat-storing cells (store fat and Vitamin A) D. Bile canaliculi (Silver stain, ATPase) Tubular space, junction complex microvilli III. Portal areas Interlobular vein Interlobular Artery Interlobular bile duct Portal triad IV. Biliary Passages Central peripheral ductules interlobular Canaliculi (Hering’s canals) bile ducts Right & Left common common Hepatic ducts hepatic duct bile duct Cystic duct V. Hepatic blood circulation Hepatic Artery IA, THA Liver Sinusoids Portal Vein Central vein sublobular vein IV, TPV Hepatic inferior vein vena cava THA: Terminal Hepatic Arteriole TPV: Terminal Portal Venule 42 VI. Lobulation 1. The classic lobule 2. Portal lobule 3. Liver acinus VII. Functions 1. Synthesis and store 2. Secreting bile 3. Detoxification 4. Immune 5. Hemopoiesis Gallbladder I. Mucosa Folds, Simple columnar epithelium, microvilli II. Muscularis III. Serosa Pancreas I. General Features Stroma: thin CT capsule, lobules, septa Parenchyma: exocrine and endocrine cells II. The Exocrine Portion A. Acini 11m2 1. compound tubuloacinar glands 2. a single layer of pyramidal cells 3. size of the central lumen 4. centroacinar cell (flattened, pale staining) cuboidal 5. typical serous cell: Basal basophilic, apical acidophilic 6. EM findings: Basal RER Free ribosome Longitudinal arranged mitochondria Zymogen granules (0.6μm) 7. No myoepithelial cell 8. trypsin inhibitor, acute pancreatitis B. Duct 1. Intercalated duct 2. Low cuboidal epithelium, centroacinar cell 3. No striated duct! 4. Intralobular duct: simple cuboidal epithelium 5. Interlobular duct: simple columnar epithelium 6. Main duct: simple high columnar epithelium 43 goblet cell enteroendocrine cell C. Secretion 1. Merocrine secretion 2. Regulation (1) Neural control: vagus nerve (2) Hormonal control: a. Secretin: bicarbonate and water b. Pancreozymin (cholecystokinin) Pancreatic enzyme 3. Enzymes: proteases (e.g. trypsin) amylase lipases RNAases DNAases III. The Endocrine Portion A. Islets of Langerhans: 1.5% of total volume one million islets Rich fenestrated capillaries loose reticular fibers B. Cell type Distribution Percentage Hormone Function A (alpha) ~ periphery 20% glucagons blood sugar glycogenolysis B (beta) ~ center 70% insulin blood sugar Diabetes Mellitus D (delta) ~ scattered 5% somatostation inhibition, paracrine (A&B cells) PP ~ scattered a few pancreatic Pancreatic polypeptide juice, gastroenteric motility 44 The Respiratory System External respiration & internal respiration The respiratory system has two parts: 1. Conducting Portion:Nose → → → Terminal Bronchiole Functions: (1) Conducting air (2) Conditioning air: cleansing, moistening & warming air (3) Olfaction (4) Phonation 2. Respiratory Portion: Respiratory Bronchiole → → → Alveoli Function: Gas exchange I. Introduction: Respiratory epithelium: pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium Ciliated column cells Mucous goblet cells Basal cells Brush cells: sensory receptors Small granule cells: neuroendocrine cells II. Nasal cavity: Median nasal septum and superior, middle & inferior conchae 1. Vestibule: anterior Epithelium posterior Mucosa Lamina propria: 2. Respiratory Portion:pink Epithelium: Mucosa Lamina propria: rich in venous plexuses & mixed glands Countercurrent heat-exchange system 3. Olfactory Potion:yellowish brown Epithelium*: pseudostratified columnar epithelium Mucosa Lamina propria: serous glands of Bowman Supporting (Sustentacular) cells: * Basal cells: Olfactory (Sensory) cells: bipolar neurons, have olfactory vesicle & olfactory cilia Paranasal sinuses: 45 III. Nasopharynx: Epithelium: Mucosa Lamina propria IV. Larynx: Epithelium: Mucosa Lamina propria: V. Trachea and Bronchi: Epithelium: 1. Mucosa Lamina propria: 2. Submucosa:mixed glands in C.T. SIgA 3. Adventitia:“C” shaped or irregular hyaline cartilage and smooth muscles, fibroelastic C.T. VI. Lungs: 1. Bronchial Tree & Pulmonary lobule: d 1mm d 0.5 mm Primary Bronchi Bronchioles Terminal Bronchioles Respiratory Bronchioles Alveolar Ducts Alveolar