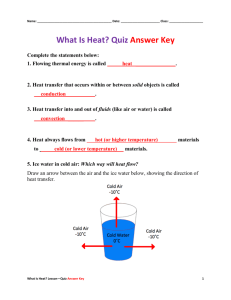
watch what happens to the liquid. Answer the questions that follow
advertisement

STATION 1 LIQUID HOT LAVA PROCEDURES: Observe the lava lamp for 45-60 seconds. Answer the following questions based on your observations. Please do not move the lamp or touch the lamp. They can break and may be HOT. 1. How is heat being transferred in the lava lamp (convection, radiation, or conduction)? Hint: there may be more than one. a. Convection: when the hot blobs move up through the liquid they are transferring heat to the top of the lamp. b. Conduction: when the air molecules (top of lava lamp) and liquid molecules touch each other they transfer some heat. The base also touches the lamp and heats a piece of metal inside the lamp. c. Even a little Radiation- the lamp is not really touching the bottom of the glass. Radiant heat transfer is occurring from the light bulb to the wax at the bottom of the lamp through the glass. 2. Describe what is happening in the lava lamp as it relates to hot and cold air and how they move in the atmosphere? a. Hot air tends to rise and as it rises it cools. As the air cools, its density increases and starts to fall back towards the ground. Once it goes back towards the ground, it is warmed by the heat from the ground and starts to rise again. This is one of the driving forces behind wind on our planet. Cool, huh? 3. Why do the blobs of material go up then back down? What is happening in terms of heat? Where does the heat from the rising blobs go once they get to the top of the lamp? a. They go up because they are being heated and their volume increases which means the density decreases (spreads out and gets lighter). The less dense blobs float upwards until they cool and fall back to the bottom of the lamp. Most of the heat is lost to the air just outside the lamp. b. Heat is being transferred to the blobs and they rise. That same heat is lost to the atmosphere, which causes the blobs to sink back to the bottom because their density increases as they cool down. c. The heat flows to areas that are cooler (remember heat is what moves, not coldness). The air right outside the lava lamp is cooler. The heat from the lava lamp radiates outwards and also warms the air through conduction (the air that is touching the top of the lava lamp gets warmer. This even results in little convection currents of warm air rising (kind of like when you drive through the desert and see the “heat” rising off the hot road. 4. Convection heat transfer can only happen in which of the three states of matter (solid, liquid, or gas)? a. Liquid or gas only. Solids do not flow. When solids flow, they are called liquids. Try it sometime. Take frozen water (an ice cube) and see if it starts to flow when you place it on the ground. Take liquid water (tap water) and pour it on the ground. Notice how the liquid water “flows”. Now, take a hot (not too hot as to burn you through conduction) shower (make sure this okay with your parents) and watch the steam rise (flow). Cool, huh? 5. Where does rising air get energy to rise? What is the source of most all energy on our planet? a. The sun. The sun, the sun, the sun STATION 2 Foiled Again (Black vs. White vs. Foil) PROCEDURES: Without touching the sheets covering the thermometers, look at the three sheets (black, white, and foil) and record the temperature for each. Answer the questions that follow. QUESTIONS: 1. Which sheet has the highest temperature reading? Why? Which has the lowest? Why? a. Black. This is because black absorbs heat better than white or the foil. Black is the absence of color (it is not a color really) the reason something appears black is because no light is reflected back to your eyes. All the colors are absorbed into the black object. Light is a form of energy. This is why black gets hotter than other colors (it is absorbing all that energy). b. The foil. This is because the foil reflects most of the light (and heat energy) back into the atmosphere. This is the same thing that happens on overcast and cloudy days. That is why it is cooler on cloudy days compared to clear days. Amazing. 2. Which land type would you expect to find hotter at mid day (desert or snow covered mountains)? Give at least two reasons why? a. The desert. First, because it is a darker color than white (snow being white). Second, areas where there is snow need to be cold so water can freeze and become snow. Also, as you go up in elevation (the mountains) the temperature drops. FYI-Temperature drops at approximately 10 F for each 1000 feet you go up in elevation. This is assuming a whole bunch of other things are not affecting the temperature (like humidity and other weird things that I do not even understand). 