Edvotek Kit #116: Genetically Inherited Disease Detection Using Pre
advertisement
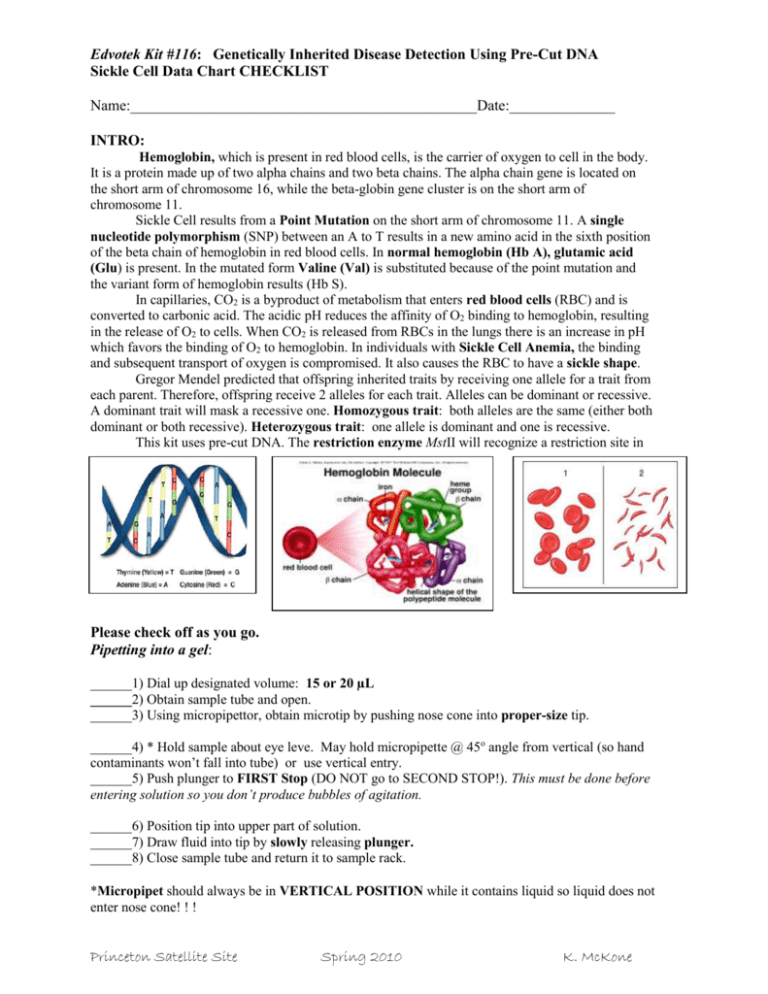
Edvotek Kit #116: Genetically Inherited Disease Detection Using Pre-Cut DNA Sickle Cell Data Chart CHECKLIST Name:______________________________________________Date:______________ INTRO: Hemoglobin, which is present in red blood cells, is the carrier of oxygen to cell in the body. It is a protein made up of two alpha chains and two beta chains. The alpha chain gene is located on the short arm of chromosome 16, while the beta-globin gene cluster is on the short arm of chromosome 11. Sickle Cell results from a Point Mutation on the short arm of chromosome 11. A single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) between an A to T results in a new amino acid in the sixth position of the beta chain of hemoglobin in red blood cells. In normal hemoglobin (Hb A), glutamic acid (Glu) is present. In the mutated form Valine (Val) is substituted because of the point mutation and the variant form of hemoglobin results (Hb S). In capillaries, CO2 is a byproduct of metabolism that enters red blood cells (RBC) and is converted to carbonic acid. The acidic pH reduces the affinity of O2 binding to hemoglobin, resulting in the release of O2 to cells. When CO2 is released from RBCs in the lungs there is an increase in pH which favors the binding of O2 to hemoglobin. In individuals with Sickle Cell Anemia, the binding and subsequent transport of oxygen is compromised. It also causes the RBC to have a sickle shape. Gregor Mendel predicted that offspring inherited traits by receiving one allele for a trait from each parent. Therefore, offspring receive 2 alleles for each trait. Alleles can be dominant or recessive. A dominant trait will mask a recessive one. Homozygous trait: both alleles are the same (either both dominant or both recessive). Heterozygous trait: one allele is dominant and one is recessive. This kit uses pre-cut DNA. The restriction enzyme MstII will recognize a restriction site in Please check off as you go. Pipetting into a gel: ______1) Dial up designated volume: 15 or 20 µL ______2) Obtain sample tube and open. ______3) Using micropipettor, obtain microtip by pushing nose cone into proper-size tip. ______4) * Hold sample about eye leve. May hold micropipette @ 45o angle from vertical (so hand contaminants won’t fall into tube) or use vertical entry. ______5) Push plunger to FIRST Stop (DO NOT go to SECOND STOP!). This must be done before entering solution so you don’t produce bubbles of agitation. ______6) Position tip into upper part of solution. ______7) Draw fluid into tip by slowly releasing plunger. ______8) Close sample tube and return it to sample rack. *Micropipet should always be in VERTICAL POSITION while it contains liquid so liquid does not enter nose cone! ! ! Princeton Satellite Site Spring 2010 K. McKone Edvotek Kit #116: Genetically Inherited Disease Detection Using Pre-Cut DNA Sickle Cell Data Chart CHECKLIST ______9) Pipet into gel by slowly pushing plunger to FIRST stop (DO NOT GO TO SECOND STOP). ______10) KEEP plunger at FIRST stop and withdraw pipet from gel. ______11) Slowly release plunger and eject tip into waste beaker. ______12) If all samples are loaded, close box top and connect color coded leads to power supply. ______13) Turn on power supply and set Volts to ~ 100. Run for 20-25 minutes. Sketch resulting bands below and write Hetero-, Homozygous-Dominant or Recessive; Include phenotype: Normal, Carrier, or Hemophilia Another diagram is provided if your samples are loaded DIFFERENTLY. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Sickle Carrier Normal Mom’s Child’s Dad’s Practice cell gene sample gene DNA DNA DNA sample sample ___ µL ___ µL ___µL ___ µL ___µL ___µL ___µL red clear blue green yellow purple Lane 1 2 3 4 5 ___ µL ___ µL ___µL ___ µL ___µL 8 Practice ___ µL Big orange Big orange 6 7 8 ___µL ___µL ___ µL Samples Volume Loaded Sample Tube Color Band Patterns & Phenotype Based on the gel: What is the genotype of the child? Homo-Dominant, Hetero, or Homo-Rec What is the phenotype of the child (circle one): Normal, Princeton Satellite Site Spring 2010 Carrier, or Sickle Cell K. McKone