Section 4 - Coppell ISD
advertisement

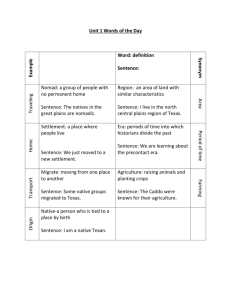
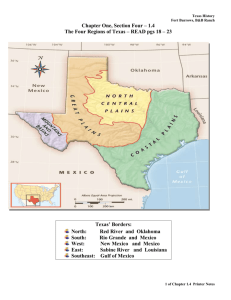
Texas History Fort Burrows Chapter One, Section Four – 1.4 The Four Regions of Texas – READ pgs 18 – 23 Borders of Texas • North: Red River & Oklahoma • East: Sabine River & Arkansas & Louisiana • South and West: Rio Grande & Mexico • West: Balcones Fault & New Mexico • Southeast: Gulf of Mexico Major mountain ranges of Texas: • The Guadalupe • Davis • Chalk • Glass Mountains. Main Idea: Vocabulary: Texas’ Borders: North: Red River and Oklahoma South: Rio Grande and Mexico West: New Mexico and Mexico East: Sabine River and Louisiana Southeast: Gulf of Mexico Main Idea: Geographers divide the State of Texas into Four regions: ↑ North Central Plains ← ↑ Great Plains ↕Coastal Plains ←Mountain & Basins 1 of Chapter 1.4 Printer Notes Texas History Fort Burrows Vocabulary: - drought – a long period of time in which rain falls at a much lower rate than normal - escarpment – a steep cliff - butte ( BYOOTS ) – steep-sided hills - mesa ( MAY – suhz ) – landforms with flat tops ( a result of erosion ) Four Regions of Texas Texas Climate Texas generally has hot summers and mild winters Snow may fall in many parts of Texas Climate differs greatly across the state Rainfall varies greatly across the state Even in the wetter areas, Texas has had problems with drought Drought is a long period in which rain falls at a much lower rate than usual The Coastal Plains Borders North: Red River South and West: Rio Grande West: Balcones Fault Southeast: Gulf of Mexico Land Western Edge: nearly 1000 ft above sea level Along the Coast: low and marshy land Vegetation Gulf Coast area: Coastal Prairie supports Rice Industry and Eastern Cross Timbers East Texas: Pine Forests of the ‘Piney Woods’ West of the ‘Piney Woods’: Forests of the Post Oak Belt The North Central Plains Borders North: Red River South: Edwards Plateau East: The North Central Plains Region West: Caprock Escarpment Land Elevation: decreases from west to east Much of the region’s land is rolling and hilly In the South: • buttes (steep-sided hills) and mesas (larger; similar landforms with flat tops) Vegetation East: the Grande Prairie Central: forests of the Western Cross Timbers West: grasslands of the Rolling Plains Farming and ranching dominate the North Central Plains 2 of Chapter 1.4 Printer Notes Texas History Fort Burrows The Great Plains Borders North: Oklahoma South: Edwards Plateau East: Caprock Escarpment West: Edwards Plateau Land Northern High Plains: mostly flat; some canyons Southern High Plains: The Llano Estacado is smooth and level South: The Edwards Plateau has hilly terrain Vegetation The Great Plains region is dry and has very few trees Much of the region is grassland Parts of the region are important farming areas The Mountains and Basins Borders North: New Mexico South and West: Rio Grande River East: Edwards Plateau Land This region includes scattered mountain ranges and flat desert basins Major mountain ranges include the Guadalupe, Davis, Chalk, and Glass Mountains Big Bend National Park is in the Mountains and Basins region Vegetation Desert: cactus, mesquite trees, and other desert plants Mountains: some forest growth El Capitan El Capitan seen from Guadalupe Peak Elevation 8,085 feet (2,464 m) Range Guadalupe Mountains Coordinates 31°52′38″N, 104°51′27″W 1. Which region has rolling and hilly land with many mesas and buttes ? A. North Central Plains B. Mountains & Basins C. Coastal Plains D. Great Plains 2. Which region has low and marshy land and includes the pine forests of the ‘Piney Woods’ ? A. Coastal Plains B. Great Plains C. Mountains & Basins D. North Central Plains 3 of Chapter 1.4 Printer Notes