Freud`s Stages of Psycho Sexual Development:
advertisement
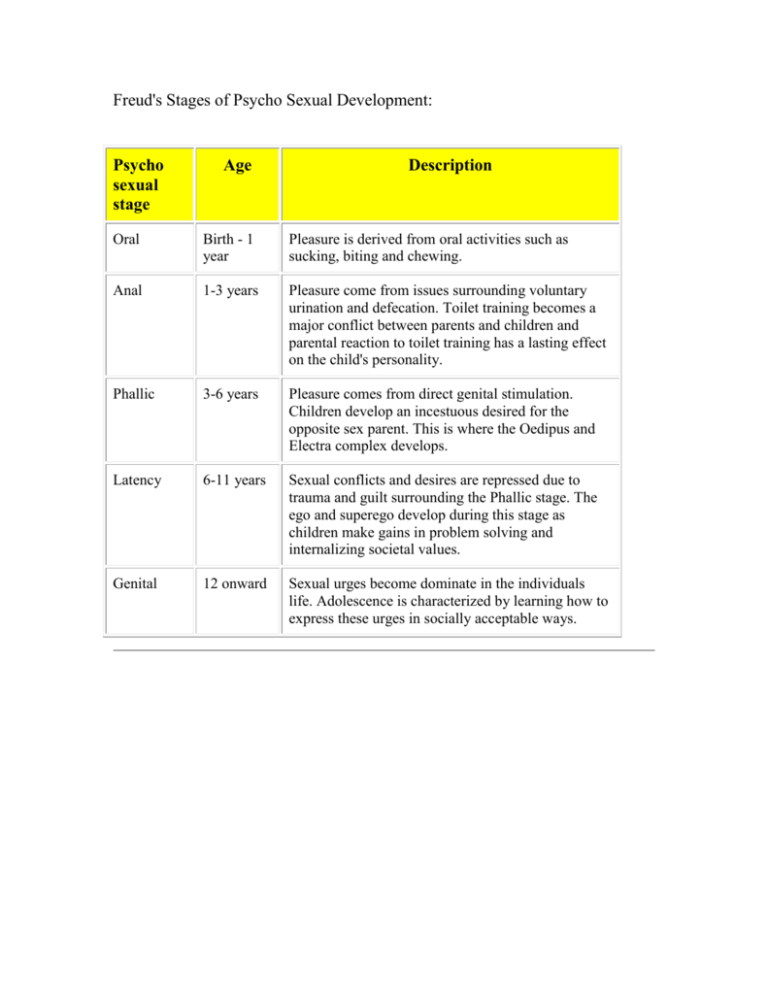
Freud's Stages of Psycho Sexual Development: Psycho sexual stage Age Description Oral Birth - 1 year Pleasure is derived from oral activities such as sucking, biting and chewing. Anal 1-3 years Pleasure come from issues surrounding voluntary urination and defecation. Toilet training becomes a major conflict between parents and children and parental reaction to toilet training has a lasting effect on the child's personality. Phallic 3-6 years Pleasure comes from direct genital stimulation. Children develop an incestuous desired for the opposite sex parent. This is where the Oedipus and Electra complex develops. Latency 6-11 years Sexual conflicts and desires are repressed due to trauma and guilt surrounding the Phallic stage. The ego and superego develop during this stage as children make gains in problem solving and internalizing societal values. Genital 12 onward Sexual urges become dominate in the individuals life. Adolescence is characterized by learning how to express these urges in socially acceptable ways. Erikson's Stages of Psycho Social Development Psycho Social Crisis Trust vs. Mistrust Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt Initiative vs. Guilt Industry vs. Inferiority Identity vs. Role Confusion Intimacy vs. Isolation Generativity vs. Stagnation Ego Integrity vs. Despair Age Description Birth - 1 Infants learn to trust others to care for them and meet year their basic needs. Inconsistent child rearing may lead the child to view the world as a dangerous place with untrustworthy people 1-3 years Child learn basic skills to care for themselves. Failure to learn these skills may make the child dependent on others and become shameful of him or herself. 3- 6 Child will take on responsibilities beyond their capacity. years These activities may conflict with the parents and cause the child to feel guilty about their behavior. The key in this stage is to achieve a balance between initiative and not infringing on the rights and privileges of others. 6-12 Child acquire social and academic skills. They begin to years compare themselves with other peers. If they feel they are lacking in industry (skills) as compared to peers, they may develop inferiority complexes that could interfere with functioning. 12-20 The major issues in this stage center around the years adolescence's question of "who am I?" This is a transition stage between childhood and adulthood where the child experiments with roles. If the child does not establish an identity then they may be confused as adults about the roles they should be playing. 20-40 The task at this age is to form strong social relationships years and establish intimate relationships. Without these relationships the individual may feel lonely and isolated which may interfere with the person's ability to form lasting relationships in the future. 40-65 Adults face the task of becoming productive members of years society and nurturing the younger generations. Those unwilling or unable to assume these roles become stagnant and self-centered. Old age The older adult assessed their life as either meaningful and productive or as a life full of disappointments. Life experiences determine how the adult will deal with this life crisis. Piaget's Stages of Development Stage Age Range Description Sensorimotor Stage Birth 2 yrs Children begin to understand objects first by reflexive reactions to them, then by interacting with them purposefully. Through these interactions children learn to make mental symbols of objects. PreOperational Stage 2-7 yrs Children begin to use mental symbols to represent objects (words, images) and begin to gain representational understanding. However they are not engaged in cognitive operations such as conservation and higher order perspective taking. ConcreteOperational Stage 7 - 11 yrs Children become less egocentric in their thinking and reasoning and begin to understand conservation concepts such as reversibility. However, children at this age still lack the ability to reason abstractly. Formal Operational Stage 11, 12 yrs and beyond This is when children begin to reason abstractly, and rationally. The formal operational stage is not necessarily obtained by all individuals and may not permeate to all areas of reasoning. Kohlberg's Stages of Moral Development Level Stage Preconventional Morality Stage 1: Punishment and Obedience Orientation Stage 2: Naive Hedonism Conventional Morality Stage 3: "Good Boy/Girl" Orientation Description Rules governing moral life are external to the self. Child use rule imposed by authority figure to guide their moral reasoning. Morality is guided by a desire to avoid punishment and is self serving. The moral judgment of an act (good or bad) is measured by its consequences. The act isn't bad if you don't get caught. Moral judgment is oriented towards personal gain. A "you scratch my back, I'll scratch yours" orientation guides moral judgment. Social norms and rules are obeyed in order to maintain and win other's approval. Social praise and the avoidance of punishment have become tangible rewards for moral behavior. Moral behavior is that which pleases, helps, or is approved by others. Other's perspectives are taken into account when making a moral judgement. Moral behavior may be dictated after the individual Stage 4: account for the perspective of the greater good of Social Order society as reflected by the law or known social mores. Maintaining Moral behavior is motivated by a want to maintain Morality social order. Postconventional Morality is defined in terms of a broader sense of Morality Justice that may or may not be reflected in societal law. Stage 5: Moral thought makes a distinction between what is legal Social and what is just. The individual sees that laws are Contact important for maintaining social norms, but may be Orientation unjust or unfair. Stage 6: The individual defines their own concepts of right and Morality of wrong based on self-chosen ethical principles that Individual reflects the individuals conscience. Moral guidelines Principles of are not concrete rules but abstract moral concepts. Conscience