3. If you were going out to build a house in the desert, what color and what direction would you want the windows to face? a. You would want a white or light color house. Your windows should have a photochromic (it becomes lighter or darker depending on the amount of light hitting the glass) or mirror tint on them as well. b. Your windows should face northeast so that the midday sun does not heat up you house like a giant greenhouse. c. FYI-When you go skiing in the mountains you usually have ski resorts that face north or northeast. Mammoth faces in this direction except for the backside (to the right of the main lodge if you are looking up the mountain or right of chair 23 (up to the Cornice) as you go up the mountain. 4. If you had to buy a Jeep to travel across the desert this summer, in search of ultimate place to read a good book, what color would you want your new Jeep to be? Why? a. White or silver. It will stay cool in the sun (especially because you could not afford the air conditioner or the convertible). b. Black cars show dirt easily compared to white. Since you are in a desert, there is too little water to wash your Jeep every week. This answered was made possible by Bruce Kantelis. This is the reason he gave for not buying the black Jeep. 5. What type of heat transfer is causing the thermometers to heat up? Write down the temperatures of the three thermometers. a. It is a combination of radiation and conduction. Radiation from the lamp causes the paper or foil to absorb heat. The heat energy that is absorbed is transferred to the thermometer through conduction. The thermometer is touching the paper and or foil and absorbs heat from it. b. White = 26 to 28, Black = 28 to 30, and Foil = 24 to 26 Celsius 6. Why is the desert so hot during the day and cold at night (think moisture here)? a. It gets really hot in the day because there is little water in the air. Water is a very, very good absorber of heat (it can store a lot of heat before increasing in temperature). It has a high heat capacity. That is why the radiator in most cars uses water to cool the engine verses air. b. At night, the air in the desert is dry and has very little moisture in it to hold heat. The temperature at night drops quickly because there is no way to store the heat from the day. STATION 3 The Thermometer Never Lies PROCEDURES: Use the readings on the three thermometers to answer the following questions concerning temperature. There should be one thermometer in a test tube of water, one in a mound of clay (putty), and one inside a test tube filled with air. Please do not touch the thermometers. All that is required is to read the temperature from each thermometer. QUESTIONS: 1) Which thermometer has the highest reading (clay, water or air in the test tube)? a) They should all be the same (21-25oC). For the most part, you should have had a temperature about the low 20s C or the mid 70s F. 2) Which object would you think would feel the coolest if you touched it? a) The water. This is because water is a very good absorber of heat (has a high heat capacity). That is why you put a wet towel on your head when you have a fever or want to cool down. 3) What is temperature a measure of? a) It is a measure of energy (heat energy) in a substance. It just like showing you how fast (like a radar gun) the molecules in a substance are moving. 4) Do the readings on the thermometers seem right? Explain? a) Yes, because all three objects are in an environment (The classroom) that has an air temperature of 21-25o C (70-77o F). We think water should be cooler because it is what we use to cool things down (like ourselves). We usually do not rub clay all over our skin to cool down Remember, water is good at absorbing heat (high heat capacity) and that is why logic would have told you that the water should have been the coolest (LOGIC was wrong this time. Ironic? No). 5) Why does the air get hotter than the ocean? Why does the ocean only change about 200 F through out the year, but the air can go from over a 1000 F to 300 F in our area? a) This is due to the ability of water to absorb large quantities of heat (energy) before rising in temperature. Try blowing on your hands with your hot breath. You feel that it is hot (because it is easier (less energy is needed) to raise the temperature of air compared to water). Do the same thing to a small cup of water and see if you notice the temperature change (probably not unless you cheated or something). 