Measurements and the Metric System
advertisement

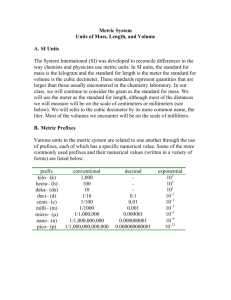
Measurements and the Metric System The Metric System • A universal measurement system • Also called the International System or SI units • Only three countries worldwide don’t use the metric system (USA, Burma, and Liberia) The Metric System • Based on multiples of ten (this makes it easy to use) • Uses prefixes to identify larger or smaller units of measure Common Symbol Multiple Prefixes kilo K 1000 centi c .01 milli m .001 Metric Conversions - Length x 1000 Km ÷ 1000 x 10 m x 10 dm ÷ 10 x 10 cm ÷ 10 mm ÷10 Metric Conversions - Volume x 1000 Kl x 10 l ÷ 1000 x 10 dl ÷ 10 x 10 cl ÷ 10 ml ÷10 Metric Conversions - Mass x 1000 Kg x 10 g ÷ 1000 x 10 dg ÷ 10 x 10 cg ÷ 10 mg ÷10 Length • A measure of linear distance • Basic unit of length is the meter (m) • Measurements made with a meter stick or metric ruler •The entire meter stick represents one meter •Each number represents a centimeter (there are 100 centimeters in a meter) •Each little line is a millimeter (there are 1000 millimeters in a meter) Area • The amount of surface included within a set of boundaries • Determined by measuring the length and width of an object, then multiplying Length = 14 cm Width = 7 cm Area = 14 cm x 7 cm = 98 cm2 (Area is always expressed in square units) Volume • Volume is the space that an object occupies • Represents the length, width, and height of an object • For solids, measurements are based on units of length (ex. cm3) and can be calculated using specific formulas Calculating the volume of a rectangular prism Volume of a rectangular prism = length x width x height (l x w x h) 4 cm Length = 10 cm Width = 3 cm Height = 4 cm 3 cm 10 cm Volume = l x w x h = 10 cm x 3 cm x 4 cm = 120 cm3 Calculating the volume of a cylinder Diameter = 10 cm 20 cm Volume of a liquid •A graduated cylinder is used to accurately measure the volume of liquids in milliliters •Determine the volume in a graduated cylinder by reading the bottom of the meniscus at eye level •Once the volume of a liquid is known, it can be converted to a “solid volume” by using the formula 1 ml = 1 cm3 Mass •Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object •Mass is measured in grams using a balance •The mass of an object remains the same, no matter where in the universe it is measured Weight Weight is a measure of the gravitational force exerted on an object by a massive body •Weight is measured in Newtons (N) using a spring scale •Weight varies from place to place depending on the strength of the gravitational force Your weight on Earth = Mass (Kg) X 9.8 m/s² (Earth’s surface gravity) For a person with a mass of 45 Kg Weight = 45 Kg X 9.8 m/s² = 441 N Gravity Gravity is the force of attraction between objects The strength of the gravitational force between objects depends on: - The distance between the objects ( the gravitational force between objects decreases with distance) -Mass ( the greater the mass of an object, the greater it’s gravitational force) Density •Density is the mass of a specific volume of an object •Density is calculated by dividing the mass of an object by its volume •Units for density are usually expressed in grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm3 ) •Since the density of water is 1 g/cm3 anything with a density less than 1 g/cm3 will float in water and anything greater will sink Calculating Density 3 cm A Volume of Object A = 5 cm x 2 cm x 3 cm = 30 cm³ Mass of Object A = 150 grams (measured on a balance) 2 cm 5 cm Density = Mass Volume Density of Object A = 150 grams = 5 g/cm³ 30 cm³