Applied Physics 090

Metric System
Applied Physics 090
Lab 1 Name ______________________________
Partner’s Name ______________________
Partner’s Name ______________________
Equipment
Vernier calipers, micrometer calipers, mass unknowns, 50 ml graduated cylinder, meter stick, triple beam balance
Purpose
The purpose of this lab exercise is to become familiar with the metric units of length, volume, and mass (weight).
Length
The unit of length is the meter, which is a little longer than a yard. Other units of length are based on the meter and differ according to the prefix of the unit, some of which are listed in the table below.
Prefix kilo- centi- milli-
Factor
1000
1
100
1
1000
Example
1 kilometer (km) = 1000 meters (m)
100 centimeters (cm) = 1 meter (m)
1 millimeter (mm) = 0.001 meter (m)
10 millimeters (mm) = 1 centimeter (cm)
Procedure
Using a meter stick, measure the following items in the units given. Measure as accurately as you can. For instance, if the measurement is 1.9 cm, don't call it 1 or 2, but rather 1.9 cm.
1. Thickness of lab table.
2. Length of lab table.
________ cm
________ m
________ mm
________ cm
3. Width of lab table.
4. Width of thumbnail.
5. Height of door.
6. Your height.
________ m
________ cm
________ m
________ m
________ cm
________ mm
________ cm
________ cm
7. Width of pencil
8. Length of this paper.
Clark College Physics Dept
________ cm
________ m
– 1 –
________ mm
________ cm ________ mm
Metric System
9. Length of a 12 inch ruler.
10. Length of one inch.
________ cm
________ cm
________ mm
________ mm
11. There are several items labeled A, B, C etc. Choose one and carefully measure its length and diameter in cm with a meterstick. item = ________ length = ________ diameter = ________
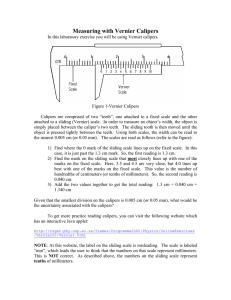
12. Use a Vernier calipers to measure the diameter of this object.*
13. Use a micrometer calipers to measure the diameter of this object.*
14. a) How accurate are the Vernier calipers? b) How accurate are the micrometer calipers?
* Please ask the lab instructor for information on the use of these devices if you are not familiar with them.
Volume
The unit of volume is the liter, which is a little larger than the quart. The liter is composed of
1000 cubic centimeters (cm3) or (cc). Each cubic centimeter is the volume of a cube or box which has sides 1 cm long.
1 cm3 (actual size)
Clark College Physics Dept
– 2 –
Metric System
Since the cm3 or cc is 1/1000 of a liter, it also has another name, milliliter (ml). A graduate is a device for measuring the volume of fluids. When a liquid is poured into a graduate, it forms a curved surface called a meniscus. See diagram.
The correct reading is 26 ml
2.
3.
4.
Mass or Weight
In this course, mass and weight will be taken to mean the same thing. The unit of mass in the metric system is the gram. This is the mass of one cm 3 of water. A nickel "weighs" about 5 g. 1000 grams is a kilogram, which weighs 2.2 pounds.
1.
Procedure
Weigh all of the sample items using the triple beam balance.
Remember 1 gram = 0.001 kilograms.
Item Weight in grams Weight in kilograms
C
D
A
B
E
Weigh an empty 50 ml graduate to the nearest 0.1 g.
Weight of empty graduate = __________ g
Fill the graduate with 30.0 ml of water and find its weight.
Weight of filled graduate = __________ g
What is the weight of the water?
Weight of water = __________ g
Clark College Physics Dept
– 3 –
5.
7.
6.
Metric System
The density of a substance is defined to be its weight divided by its volume, or in formula form:
or even shorter form:
Determine the density of water:
Remember cm3 is the same as ml. Read g/cm3 as grams per cubic centimeter.
The volume of a cylinder is given as
0.785 D2 x H or 0.785 x Diameter x Diameter x Height.
Find the volume of the object you chose in Part 2, Item 11.
(Use the value for the diameter from Part 2, Item 13.)
0.785 x _______ x _______ x _______ =
Now find the density of this object. You found its weight in Part 3, Item 1.
Clark College Physics Dept
– 4 –
Metric System
Questions
1.
2.
What is your weight in kilograms? _____________________
(There is a kilogram scale in the lab.)
Which is more accurate, a Vernier calipers or micrometer calipers?
3. Which is more dense, a pound of feathers or a pound of lead? _____________
4. Following is a list of densities. Determine the material that you were working with in Part 3 by comparing its density to those in the table.
Density (g/cm3)
1.75
2.70
7.86
8.44
8.93
11.30
7.13
I had item ___________.
My material was ___________.
Material magnesium aluminum iron brass copper lead zinc
Clark College Physics Dept
– 5 –