6) What does density have to do with heat conduction? a) Things that have low densities tend to not absorb heat well (air, wood, fiberglass insulation (mainly air)). Things that have higher densities tend to absorb heat very well (metals). Air is a bad conductor of heat (low density and little matter). STATION 4 Heat by Touchy, Touchy PROCEDURES: Touch each of the three items on the counter (metal, plastic, and wood). Answer the questions that follow. QUESTIONS: 1) Which material feels the coolest? Why? a) The metal. This is because metal is a very good conductor of heat (and electricity for that matter). That is why we cook with metal pots and not plastic or wood pots and pans. 2) How is heat being transferred when you touch one of the objects? a) Conduction – heat by touchy, touchy 3) What is absorbing the heat? Your hand or the object? a. The object is absorbing heat or energy from my hand. I am not absorbing cold from the object. Heat is the only thing that flows (in the universe). That is how ice cubes work. They absorb heat from your drink and in the process melt. Cool, huh? 4) In the real world where does this type of heat transfer take place? a) Conduction occurs when hot and cold air masses meet. It can also occur when air is warmed by the heat from the ground (air molecules touching the earth) on a hot day. It occurs when you cook food in a pan or lay down on warm sand after being in contact with the cold water where through conduction with the water you lose heat to the water. 5) Define the three types of heat transfer (short definition): Conduction: heat transfer through touch Convection: heat transfer through movement (flow) of a liquid or air. Radiation: heat transfer through space (not matter) in the form of waves. PART II ove THE L METER (a.k.a. Mr. Love Bird) Hold Mr. Love Bird’s belly with one hand (do not hold it too tight, it may kill the love bird) watch what happens to the liquid. Answer the questions that follow. Do not spend the entire time seeing if you are a good lover. Please do not break. 1. What type of heat transfer is this? Explain why. a. Conduction. Why not? It is conduction because your hand is touching the glass. Heat is being transferred from your hand to the glass and into the liquid. The liquid has a low boiling point (around 85o F to 95o F) (water is 212o F or 100o C) and boils after a few seconds of being heated by your hand. You could also say convection because the heated liquid is moving up the tube and cools at the top and comes back down and repeats the cycle over and over and over again. 2. What is happening to the liquid as you hold you hand against the bottom? a. It is boiling because heat is being absorbed from your hand and transferred to the liquid by direct contact. This causes some of the liquid to evaporate (turn from liquid to gas). STATION 5 Let There be Light PROCEDURES: Have your partner stand a few feet away (1-2 feet) from you. Turn on the light (little red button on backside of lamp) and shine it towards your partner’s hand (but, do not pick the light up). Turn off the light and switch with your partner. Repeat the above procedures. Turn off the light before answering the questions that follow. 1. What type of heat transfer might this demo represent? a. It is mainly radiation (like the sun to the Earth). There is a little conduction (air molecules that are touching the glass) between the air molecules, but the great majority of heat transfer is radiation (because the sun is rad and stuff). b. FYI (It could be convection if a fan was blowing the heat away from the hot metal parts and allowed to blow the warm air around the room). 2. Did you feel the heat from the light when standing 1-2 feet away? a. Yes you did, yes you did. 3. Does this type of heat transfer need matter to occur? In what form is the heat transferred? a. No, it does not need matter or air to occur. It travels through space and space is a vacuum (yes, space does suck because it is a vacuum). b. The heat is being transferred in WAVES – HEAT WAVES. 4. Give an example of this type of heat transfer? a. Tanning salon, heat lamps at McDonalds, the sun, or heat from a campfire. 5. Some people (Mr. Mathot) say that physics makes the world go around. Some people (Mr. Mathot again) have just realized that the sun makes the world go around. Explain what I mean by this. Use 3 to 86 sentences to explain. a. All the energy on this planet (heat) came from the sun (except from heat from inside the Earth). This includes all the planets, food, gas in our cars and materials we use each day (that were once living). Energy from the sun is what makes air and water heat up and move and that movement of air and water is what creates weather on our beautiful planet. Oh yes, the suns gravitational force is what keeps us in orbit along with our inertia. STATION 6 PLASMA BALL PROCEDURES: Place your hand on top of the sphere. Use your observations of what is happening and L O G I C to answer the following questions. 