Sacs Alveoli 2. Conducting Portion: (1) Cavity and wall: (2) Epithelium: (3) Goblet Cells: (4) Glands: (5) Cartilage: (6) Smooth Muscle: (7) Elastic fibers: Terminal Bronchioles: Clara cells: dome-shaped apex, secretory granules Ciliated cells: 3. Respiratory Portion: Respiratory Bronchioles Alveolar Ducts Alveolar Sacs Alveoli Alveoli Epithelium: (1) Type I Cells (Squamous Alveolar Cells) LM: squamous and thin EM: pinocytotic vesicle, junctional complex Functions: (2) Type II Cells (Great Alveolar Cell) LM: cuboidal cells, spherical nucleus & foamy cytoplasm 46 EM: lamellar bodies Functions:Synthesize and secrete pulmonary surfactant. Respiratory distress syndrome (hyaline membrane disease) (3) Blood-Air Barrier: Surfactant + Type I Alveolar cells + Basal Lamina Interstitial Space Capillary's Basal lamina + Endothelium (4) Alveolar Septum: C.T., rich in capillary and elastic fibers. (5) Alveolar Pore: (6) Pulmonary Macrophage: alveolar macrophage dust cell & heart failure cell 4. Blood Vessels: Pulmonary Circulation: functional circulation Bronchial Circulation: nutritional circulation 5. Pleura 47 The Urinary System Kidney I. Gross structure of the kidney 1. Renal capsule 2. Cortex (outer) dark brown and granular structure Cortical labyrinths + renal columns (of Bertin) 3. Medulla (inner) pale and radially striated structure Medullary pyramids + medullary rays • Renal lobe: medullary pyramid + renal column • Renal lobules: medullary ray + cortical labyrinths II. Histological structure of the kidney 1. Introduction: • Uriniferous tubules: Nephrons + Collecting tubules • Nephrons: Renal corpuscle + Tubule system • Renal corpuscle Glomerulus + Bowman’s capsule • Tubule system Proximal tubule + Thin limb + Distal tubule • Henle’s Loop: straight portion of the proximal tubule or thick descending limb the thin limb the distal straight tubule or thick ascending limb • Cortical nephrons • Juxtamedullary nephrons juxtamedullary nephron cortical nephron location adjacent to medulla size larger outer cortex smaller number loop few (15%) long numerous (85%) short function urine concentration reabsorption 48 2. Nephrons structural and functional unit 1) Renal corpuscle (1) Structure: Glomerulus + Bowman’s capsule + Bowman's space (urinary space) Vascular pole & Urinary pole a. Glomerulus (glomerular capillaries; glomerular tuft) Fenestrated capillaries Afferent arteriole Fenestrated capillaries Efferent arteriole Mesangium mesangial matrix intraglomerular mesangial cells Location: Function: supporting, producing mesangial matrix, phagocytosing, contracting, secreting chemical mediators b. Bowman’s capsule: double - walled epithelial capsule Parietal layer Visceral layer: modified Podocytes: Location: LM: EM: primary processes, secondary processes (pedicels), filtration slits and slits membrane Function: (2) Function of renal corpuscle: Filtration barrier (membrane): Structure • filtration slits diaphragm • Glomerular basement membrane (GBM): Lamina Rare Interna: fibronectin, proteoglycans (heparin sulfate) Lamina Densa : type IV collagen, laminin Lamina Rare Externa : fibronectin, proteoglycans • endothelium Function : selective filter (physical barrier, charge barrier) 2) Proximal Tubule Convoluted : in cortical labyrinths (CL) Straight : in medullary rays (MR) or medullary pyramids (MP) LM: small, uneven lumen, large acidophilic cuboidal cells, brush border EM: microvilli, canaliculi, lateral processes, membrane infoldings, large amount of Mit. Function: reabsorption, secretion 3) Thin limbs (1) Structure: simple squamous epithelium (2) Function: 4) Distal tubule Straight : in MR or MP Convoluted : in CL 49 LM: shorter, larger lumen, smaller, lighter cells EM: lack brush border, (Tamm-Harsfal protein) Function: regulated by Aldosterone & ADH LM number lumen simple cuboidal epithelium spherical nucleus cytoplasm EM brush border lateral boundary of the cell basal vertical striation apical microvilli apical canaliculi and vesicle lateral cell processes basal cell