PHYSICS 20: Math of Physics * Measurement
advertisement

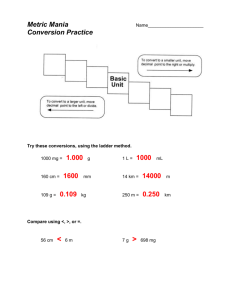
SCIENCE 9: Atoms & Elements – Measurement 1. Measurements: all measurements have some uncertainty because of the instrument used to make the measurement. Measuring instruments have markings called graduations. There are spaces between the graduations and these spaces are the source of the uncertainty. The larger the spaces, the greater the uncertainty. The last digit in any measurement is an estimate by the person carrying out the measurement. a. If the measurement falls directly on a graduation, then the measurement should end in a zero (0) to show that the measurement is directly on the graduation. cm 0 10 20 30 40 50 b. If a measurement falls between two graduations, then the experimenter should estimate where the measurement falls between the graduations. cm 0 10 20 30 40 50 2. Units of Measure: All measurements include some form of unit used to express the type of measurement. a) Length units: metre, cm, mm, km, light-year b) Time: second, minute, hour, year c) Mass: gram, kg, mg, tonne d) Volume: litre, ml, cm3, cc e) Temperature: ºC, Kelvin Measurement Practice: LENGTH: This page: Length = cm This line: cm VOLUME: Example #1: Example #2: Example #3: Width = cm MASS: Example #1: g Example #2: g Example #3: g Example #4: g TEMPERATURE: Example #1: Example #2: SCIENCE 9: METRIC MEASUREMENT Length Measurement: o millimeter – mm o centimeter – cm o metre – m o kilometer – km Mass Measurement: o gram – g o kilogram – kg Volume Measurement: o cubic centimeter – cm3 – cc o millilitre – mL o litre – L Metric Prefixes: kilo (k) = 1000 Move DECIMAL to the RIGHT hecto (h) = 100 deka (dk) = 10 BASE UNIT (metre or gram or litre) deci (d) = 1/10 = 0.1 Move DECIMAL to the LEFT centi (c) = 1/100 = 0.01 milli (m) = 1/1000 = 0.001 Common Conversions 1 km = 1000 m 1 cm = 1/100 m = 0.01 m 1 m = 100 cm 1 mm = 1/1000 m = 0.001 m 1 m = 1000 mm 1 kg = 1000 g 1 L = 1000 mL 1 m3 = (100 cm)3 = 1 000 000 cm3 1 cm3 = 1 mL FOR H2O: 1 cm3 = 1 mL = 1 g SCIENCE 9: METRIC CONVERSION 1. 2.5 m = cm = mm 2. 3.8 m = mm 3. 3.4 km = m= cm 4. 10.2 km = m= cm 5. 1.7 kg = 6. 3.6 kg = 7. 6.4 L = mL 8. 8.8 L = mL 9. 150 cm = m 10. 225 cm = m 11. 28 mm = cm 12. 45 mm = cm cm = g g 13. 450 g = kg 14. 715 g = kg 15. 591 mL = L 16. 1250 mL = L 17. 591 mL = cm3 18. 325 cm3 = mL 19. 800 mg = g 20. 450 mg = g Graduated Cylinder Worksheet A graduated cylinder can have numerous scales. 1) Determine the value for the minor grids on the cylinder. a) ______ mL a) __________ mL b) _______ mL c) _______ mL b) _________ mL c) _______ mL 3) Draw in the meniscus for the following readings: a) 49.21 mL b) 18.2 mL c) 27.65 mL d) 63.8 mL d) _______ mL d) _________ mL