1. What happens when you put your hand on the sphere? a. The “lightning” is attracted to where your hand is placed on the sphere. This is because there is a buildup of negative charges on the metal ball inside the sphere. Your hand is more positive than the middle, so it attracts the negative charges (opposites attract, likes repel). The place where your hand is touching starts to get warmer because energy is being transferred from the little light bolts, to the glass, and then to where your hand is touching. 2. What type of heat transfer might this demo represent? a. Conduction (heat transfer through contact). Your hand gets hot from touching the glass if you keep it there long enough (but not too long). 3. Where is the heat coming from and then going to? In other words, what is absorbing heat and from where is it absorbing the heat? a. The heat is coming from the electrons (which have energy) that are hitting the glass at the place where your hand is touching. This causes a buildup of energy (heat) due to all of those little electrons colliding with the glass. b. Your hand absorbs this energy from the plasma ball. The longer you keep your hand there the hotter it will get because you are absorbing more energy. 4. Why does the sphere act as it does when you touch it (think about air compared to your skin and which is the better insulator and which the better conductor of electricity)? a. The electrons are “looking” (seeking might be a better word) for the path of least resistance. Your hand conducts electricity better than the gas in the sphere. That is why lightning has a zigzag pattern and not a straight lightning bolt (air is a good insulator and a poor conductor of heat and electricity). (Bonus question & answer) What is really happening in the plasma ball? Electrons are building up in the center sphere and are being pushed towards the glass. Now, the electrons really do not want to jump from the middle to the outside of the sphere put the voltage is strong enough to get them moving. Remember, like charges repeal. All this negative charge in the middle cause many unhappy particles. There is not enough room for all this negativity so some of the electrons are forced to leave. The electrons do not like traveling through the gas because the gas does not conduct electricity very well. It is an insulator. The reason you see light is because the electrons in the gas are getting excited about all the hoopla and need to release the extra energy they are receiving. They release the energy as light (photons). The reason why the lightning goes towards your hand is because your hand is a better conductor of electricity compared to the gas in the sphere or the glass itself. Your hand has a positive charge compared to the charge inside the plasma ball. NOTE: Some people attract the negative charges better than others do. Don’t worry, it doesn’t mean you’re a good or bad lover (unlike the love meter). BACKGROUND - Lightning Lightning is caused by a buildup of electrical charges in the atmosphere. This occurs when clouds rub past one another. Things in nature like to be balanced so you get lightning. Use the plasma ball to assist you in answering the questions. 5. When is there lightning (what type of weather)? Where does lightning tend to strike (what objects on the ground)? Where might you want to be in a lightning storm? a. During thunderstorms or unstable weather. This would be when two different air masses meet. b. It tends to strike tall objects (trees, building, and people standing up in open fields) and metal objects (lightning rods). This is because it is looking for the shortest path between the clouds and the ground (or the ground and the clouds- about 10 to 20 % of lightning goes from the ground to the sky (because of the buildup of charges in the ground). Remember, air is an insulator and not a good conductor of electricity. You conduct electricity better than the air. c. Inside of a building, inside a car and not touching any metal parts, in a tight ball in an open field. YOU DO NOT WANT TO HIDE UNDER TREES, METAL THINGS OR LIE DOWN IN A FIELD (all very bad and potentially deadly). 6. Why do you see lightning before you hear the thunder? a. Light travels faster than sound. Light travels at 300,000 meters/second or 186,000 miles per hour and sound travels at 1200 km/h or 750 miles per hour. You can tell how far lightning is by counting as soon as you see the lightning. Once you hear the thunder, stop counting. Every 5 seconds is roughly equal to 1 mile away from you. 7. Where does lightning come from and go to (strike)? (more than 1 answer) a. 50 to 70 % of lightning goes from cloud to cloud (like static cling in your clothes drier), 20-30% from cloud to ground and 10-20% from ground to sky.