membrane infoldings Proximal tubule abundant smaller, irregular higher Distal tubule few larger, regular lower large, located centrally acidophilic, densely staining obvious invisible small, located near the lumen acidophilic, lighter staining absent visible faint long, abundant numerous prominent short, few absent extensive deeply few more deeply numerous more numerous elongated mitochondria Function 3. Collecting tubules and ducts collecting tubules cortical collecting ducts medullary collecting ducts papillary ducts cuboidal. columnar 1) Structure: pale-staining cytoplasm, lateral boundary of adjacent cells is clearly visible 2) Function: urine concentration Regulated by Aldosterone & ADH 4. Intrarenal collecting system Renal papilla minor calyx major calyx renal pelvis transitional epithelium C.T. smooth muscle 50 5. Juxtaglomerular apparatus (Juxtaglomerular complex) 1) Structure (1) Macula densa • Structure: in the distal convoluted tubule tall, narrow cells, densely staining nuclei closely packed together • Function: sensor of [Na+] (2) Extraglomerular mesangial cell (polar cushions) • Structure: • Function: signal transduction (3) Juxtaglomerular cells: • Structure: modified smooth muscle cells large cuboidal cells with secretory granules • Function: secretion of renin (vasoconstrictor) renin angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) angiotensinogen angiotensin I angiotensin II 2) Function: regulate blood pressure 6. The renal interstitium Interstitium: fibroblast, collagen, proteoglycan Interstitial cells: synthesis of prostaglandins, prostacyclin, Erythropoietin (EPO) 7. Vascular supply vasa recta (arteriolae rectae ) renal A. renal V. interlobar A. interlobar V. arcuate A. straight v. arcuate V. interlobular A. straight a. interlobular V. peritubular cap. network afferent arteriole glomerulus cap. network in capsule & outer cortex 51 efferent arteriole stellate V. Ureters, Bladder, Urethra 1. Mucosa 1) Epithelium: Ureters, Bladder: transitional epithelium layers ↑ Urethra: transitional epithelium → stratified squamous epi. 2) Lamina propria 2. Muscularis Ureters upper 2/3: inner longitudinal, outer circular lower 1/3: inner longitudinal, middle circular and outer longitudinal Urinary bladder: thick, helical arrangement 3. Adventitia 52 The Male Reproductive System I. Introduction: II. Testis Migration of primordal germ cells (PGCs) & Descent of testis Cryptorchidism Structure of testis: 1. Testicular capsule: (1) tunica vaginalis: surrounding the anterolateral aspect of each testis (2) tunica albuginea mediastinum testis lobuli testis (3) tunica vasculosa 2. Seminiferous tubule total length is nearly 0.5 km (1) tunica propria muscle-like myoid cells (2) basal lamina (3) seminiferous (or germinal) epithelium stratified epithelium 1) Spermatogenic cells Spermatogenesis & meiosis a. Spermatogonia: located in basal compartment, mitosis Dark type A spermatogonia: heterochromatin Pale type A spermatogonia: euchromatin Type B spermatogonia: b. Primary spermatocyte: the largest male germ cells, having chromosome within their nuclei. c. Secondary spermatocytes: short-lived cells d. Spermatid Spermiogenesis: round spermatids elongated spermatids, through shedding of much of their cytoplasm, rearrangement of their organelles, and formation of flagella Nucleus becomes condensed and elongated sperm head Golgi apparatus acrosome (acrosomal cap) (a specialized lysosome) proacrosomal granules acrosomal granule within a acrosome vesicle Centriole flagellum Mitochondria mitochondrial sheath Microtubuli manchette (caudal tube) Residual bodies are shed, and phagocytosed by Sertoli cell e. Spermatozoon morphologically mature Head Neck Tail: middle piece, principal piece, end piece Clonal nature of the germ cells 53 Cytoplasmic bridges & Syncytium of germ cells The cycle of seminiferous epithelium The waves of seminiferous epithelium 2) Sertoli cells a. Structure: LM: tall columnar cell; a large, pale, oval or irregular shaped nucleus with a prominent