Weather and Water
advertisement

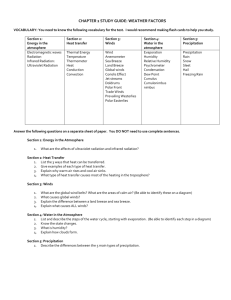
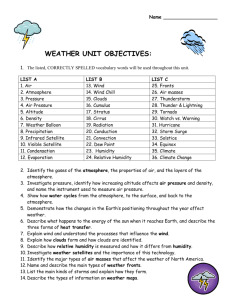
Weather and Water Part 1: What is Weather? Weather – conditions of the atmosphere at a given time with respect to heat, moisture, pressure and motion Weather tools (thermometer measures temperature in degrees C, barometer measures air pressure in MB’s, hygrometer measures humidity in %, anemometer measures wind speed in MPH, wind vane measures wind direction in N,S,E and W, psychrometer measures relative humidity) Part 2: Where is the Air? Mass – amount of matter in an object Atmosphere – a thin layer of gases that surround the Earth Weight – a pull or force between Earth and the matter of an object compressed - something being forced into a smaller space Know Layers of the Atmosphere - (Troposphere is where all weather takes place, Stratosphere contains the Ozone layer, Mesosphere, Thermosphere the hottest layer, Exosphere is the last layer separating our atmosphere and space) Name the three most abundant gases in the atmosphere: Nitrogen 78%, Oxygen 21%, Argon 1% As you rise higher in the atmosphere what happens to air pressure and temperature? They both go down Part 3: Season and Sun Know the different seasons (the positioning of the earth) Define these terms: Equinoxes (2) - Vernal/Spring Equinox March 21st (Equal Day length)/ Autumnal/Fall Equinox September 21st (Equal Day length) The Earth’s tilt is not pointed toward or away from the sun Solstices (2) – Winter solstice December 21st (Shortest day and Earth’s tilted away from the sun) Summer Solstice June 21st (Longest Day and Earth is titled toward the sun) Revolve/ Revolution - counter clockwise and it takes 365 and ¼ days, also cause season (With Tilt) Rotate/ Rotation – counter clockwise and it takes 24 hours, also causes day and night Solar Angle – the angle at which light strikes the Earth’s surface Beam Spreading – the way a light beam covers a surface when light hits the Earth’s Seasons are caused by the Earth’s tilt, 23.5 degrees, and Revolution Know which receives more direct sunlight summer or winter and why? Winter, because earth is tilted toward the sun Understand the importance of the North Star = Earth’s tilt always points to the North Star Part 4: Heat Transfer Radiant Energy – Energy that comes from the sun Radiation – is the energy and can be visible or invisible Differential Heating – when different materials heat up at different rates Conduction – Energy transfers of energy between molecules or atoms when they come into contact with one another Reradiation – all matter gives off energy and it travels from hot to cold Part 5: Convection Density – Mass per unit volume = Mass / Volume Convection – the movement of air based on density, because less dense air rises and dense air falls. Explain and Draw the Convection Cell: Part 6: Water in the Air Condensation - when water changes from a gas to a liquid Humidity – amount of water vapor in the air Saturation – when air contains as much water vapor as it can hold Relative Humidity – amount of water vapor in the air compared to the amount of water vapor needed to saturate the air Transpiration – when water leaves plants as vapor Condensation Nuclei - particles on which water vapor condenses Evaporation – is when water turns into a gas Dew Point – the temperature at which water condenses Water vapor – water in the air in the form of a gas Precipitation – any form of water that falls from a cloud Draw and label how a cloud is formed: Part 7: The Water Planet Review how the water on this planet is distributed: 97% of Earth’s water is Ocean water Most of the Fresh water is in Glaciers and Icecaps How much of the Earth’s surface is covered by water? 70% Draw and label the water cycle? Part 8: Air Pressure and Wind Anemometer – tool used to measure wind speed Barometer – tool used to measure air pressure, millibars is the unit used Wind – caused by differences in air pressure Isobars – lines on maps connecting places together with the same air pressure Global winds – Winds that happen on a larger scale, move from H to L pressure, predictable winds Local Winds – winds that happen on a smaller scale , move from H to L pressure Coriolis Effect - the bending of winds east or west because of Earth’s rotation Prevailing Winds – predictable Global Winds Explain how air pressure creates wind (Nature’s Balancing Act)? Air moves from High Pressure areas to low pressure areas Know and be able to explain the four local winds (Mountain Breeze, Sea Breeze, Valley Breeze, and Land Breeze) Be able to read a pressure map Part 9: Weather and Climate Stagnant Air – air that does not move Source Regions – the place that an air mass gets its name from Air Masses – large thick bodies of air that are uniform in Humidity and Temperature Staff/ shaft – line that extends from cloud coverage, names Wind direction Barbs – are the small lines at the end of a shaft/ staff gives wind speed Weather – conditions of the atmosphere at a given time Climate – the average weather conditions over a long period of time; two main factors in determining climate is temp and annual rain fall Global Warming – when Earth’s temperature rises because of an increase in carbon dioxide Greenhouse Effect – process by which gases hold heat in the atmosphere (Increased CO2) Ozone Layer – a layer in the Stratosphere that absorbs ultraviolet radiation Stationary Front – When a warm air mass and a cold air mass meet and do not move Be able to identify and label different air masses (Continental are dry and form over land, Maritime are humid and form over water, Polar are cold and they move east and south, Tropical warm and mover north and east) Draw and label a warm front and a cold front Be able to read and interpret a weather map (Look at the sample weather map) Know the Temperature Zones? Polar, Tropical and Temperate zones