nucleolus; invisible lateral cellular limits. EM: lateral and apical cell membrane & nucleus with infoldings; many organelles; tight junctions & gap junctions. Blood-testis barrier Basal compartment Adluminal compartment b. Functions: Support, protection and nutrition of developing germ cells. Phagocytosis of residual bodies. Secretion. e.g.: androgen-binding protein (ABP), anti-müillerian hormone & inhibin, and a fructose - rich medium. Formation of blood-testis barrier. Regulation the release of spermatozoa 3. Interstitial tissue (1) Interstitial cell (Leydig cell): 1) Structure: LM: always in clusters; large, polyhedral cells, acidophilic cytoplasm, central located nucleus. EM: typical steroid-producing cells, containing large amounts of sER, mitochondria with tubular cristae, and numerous of lipid droplets. 2) Function: secretion of testosterone. (2) Others: including C.T., nerve, blood & lymphatic vessels. 4. intratesticular genital ducts: (1) tubuli recti (straight tubules): Lined by Sertoli cells in proximal half and simple cuboidal epithelium in distal half, supported by loose C.T. (2) Rete testis: A system of labyrinthine spaces housed within the mediastinum testis, lined by simple low cuboidal epithelium, supported by vascular C.T. (3) Ductuli efferentes: Undulated lumen lined by pseudostratified columnar E., supported by loose C.T., forming the head of the epididymis. III. Extratesticular genital ducts 1. Ductus epididymidis Forming the body and tail of the epididymis Lined by pseudostratified columnar epithelium of uniform height, composed of basal cells and tall principal cells, the latter have many long 54 stereocilia and are actively reabsorptive. Epithelium is supported by loose C.T. and abundant circularly arranged smooth muscles. 2. Ductus deferens (Vas deferens) A narrow lumen and a thick-walled tube lined by pseudostratified columnar epithelium with stereocilia, and surrounded by 3 layers of smooth muscle: inner and outer longitudinal layers and middle circular layer. Ampulla Spermatic cord: passes through the inguinal canal, including arteries, veins and ductus deferens. Pampiniform plexus Countercurrent heat-exchange system 3. Ejaculatory duct Lined by a simple columnar epithelium, and supported by loose C.T. 4. Urethra (1) Prostatic urethra Transitional E. (2) Membranous urethra Pseudostratified columnar E. (3) Spongious part (bulbous part and pendulous part) Pseudostratified columnar E. Glands of Littre IV. Accessory sex glands 1. Seminal vesicles Highly coiled tubuli, lined by pseudostratified columnar epithelium, and supported by fibroelastic C.T. and smooth muscles, producing fructose rich seminal fluid that is energy source for sperm motility. 2. Prostate gland An collection of branched tubuloalveolar glands, the epithelium ranges from simple cuboidal - columnar to pseudostratified columnar depending on the man's hormonal states, and the glands are embedded within a fibromuscular stroma. Three groups of glands concentrically arranged around the urethra: (1) Mucosal glands (central zone) (2) Submucosal glands (transition zone) (3) Main glands (peripheral zone) Prostatic concretions (corpora amylacea) 3. Bulbourethral glands Tubuloalveolar, mucus-secreting glands, lined by a simple cuboidal or columnar epithelium. V. Penis 1. Structure: Each of three columns of erectile tissue, which is encircled by tunica albuginea, has large venous sinuses separated by trabeculae. (1) Corpora cavernosa of the penis: Paired, located dorsally. 55 Helicine arteries & Intimal cushion (2) Corpus cavernosum of the urethra (corpus spongiosum): ventrally located, containing penile urethra. 2. Functions: (1) Urination (2) Copulation organ Penile erection: a hemodynamic event 56 The Female Reproductive System I. Ovary 1. Oogenesis: miosis of oocyte oogonia primary oocytes ①secondary oocytes ② ovum + + polar body polar body stopped in prophase of meiosis I, completed before ovulation stopped in metaphase of meiosis II, completed when fertilization taken place 2. General structures 1) Ovarian surface epithelium: simple squamous/cuboidal epithelium 2) Tunica albuginea dense C.T. 3) Cortex stroma: C.T., stromal cells, smooth muscle gamete - producing structures & derivatives 4) Medulla: loose C.T. 5) Hilum hilus cells: secrete androgen 3. Structures in cortex 1) Follicular growth follicle: an oocyte + follicular cells basement membrane surround the follicles growing follicles (1) Primordial follicles primary oocyte + a single layer of flattened follicular cells (2) Primary follicles • primary oocyte: growth rapidly • granulosa cells (follicular cells) flattened cuboidal, unilaminar multilaminar • zona pellucida structures: ZP1, ZP2, ZP3 functions: (3) Secondary follicles • follicular cavity (antrum): follicular fluid • cumulus oophorus: primary oocyte + corona radiata • stratum granulosum • basement membrane 57 • theca folliculi: theca interna: theca cells, cap. theca externa: C.T., smooth muscle cells • estrogen produced: theca interna – follicular cell synergism (4) mature (Graafian) follicles oocyte: primary secondary granulosa layer: proliferation decreased 2) Ovulation after LH surge Process: stigma secondary oocyte + zona pellucida + corona radiata 3) Corpus luteum (1) Formation (2) Structure granulosa lutein cells: centrally located, numerous, large, acidophilic theca lutein cells: peripherally located, smaller (3) Function secrete progesterone, estrogen (4) Types • corpus luteum of menstruation • corpus luteum of pregnancy relaxin 4) Corpus albicans 5) Follicular atresia oocyte degeneration, granulosa cells degeneration happened at any stage of follicle interstitial glands structure: hormones: 4. Function of ovary • produce ovum • secrete female sexual hormone II. Oviducts (Uterine Tubes) 1. Gross structure Infundibulum, Ampulla, Isthmus, Intramural Portion 2. Microscopic Structure 1) Mucosa simple columnar epithelium hormone sensitively • ciliated cell • secretory cells (peg cells) lamina propria 2) Muscularis inner circular layer, outer longitudinal layer 58 3) Serosa longitudinal folds smooth muscle infundibulum: fimbriae ampulla: isthmus: intramural portion: III. Uterus body (corpus), fundus, cervix 1. Structure of uterine body 1) Perimetrium serosa 2) Myometrium 3 layers: inner longitudinal layer, middle circular layer, outer longitudinal layer large blood vessels in middle layers bundles of smooth muscle fibers + C.T. 3) Endometrium (1) Simple columnar epithelium ciliated cells, secretory cells (2) Lamina propria: stromal cell uterine glands: (3) Basalis • the closed tips of the uterine glands • straight arteries • not shed (4) Functionalis • cyclic changes • hormone responsive • spiral arteries 2. Cyclic changes in the endometrium Menstrual cycle menstrual proliferative phase secretory phase phase time (day) 1-4 5-14 15-28 ovary phase follicular phase luteal phase hormone reduction estrogen progesterone estrogen spiral A. elongated elongated constricted relaxed coiled highly coiled broken uterine glands broken straight highly coiled epithelial cells necrosis proliferated secreting glycogen stroma cells necrosis proliferated differentiated functionalis detached regenerated edema 59 3. Uterine Cervix 1) Mucous (1) Epithelium not desquamate cervical canal: simple columnar epithelium protio vaginalis: stratified squamous epithelium (2) Cervical glands 2) Myometrium few smooth muscle fibers , mainly C.T. 3) Adventitia IV. Vagina fibromuscular tubular structure 1. Mucosa 1) Epithelium stratified squamous nonkeratinized epithelium glycogen → lactic acid 2) lamina propria loose C.T., rich in elastic fibers, highly vascular 2. Muscularis 3. Adventitia dense C.T., rich in elastic fibers V. Mammary Glands dense C.T. + adipose tissue + compound tubuloalveolar glands 1. Structures: 1) Compound tubuloalveolar glands alveoli intralobular ducts interlobular ducts lactiferous ducts lactiferous sinuses opening simple cuboidal epithelium simple columnar stratified cuboidal/columnar stratified squamous epithelium 2) Alveoli secreting cell: milk secretion myoepithelial cells 2. Different state of mammary gland 1) Inactive (resting) mammary gland inactive duct system 2) Active mammary gland pregnancy: alveoli proliferate lactation: milk secretion & accumulation 60 The Eye and the Ear Eye The Eyeball I. The wall of eyeball A. Tunica fibrosa (external layer) Cornea limbus cornea sclera 1. Cornea: (1) Epithelium: stratified squamous non - keratinizing epithelium (2) Bowman’s membrane (anterior limiting membrane) (3) Stroma (substantia propria) collagen fibers, chondroitin sulfate, keratan sulfate (4) Descemet’s membrane (posterior limiting membrane) collagen fibrils (5) Endothelium: simple squamous epithelium 2. Limbus cornea trabecular meshwork, sinus venosus sclerae (canal of Schlemm) 3. Sclera many bundles of collagen fibers scleral spur lamina cribrosa B. Uveal coat (vascular layer) iris ciliary body choroids 1. Iris: pupil, anterior chamber, posterior chamber (1) Anterior border layer: fibroblasts & melanocytes (2) Iris stroma: blood vessels, melanocytes (3) Epithelial layer a. The anterior layer: dilator pupillae muscle (sympathetic) sphincter pupillae muscle (parasympathetic) b. The posterior layer: pigmented epithelial layer cuboidal epithelial cells 2. Ciliary body (1) Ciliary muscle: (2) Vascular layer (3) Ciliary epithelium a. The outer layer: pigmented, simple cuboidal epithelium b. The inner layer: nonpigmented, simple cuboidal epithelium secreting aqueous humor forming ciliary zonule 61 3. Choroid (1) The outer layer: large vessels, melanocytes (2) The middle layer: choriocapillary layer (3) The inner layer: glassy or Bruch’s membrane C. Retina Retina ora serrata double - layered epithelium 1. Pigment epithelium melanin, lamellar debris, vitamin A, rhodopsin 2. Photoreceptors: (1) Rods: 120milion a. The outer segment: membranous discs 11-cirretinae + opsins rhodopsin b. The inner segment: M, rER, ribosomes (2) Cones: 700milion a. The membranous discs are continuous b. Visual pigments (blue, green, red) c. enriched in fovea 3. Bipolar cells: synapses 4. Ganglion cells: synapses 5. Ten layers (1) Pigment epithelial layer * (2) Layer of rods & cones * (3) Outer limiting membrane (4) Outer nuclear layer * (5) Outer plexiform layer (6) Inner nuclear layer * (7) Inner plexiform layer (8) Ganglion cell layer * (9) Nerve fiber layer (10) Inner limiting membrane 6. Macula lutea: 3-4mm, fovea centralis only cones 7. Optic disc and Optic nerve Papilla of optic verve II. The Refractive Media A. Lens 1. Lens capsule: collagen fibrils 2. Lens epithelium: simple cuboidal epithelium 3. Lens fibers: hexagonal prismatic 4. Accommodation B. Aqueous humor 1. Production 2. Drain passage C. Vitreous body 62 1. Hyaluronic acid, vitrein, collagen fibrils 2. Hyalocyte III. Light conducting passage Accessory Organs of the Eye I. Eyelids A. Skin: eyelash, glands of Zeis glands of Moll B. Hypodermis C. Muscular layer: Orbicularis oculi muscle Palpebralis Palpebral muscle D. Tarsal plates: tarsal (Meibomian) glands E. Conjunctiva II. Lacrimal gland The Ear I. External ear A. Auricle B. External auditory meatus: ceruminous gland C. Tympanic membrane II. Middle ear A. Tympanic cavity: malleus, incus, stapes Simple squamous or low cuboidal epithelium B. Eustachian tube III. Internal ear A. Osseous labyrinth 1. Vestibule and semicircular canals: Oval window, Round window 2. Cochlea modiolus, scala vestibuli & scala tympani Helicotrema, cochlear duct B. Membranous labyrinth 1. Membrane semicircular canals, Utricle, Saccule simple squamous or cuboidal epithelium (1) Macula utriculi and macula sacculi a. Supporting cells b. Hair cells: stereocilia, kinocilium c. Otolithic membrane, otoliths (2) Crista ampullaris: Cupula 63 2. Cochlear duct (1) Vestibular membrane (2) Spiral ligament, stria vascularis (endolymph) (3) Osseous spiral lamina Membranous spiral lamina (Basilar membrane) Auditory string (4) Tectorial membrane (5) Organ of Corti (spiral organ) a) Pillar cell b) Phalangeal cell c) Hair cell 64